Ultrasound-guided core-needle biopsy diagnosis of thyroid T-cell lymphoma: a case report
-
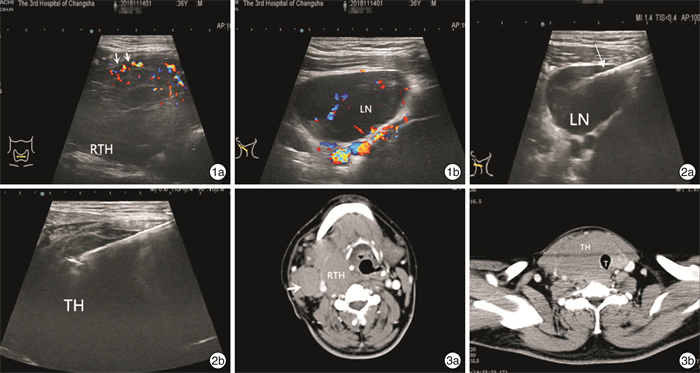
Abstract: The rare entity of primary T-cell lymphoma of thyroid gland may pose great diagnostic challenges to the clinician. We report a case of malignant T-cell lymphoma of the thyroid gland that developed in a 36-year-old man with a past history of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. The chief complaint was a rapidly growing neck mass and pressure symptoms. This man, diagnosed with Hashimoto's thyroiditis for the previous several years. CT and ultrasonographic examination revealed a diffuse large thyroid gland with cervical lymphadenopathy. It was suspected that thyroid lymphoma involved regional lymph nodes. Fine needle aspiration cytology diagnosed chronic thyroiditis, and ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy was performed. Finally, peripheral T cell lymphoma was diagnosed.
-
Key words:
- thyroiditis /
- ultrasonography /
- puncture biopsy /
- T-cell lymphoma
-

-
[1] Pavlidis ET, Pavlidis TE. A Review of Primary Thyroid Lymphoma: Molecular Factors, Diagnosis and Management[J]. J Invest Surg, 2019, 32(2): 137-142. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2017.1383536
[2] 赵欣, 旦增贡色, 张志斌, 等. 甲状腺结节硬度对粗、细针穿刺活检标本满意度的影响[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(11): 1011-1013. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202011013.htm
[3] Yokoyama J, Ito S, Ohba S, et al. Problems of primary T-cell lymphoma of the thyroid gland——a case report[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2012, 10: 58-58. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-10-58
[4] Chen C, Yang Y, Jin L, et al. Primary thyroid T-lymphoblastic lymphoma: a case report and review of the literature[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2013, 7(1): 443-450.
[5] 刘俊峰, 温德惠, 李晓娟, 等. 2015ATA、2016KTA/KSThR和2017ACR指南超声模式在不确定意义甲状腺结节的应用价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(5): 388-392, 397. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201905002.htm
[6] Gharib H, Papini E, Garber JR, et al. AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS, AMERICAN COLLEGE OF ENDOCRINOLOGY, AND ASSOCIAZIONE MEDICI ENDOCRINOLOGI MEDICAL GUIDELINES FOR CLINICAL PRACTICE FOR THE DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF THYROID NODULES--2016 UPDATE[J]. Endocr Pract, 2016, 22(5): 622-639.
[7] Chen BT, Jain AB, Dagis A, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy versus fine-needle aspiration for evaluating thyroid nodules[J]. Endocr Pract, 2015, 21(2): 128-135. doi: 10.4158/EP14303.OR
[8] Suh CH, Baek JH, Lee JH, et al. The role of core-needle biopsy in the diagnosis of thyroid malignancy in 4580 patients with 4746 thyroid nodules: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Endocrine, 2016, 54(2): 315-328. doi: 10.1007/s12020-016-0991-9
[9] Suh CH, Baek JH, Park C, et al. The Role of Core Needle Biopsy for Thyroid Nodules with Initially Indeterminate Results on Previous Fine-Needle Aspiration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2017, 38(7): 1421-1426. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A5182
[10] Bernardi S, Michelli A, Bonazza D, et al. Usefulness of core needle biopsy for the diagnosis of thyroid Burkitt's lymphoma: a case report and review of the literature[J]. BMC Endocr Disord, 2018, 18(1): 86-86. doi: 10.1186/s12902-018-0312-9
-




 下载:
下载: