-
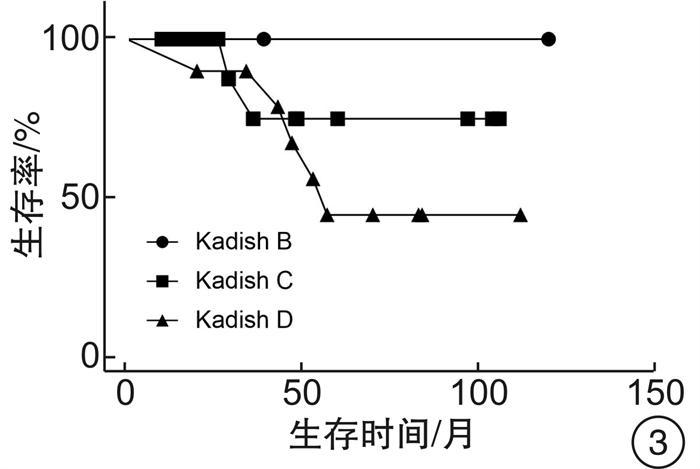
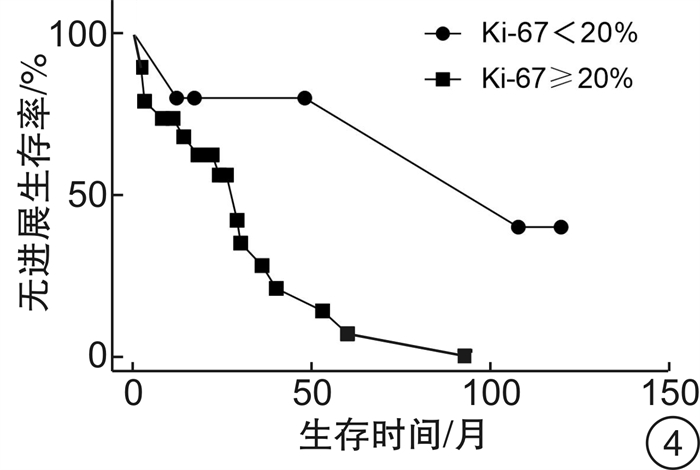
摘要: 目的 探讨嗅神经母细胞瘤的治疗效果及预后危险因素。方法 回顾性分析31例嗅神经母细胞瘤患者的临床资料,采用Kaplan-Meier法进行生存分析,计算总体生存率和无进展生存率。结果 31例患者均行手术治疗,随访死亡7例,其中因单纯颅脑侵犯死亡4例,因同时合并远处转移(肺和脊髓)死亡3例,平均生存时间40.7个月。颅脑侵犯(P=0.035)、年龄≥60岁(P=0.042)、Ki-67≥20%(P=0.018)与患者不良预后密切相关。推测T分期和改良Kadish分期的增加也是预后不良的预测指标。初次手术患者1年和5年总体生存率分别为100.0%和72.5%,1年和5年无进展生存率分别为87.8%和33.6%。结论 嗅神经母细胞瘤行手术切除和放化疗是目前主要的治疗方式,但是术后常见复发转移,死亡率较高。高龄、颅内侵犯和Ki-67≥20%与不良预后密切相关。我院初次手术根治性切除肿瘤及病变局限鼻腔鼻窦是预后良好的关键因素。Abstract: Objective To explore the therapeutic effect and prognostic risk factors of olfactory neuroblastoma.Methods Retrospective analysis of clinical data of 31 patients with olfactory neuroblastoma. The Kaplan-Meier method was used for survival analysis to calculate the overall survival rate and progress-free survival rate.Results All 31 patients underwent surgical treatment and 7 patients died, of which 4 patients died of simple intracranial invasion and 3 patients died of concurrent distant metastasis (lung and spinal cord). The average death time was 40.7 (20-57) months. Statistical analysis showed that craniocerebral invasion (P=0.035), age ≥60 years (P=0.042), and Ki-67≥20%(P=0.018) were closely related to the poor prognosis. It is speculated that the increase of T staging and modified Kadish staging are also predictors of poor prognosis. The 1-year and 5-year overall survival rates were 100.0% and 72.5%, and the 1-year and 5-year progress-free survival rates were 87.8% and 33.6% after first surgery.Conclusion Surgery combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy are the main treatments for olfactory neuroblastoma, but postoperative recurrence and metastasis are common. About 22.6% of the patients died during the follow-up. Advanced age, intracranial invasion and Ki-67≥20% are closely related to poor prognosis. The tumor was completely removed by the initial surgery and restricted in nasal cavity and sinuses are the key factors for a good prognosis.
-
Key words:
- olfactory neuroblastoma /
- endoscopic surgical procedures /
- radiotherapy /
- chemotherapy /
- metastasis /
- recurrence
-

-
表 1 ONB患者的临床资料
分类 例数 死亡率/% 复发率/% 转移率/% 性别 男 23 17.4 56.5 26.1 女 8 37.5 37.5 50.0 年龄 ≥60岁 11 45.5 54.5 45.5 < 60岁 20 10.0 50.0 25.0 S-100 阴性 17 29.4 64.7 29.4 阳性 7 28.6 28.6 42.9 Ki-67 ≥20% 19 36.8 63.2 42.1 < 20% 5 0 20.0 20.0 Hymas分级 低级别 7 0 14.3 14.3 高级别 4 0 50.0 0 颅内侵犯 是 21 33.3 57.1 23.8 否 10 0 40.0 50.0 Kadish分期 B期 5 0 20.0 0 C期 16 12.5 62.5 0 D期 10 50.0 50.0 100.0 T分期 T1期 5 0 20.0 0 T2期 14 14.3 57.1 7.1 T3期 7 14.3 57.1 57.1 T4期 5 80.0 60.0 100.0 手术+ 放化疗 13 23.1 30.8 30.8 手术+ 放疗 14 21.4 64.3 35.7 手术 4 25.0 75.0 25.0 -
[1] 吴涛, 刘丕楠. 嗅神经母细胞瘤的诊治相关研究进展[J]. 中华神经外科杂志, 2020, 36(1): 84-87. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2346.2020.01.021
[2] Abdelmeguid AS. Olfactory Neuroblastoma[J]. Curr Oncol Rep, 2018, 20(1): 7-7. doi: 10.1007/s11912-018-0661-6
[3] Fiani B, Quadri SA, Cathel A, et al. Esthesioneuroblastoma: A Comprehensive Review of Diagnosis, Management, and Current Treatment Options[J]. World Neurosurg, 2019, 126: 194-211. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.03.014
[4] Goshtasbi K, Abiri A, Abouzari M, et al. Hyams grading as a predictor of metastasis and overall survival in esthesioneuroblastoma: a meta-analysis[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2019, 9(9): 1054-1062. doi: 10.1002/alr.22373
[5] Bell D. Sinonasal Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Current Challenges and Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment, with a Focus on Olfactory Neuroblastoma[J]. Head Neck Pathol, 2018, 12(1): 22-30. doi: 10.1007/s12105-018-0887-5
[6] Arnold MA, Farnoosh S, Gore MR. Comparing Kadish and Modified Dulguerov Staging Systems for Olfactory Neuroblastoma: An Individual Participant Data Meta-analysis[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2020, 163(3): 418-427. doi: 10.1177/0194599820915487
[7] 赖银妍, 林腾蛟, 江丽洁, 等. 结合改良Kadish分期及Hyams分级评估嗅神经母细胞瘤预后的预测模型回顾性分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(7): 599-602. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201907006.htm
[8] Ow TJ, Bell D, Kupferman ME, et al. Esthesioneuroblastoma[J]. Neurosurg Clin N Am, 2013, 24(1): 51-65. doi: 10.1016/j.nec.2012.08.005
[9] Turri-Zanoni M, Maragliano R, Battaglia P, et al. The clinicopathological spectrum of olfactory neuroblastoma and sinonasal neuroendocrine neoplasms: Refinements in diagnostic criteria and impact of multimodal treatments on survival[J]. Oral Oncol, 2017, 74: 21-29. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.09.010
[10] Singh L, Ranjan R, Madan R, et al. Microvessel density and Ki-67 labeling index in esthesioneuroblastoma: is there a prognostic role?[J]. Ann Diagn Pathol, 2015, 19(6): 391-396. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2015.06.008
[11] Marinelli JP, Van Gompel JJ, Link MJ, et al. Volumetric analysis of olfactory neuroblastoma skull base laterality and implications on neck disease[J]. Laryngoscope, 2018, 128(4): 864-870. doi: 10.1002/lary.26843
[12] Peacock JG, Harmsen WS, Link MJ, et al. Risk of Delayed Lymph Node Metastasis in Clinically N0 Esthesioneuroblastoma[J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base, 2017, 78(1): 68-74.
[13] Alotaibi HA, Priola SM, Bernat AL, et al. Esthesioneuroblastoma: Summary of Single-center Experiences with Focus on Adjuvant Therapy and Overall Survival[J]. Cureus, 2019, 11(6): e4897.
[14] Mays AC, Bell D, Ferrarotto R, et al. Early Stage olfactory neuroblastoma and the impact of resecting dura and olfactory bulb[J]. Laryngoscope, 2018, 128(6): 1274-1280. doi: 10.1002/lary.26908
[15] 高炜, 汪银凤, 王亚林, 等. 嗅神经母细胞瘤内镜手术与传统手术联合放疗疗效分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(2): 128-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202002007.htm
[16] Fu TS, Monteiro E, Muhanna N, et al. Comparison of outcomes for open versus endoscopic approaches for olfactory neuroblastoma: A systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis[J]. Head Neck, 2016, Suppl 1: E2306-2316.
[17] Su SY, Bell D, Ferrarotto R, et al. Outcomes for olfactory neuroblastoma treated with induction chemotherapy[J]. Head Neck, 2017, 39(8): 1671-1679. doi: 10.1002/hed.24822
[18] Batacchi Z, Andeen NK, Trikudanathan S. An unusual manifestation of olfactory neuroblastoma[J]. BMJ Case Rep, 2018, 2018: bcr2017221661.
-

| 引用本文: | 陈小燕, 孙钰博, 鞠建宝, 等. 31例成人嗅神经母细胞瘤临床诊疗及预后危险因素分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(3): 224-228. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.03.007 |
| Citation: | CHEN Xiaoyan, SUN Yubo, JU Jianbao, et al. Diagonistic and prognostic analysis of olfactory neuroblastoma[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2021, 35(3): 224-228. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.03.007 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.



 下载:
下载: