The development of consonant perception in pediatric cochlear implants of 1-3 years old
-
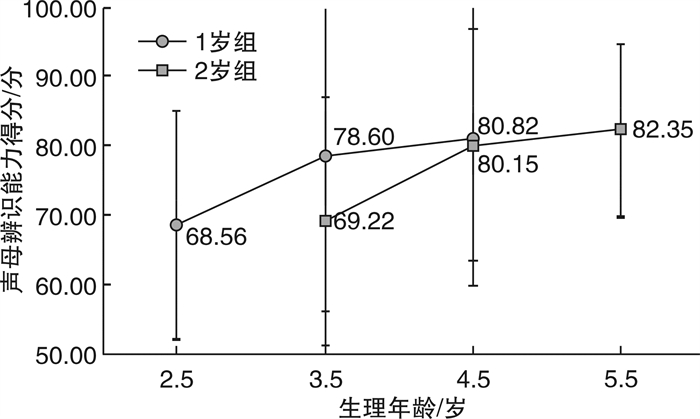
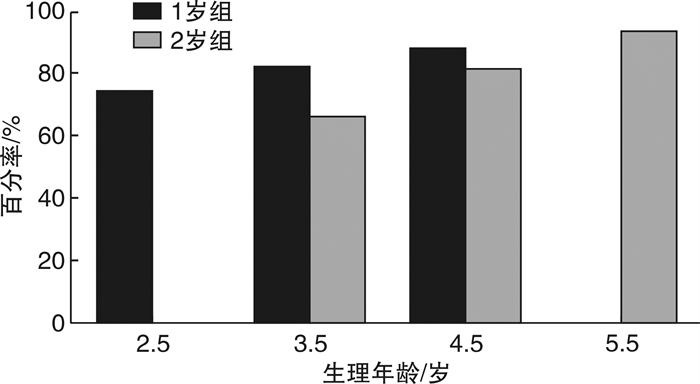
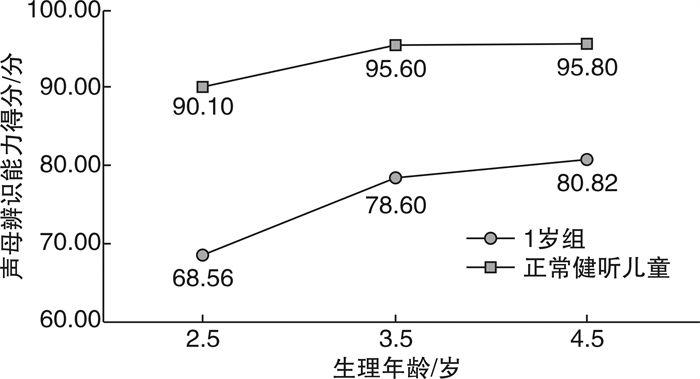
摘要: 目的 初步探讨植入年龄为1~3岁行单侧人工耳蜗植入术(CI)的语前双耳极重度感音神经性听力损失儿童术后3年内声母辨识能力的发育规律。方法 采用回顾性研究的方法, 分析完成CI开机的听力损失儿童声母辨识能力的相关情况。根据植入年龄分为1岁组(1~ < 2岁)和2岁组(2~ < 3岁)。采用普通话早期言语感知测试, 在开机后1、2、3年时测试CI儿童声母辨识能力, 并将1岁组与同龄健听儿童的声母辨识能力的发展趋势进行对比。结果 ① 两组CI儿童的声母辨识能力均随着生理年龄的增长而显著提高(P=0.038, P=0.012);②1岁组的声母辨识能力明显高于2岁组(P < 0.05), 但与同龄健听儿童相比还存在很大的差异。结论 术后3年内, 植入年龄小于3岁的儿童随着CI佩戴时间的增加其声母辨识能力均有相应提高, 但与同龄健听儿童相比还存在着一定的差异; 植入年龄越小, 声母辨识能力越好。Abstract: Objective To explore the development of consonant perception in early implanted pediatric with prelingual bilateral profound sensorineural hearing loss at 1 to 3 years of age.Methods A retrospective study was conducted to prospectively analyze the pediatric with hearing impaired who had cochlear implantation. According to the age of implantation, all participants were divided into two groups as 1 year old group(1- < 2) and 2 years old group(2- < 3). It was compared the consonant perception of Mandarin early speech perception test scores at 1, 2, 3 years after implantation as well as the trends in consonant perception between 1 year old group and normal hearing pediatrics of the same age.Results ① The scores improved notably in two groups with the increase of physiological age(P=0.038, P=0.012); ②The consonant perception of 1 year old group was significantly better than that of 2 years old group(P < 0.05), however, there are great difference between 1 year old group and normal hearing pediatrics of the same age.Conclusion With the increase of physiological age, the consonant perception will be improved correspondingly within 3 years of pediatric cochlear implants under the age of 3 however there are differences with normal hearing pediatrics of the same age; the earlier the age of implant, the better the consonant perception is.
-
Key words:
- cochlear implantation /
- child /
- prelingual deafness /
- consonant perception
-

-
表 1 CI儿童随访评估情况
组别 生理年龄 合计 2.5岁 3.5岁 4.5岁 5.5岁 1岁组 9 20 11 - 40 2岁组 - 27 39 17 83 合计 9 47 50 17 123 -
[1] Liang Q, Mason B. Enter the dragon——China's journey to the hearing world[J]. Cochlear Implants Int, 2013, 14 Suppl 1: S26-S31.
[2] 黄伯荣, 廖序东. 语音概说[M]//黄伯荣, 廖序东. 现代汉语增订版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2017: 23-28.
[3] 韩德民, 许时昂. 小儿听力言语语言康复及聋儿教育[M]//韩德民, 许时昂. 听力学基础与临床. 北京: 科学技术文献出版社, 2004: 472-477.
[4] 刘洁芬, 吴立平, 宋晓华, 等. 聋童语音的声学参数分析[J]. 中国特殊教育, 1999(2): 16-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDTJ902.004.htm
[5] Wang NM, Huang TS, Wu CM, et al. Pediatric cochlear implantation in Taiwan: long-term communication outcomes[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2007, 71(11): 1775-1782. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2007.08.004
[6] Baumgartner WD, Pok SM, Egelierler B, et al. The role of age in pediatric cochlear implantation[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2002, 62(3): 223-228. doi: 10.1016/S0165-5876(01)00621-8
[7] 郑芸, 孟照莉, 王恺, 等. 普通话早期言语感知测试(MESP)[J]. 中国听力语言康复科学杂志, 2011, 9(5): 19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4933.2011.05.004
[8] Zheng Y, Soli SD, Meng Z, et al. Assessment of Mandarin-speaking pediatric cochlear implant recipients with the Mandarin Early Speech Perception(MESP)test[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2010, 74(8): 920-925. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2010.05.014
[9] Zheng Y, Meng ZL, Wang K, et al. Development of the Mandarin early speech perception test: children with normal hearing and the effects of dialect exposure[J]. Ear Hear, 2009, 30(5): 600-612.
[10] 吴艳, 李刚, 马莹, 等. 1~3岁植入人工耳蜗患儿韵母辨识能力的发育规律研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(10): 918-922. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201910006.htm
[11] Li G, Soli SD, Zheng Y. Tone perception in Mandarin-speaking children with cochlear implants[J]. Int J Audiol, 2017, 56(sup2): S49-S59. doi: 10.1080/14992027.2017.1324643
[12] 李莹, 邢燕, 李晓璐, 等. 语前聋儿童人工耳蜗植入术后康复效果评估的研究[J]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2014(6): 1022-1025. doi: 10.3969/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2014.06.008
[13] 毛昳楠, 李广盛, 汪贺媛, 等. 儿童人工耳蜗植入不同时段声母和韵母识别状况研究[J]. 中外医学研究, 2017, 15(10): 24-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJZY201710010.htm
[14] 易海燕, 刘巧云. 人工耳蜗植入儿童与健听儿童音位对比式听觉识别能力的比较研究[J]. 中国听力语言康复科学杂志, 2017, 15(4): 278-281. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4933.2017.04.009
-




 下载:
下载: