-
摘要: 目的 探讨婴幼儿声门下血管瘤围术期气道事件的相关影响因素, 并进一步讨论其围术期的气道管理方法。方法 收集从2007年7月-2017年4月药物治疗无效后采用手术治疗的36例婴幼儿声门下血管瘤患儿资料, 并对其相关因素进行记录, 包括: 性别、年龄、出生体重、目前体重、首发时间、气道狭窄程度、基础疾病史(先天性心脏病史和呼吸道病史)。婴幼儿声门下血管瘤围术期气道事件包括: 术中SpO2下降、术中急症气管插管、术中急症气管切开、术后是否带管、术后紧急插管。对围术期气道事件的相关影响因素进行分析并将有意义的统计学指标进行成组Logistic回归分析, 用OR值和95%可信区间(CI)对其相关性进行评价。根据各气道事件不同影响因素的相关性, 探讨围术期的气道管理。结果 ① 气道狭窄程度是SpO2下降的危险因素, 95%CI为(2.121~33.818);②气道狭窄程度、合并心血管病史和合并呼吸道病史是术中急症气管插管的因素, 95%CI分别为(0.863~21.692)、(0~+∞)、(1.741~232.403);③气道狭窄程度是术后紧急插管的影响因素, 95%CI为(1.277~20.421);④气道狭窄程度是术后是否带管的危险因素, 95%CI为(1.523~13.296)。结论 ① 术前合并基础疾病史的患儿术中更易出现气道不稳定、SpO2下降的情况, 应术前术中予以重视, 术中一旦出现SpO2下降, 及时行气管插管; ②术前气道狭窄Ⅲ度, 特别是合并心脏病史或呼吸道病史的患儿, 应术前予气管切开; ③气道狭窄程度在婴幼儿声门下血管瘤围术期的气道管理中是极为重要的影响因素, 对于气道狭窄大于60%气道管径的患儿术中应密切监测呼吸道通畅情况, 出现SpO2下降及时行气管插管, 术后推荐保留气管插管以保证气道稳定, 待48~72 h后延迟拔管; ④手术方式的选择对围术期的气道管理无明显影响。Abstract: Objective To investigate the relevant influencing factors for perioperative airway events of infantile subglottic hemangioma, and to further discuss the strategies of perioperative airway management.Methods A total of 36 infants with subglottic hemangioma that had no response to the drug therapy and underwent surgical treatment from July 2007 to April 2017 were enrolled. The relevant influencing factors, including gender, age, birth weight, age of onset, degree of tracheal stenosis and histories of underlying diseases(congenital heart disease and respiratory disease), were also recorded simultaneously. Intraoperative SpO2 decline, intraoperative emergency tracheal intubation, intraoperative emergency tracheotomy, whether preserving tracheal intubation after operation or not, and postoperative emergency tracheal intubation were included in the perioperative airway events of infantile subglottic hemangioma. The relevant influencing factors of perioperative airway events were analyzed so that meaningful statistical indicators were selected for grouped logistic regression analysis, and the correlation was evaluated based on OR value and 95% confidence interval(CI). Based on the correlation between influencing factors and airway events, perioperative airway management was discussed.Results ① The degree of tracheal stenosis was a risk factor for SpO2 decline(95%CI[2.121-33.818]); ②The degree of airway stenosis, history of comorbid cardiovascular disease and respiratory disease were the influencing factors for intraoperative emergency tracheal intubation(95%CI[0.863-21.692], [0-+∞] and [1.741-232.403], respectively); ③The degree of airway stenosis was the influencing factor for postoperative emergency tracheal intubation(95%CI[1.277-20.421]); ④The degree of airway stenosis was a risk factor for whether preserving postoperative tracheal intubation or not(95%CI[1.523-13.296]).Conclusion ① Infants with a history of preoperative underlying diseases are more likely to present with intraoperative airway instability and SpO2 decline, which deserves more preoperative and postoperative attention. Tracheal intubation should be performed timely in case of intraoperative SpO2 decline. ②Preoperative tracheotomy should be performed in infants with preoperative grade Ⅲ airway stenosis, especially those with comorbid heart diseases or respiratory diseases. ③The degree of airway stenosis is an extremely important influencing factor for perioperative airway management of infantile subglottic hemangioma. For infants whose airway stenosis were greater than 60% of airway diameter, the airway maintenance should be closely monitored. Once SpO2decreases, tracheal intubation should be performed immediately. It's recommended to preserve tracheal intubation so as to ensure the airway stability. The tracheal intubation could be prolonged to 48-72 hours postoperatively. ④The surgical approach has no significant effect on perioperative airway management.
-
Key words:
- infant /
- subglottic hemangioma /
- Perioperative period /
- airway events
-

-
表 1 患儿气道狭窄程度
治疗方式 气道狭窄程度 合计 Ⅰ度 Ⅱ度 Ⅲ度 药物治疗 42 18 10 70 手术治疗 20 11 5 36 合计 62 29 15 106 表 2 围术期气道事件相关因素单因素分析
因素 术中SpO2下降 术中急症气管插管 术中急症气管切开 术后紧急插管 术后是否带管 统计量 P 统计量 P 统计量 P 统计量 P 统计量 P 年龄 -0.631 0.528 -0.631 0.528 -0.279 0.781 -0.192 0.848 -0.192 0.848 性别 0.731 0.738 0.698 0.223 0.157 出生体重 0.590 0.559 0.590 0.559 -0.551 0.586 -2.148 0.039 -1.898 0.066 目前体重 -1.566 0.127 -1.566 0.127 -0.482 0.633 -1.399 0.171 -1.928 0.062 首发时间 -0.607 0.544 -0.607 0.544 -1.387 0.165 -0.255 0.837 -0.477 0.634 狭窄程度 -3.501 <0.001 -3.784 <0.001 -1.835 0.066 -2.528 0.011 -2.943 0.003 基础疾病史 7.393 0.025 20.267 < 0.001 5.029 0.170 9.169 0.010 9.450 0.009 手术方式 1.504 0.471 1.692 0.429 2.647 0.266 7.389 0.025 0.474 0.789 手术治疗史 0.150 1.000 0.598 0.618 0.244 表 3 围术期气道事件相关因素多因素分析
气道事件 相关影响因素 回归系数 标准误 OR 95%CI P 术中SpO2下降 气道狭窄程度 2.136 0.706 8.470 (2.121~33.818) 0.002 术中急症气管插管 气道狭窄程度 1.464 0.823 4.326 (0.863~21.692) 0.075 心脏病史 22.597 17 359.287 6 510 493 317.000 (0~+∞) 0.999 呼吸道病史 3.001 1.249 20.113 (1.741~232.403) 0.016 术中急症气管切开 无 术后紧急插管 气道狭窄程度 1.630 0.707 5.106 (1.277~20.421) 0.021 术后是否带管 气道狭窄程度 1.504 0.553 4.500 (1.523~13.296) 0.007 -
[1] Cooper M, Slovis TL, Madgy DN, et al. Congenital subglottic hemangioma: frequency of symmetric subglottic narrowing on frontal radiographs of the neck[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1992, 159(6): 1269-1271. doi: 10.2214/ajr.159.6.1442399
[2] Filauro M, Mazzola F, Missale F, et al. Endoscopic Preoperative Assessment, Classification of Stenosis, Decision-Making[J]. Front Pediatr, 2020, 7: 532. doi: 10.3389/fped.2019.00532
[3] Onder SS, Gergin O, Karabulut B. A Life Threatening Subglottic and Mediastinal Hemangioma in an Infant[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2019, 30(5): e402-e404. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000005340
[4] 程岚, 黄琦, 吴皓, 等. 婴幼儿先天性声门下血管瘤的诊断和治疗[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2009, 23(15): 693-696. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH200915012.htm
[5] Cotton RT, Gray SD, Miller RP. Update of the Cincinnati experience in pediatric laryngotracheal reconstruction[J]. Laryngoscope, 1989, 99(11): 1111-1116.
[6] Bajaj Y, KapoorK, Ifeacho S, et al. Great Ormond Street Hospital treatment guidelines for use of propranolol in infantile isolated subglottic haemangioma[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2013, 127(3): 295-298. doi: 10.1017/S0022215112003192
[7] 刘洪全, 祁建春. 平阳霉素治疗血管瘤61例临床观察[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 1998, 14(3): 194-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKQ803.015.htm
[8] 郭恩谭. 现代整形外科学[M]. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2000: 479-486.
[9] Ada M, Gfivenc MG, Yilmaz S. Infantile supraglottic henmngionm: a case repoA[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2006, 85(4): 388-390.
[10] 张海萍, 蔡宏伟, 李远斌. 小儿喉乳头状瘤摘除术的麻醉体会[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2003, 9(2): 118-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZEBY200302027.htm
-

| 引用本文: | 卢奇, 梁玉丹, 汪照炎, 等. 婴幼儿声门下血管瘤围术期的气道管理[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(6): 501-504. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.06.004 |
| Citation: | LU Qi, LIANG Yudan, WANG Zhaoyan, et al. Perioperative airway management of infantile subglottic hemangioma[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2021, 35(6): 501-504. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.06.004 |
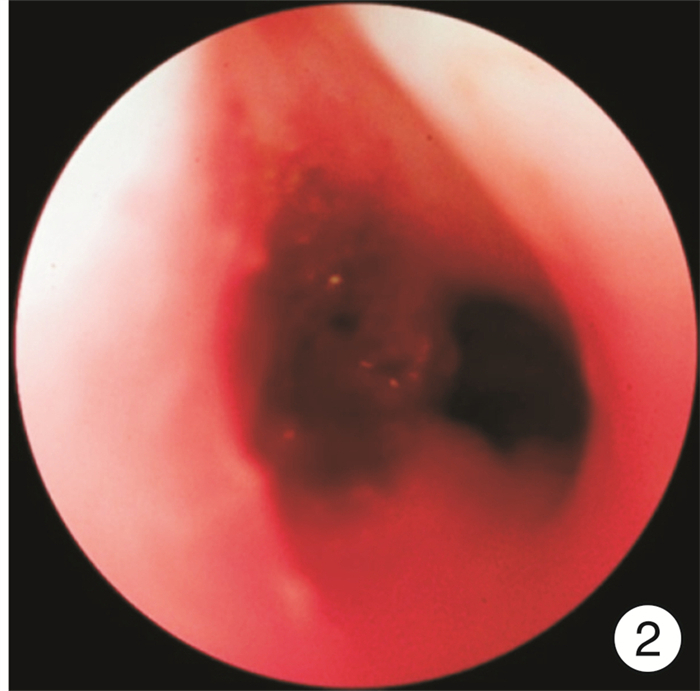
- Figure 1.
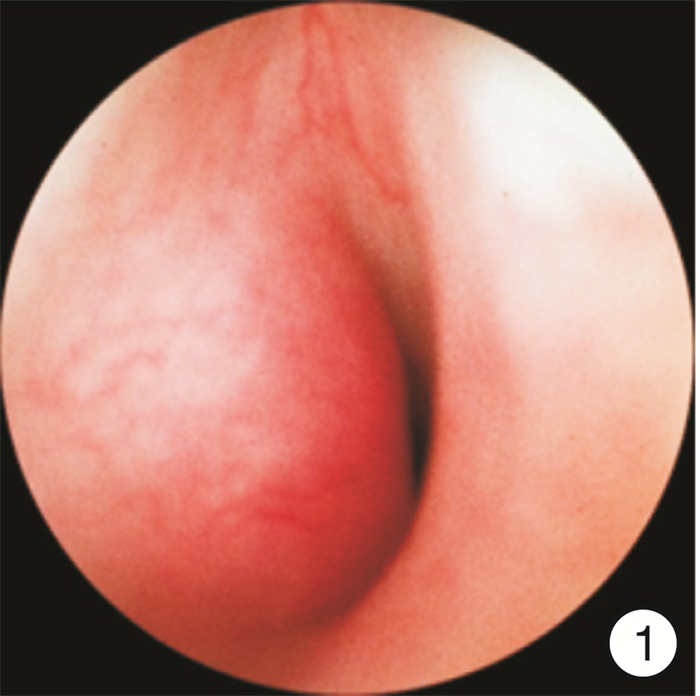
- Figure 2.



 下载:
下载: