The role of nasal nitric oxide in diagnosis and endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp
-
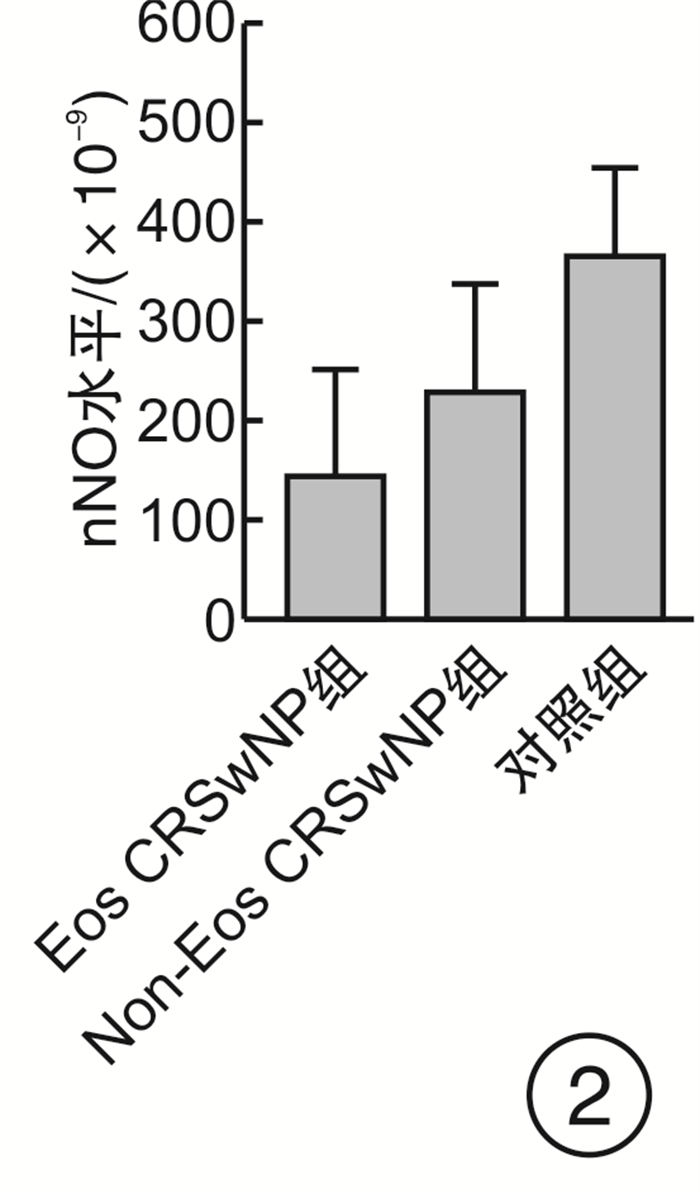
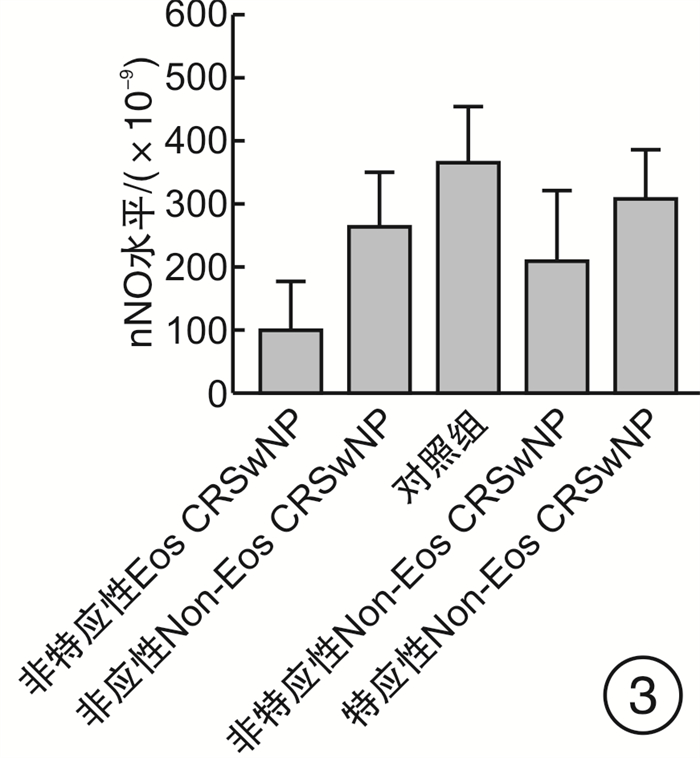
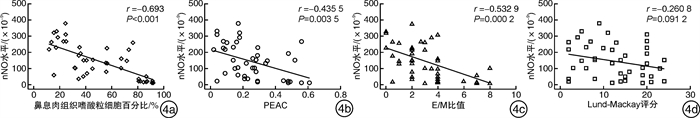
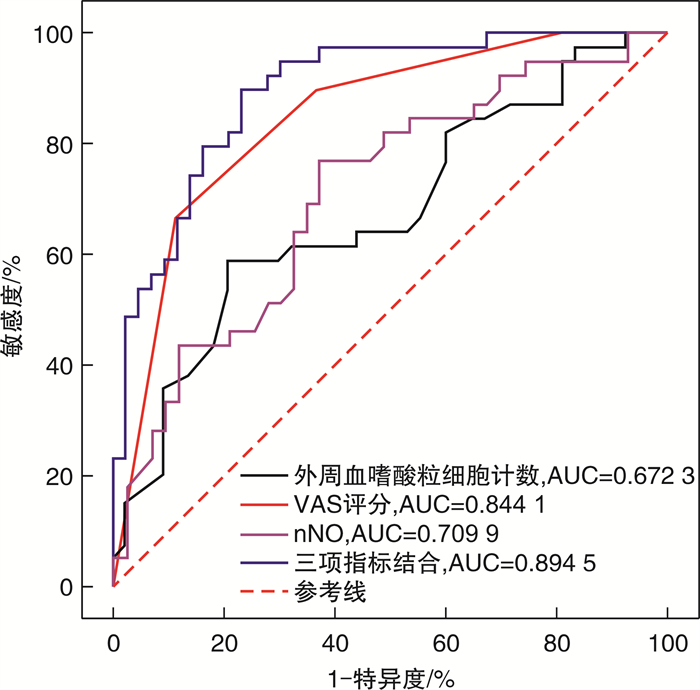
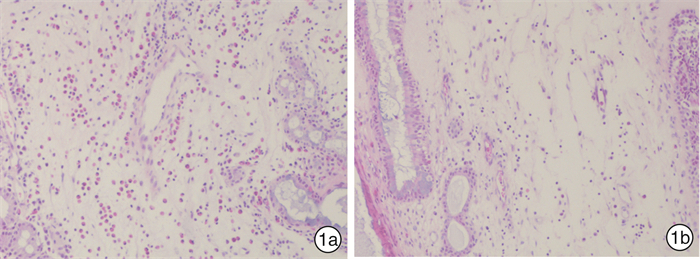
摘要: 目的 探讨鼻呼出气一氧化氮(nNO)无创检测在慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉(CRSwNP)诊断及分型中的临床应用价值。 方法 采用病例对照设计,共纳入82例CRSwNP患者(病例组)和30例健康志愿者(对照组)。根据组织病理中嗜酸粒细胞浸润程度将病例组分为嗜酸粒细胞性CRSwNP(Eos CRSwNP)组和非嗜酸粒细胞性CRSwNP(non-Eos CRSwNP)组。使用瑞典NIOX MINO仪器检测nNO水平。用t检验、χ2检验和Mann-Whitney U分析比较临床症状主客观评分差异,受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)及Logistic回归模型评估nNO测定在CRSwNP诊断和分型中的应用价值。 结果 ① Eos CRSwNP组患者的nNO水平明显低于Non-Eos CRSwNP组患者[(143.9±106.2)×10-9 vs(228.3±109.2)×10-9,P=0.000 9]和对照组[(143.9±106.2)× 10-9 vs(366.5±88.0)×10-9,P < 0.000 1]。②与非特应性患者相比,特应性患者表现出更高的nNO水平(P < 0.05)。③ROC分析表明nNO对Eos CRSwNP的诊断具有较高的预测价值(AUC=0.939),对non-Eos CRSwNP的诊断具有中等的预测价值(AUC=0.83)。而nNO对CRSwNP分型的鉴别有中度的预测价值(AUC=0.710)。④单因素、多因素Logistic回归分析均表明nNO与CRSwNP的分型存在相关性,OR及其95%CI分别为1.007(1.003~1.011),P=0.001;1.010(1.003~1.016),P=0.002。nNO联合外周血嗜酸粒细胞计数、VAS评分对CRSwNP分型的诊断价值高于单一指标(AUC=0.894,95%CI=0.807~0.951,P < 0.000 1,敏感度76.74%,特异度89.74%)。 结论 nNO检测有助于早期预测及区分CRSwNP亚型。将nNO、外周血嗜酸粒细胞计数和VAS评分三者结合可以更好地在临床上预测CRSwNP分型。CRSwNP患者的特应性状况影响nNO的水平。Abstract: Objective To investigate the roles of nasal nitric oxide(nNO) in diagnosis and endotypes of CRSwNP. Methods Eighty-two CRSwNP patients and thirty healthy volunteers were recruited for this study. The patients were classified into eosinophilic CRSwNP (Eos CRSwNP) and non-eosinophilic CRSwNP (non-Eos CRSwNP) endotypes by tissue eosinophil percentage. nNO levels were measured with an electrochemical sensor-based device. nNO levels and clinical factors were compared among the groups. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve and logistic regression analyses were performed to evaluate the predictive ability of the nNO for diagnosis and endotypes of CRSwNP. Results Eos CRSwNP patients(143.9±106.2) ×10-9 had lower nNO levels than non-Eos CRSwNP[(228.3±109.2) ×10-9, P=0.000 9) and healthy subjects(366.5±88.0) ×10-9, P < 0.000 1). Patients with atopy exhibited significantly higher levers of nNO compared with patients without atopy(P < 0.05). For Eos CRSwNP diagnosis, nNO had the highest predictive value(AUC: 0.939; sensitivity: 76.74%; specificity: 96.67%; cut-off value: 231×10-9, P < 0.001). Furthermore, nNO levels were associated with CRSwNP endotypes(odds ratio: 1.010; 95% confidence interval: 1.003%, 1.016%; P=0.002). When the nNO concentration was 158 ×10-9, we could discriminate Eos CRSwNP from non-Eos CRSwNP(AUC=0.710, sensitivity: 76.92%; specificity, 60.47%, P=0.001). After it was combinated by nNO, periphera blood eosinophil count(PEAC) and VAS score, the AUC was increased to 0.894(95%CI=0.807 to 0.951, P < 0.000 1, sensitivity: 76.74%, specificity: 89.74%). Conclusion nNO may has potential for non-invasive diagnosis and endotype of CRSwNP. nNO combined with PEAC and VAS score may be an ideal diagnostic tool for endotyps of Eos CRSwNP. However, the atopic status of the patients influenced the levels of nNO.
-
Key words:
- sinusitis /
- nasal polyps /
- eosinophil /
- nitric oxide
-

-
表 1 CRSwNP组与对照组临床特征的比较
临床特征 对照组 Eos CRSwNP组 non-Eos CRSwNP组 P 例数 30 43 39 年龄/岁 40.5(30, 51.3) 46(32, 50) 50(37, 56) 0.056 吸烟 0.280 是 4 12 7 否 26 31 32 哮喘 0 7 4 0.071 AR 0 4 2 0.221 组织嗜酸粒细胞计数/(×109·L-1) - 65(32, 127) 3(0, 9) 0.001 组织嗜酸粒细胞/% - 45.16(25.2, 80.8) 2.02(0, 5.7) 0.001 Lund-Mackay评分 - 13(7, 20) 12(6, 17) 0.561 E/M比值a) - 3(2, 4) 2.1(0.5, 2) 0.010 Lund-Kennedy评分 - 8(6, 10) 8(6, 10) 0.951 VAS评分 鼻塞 - 3.00(2, 5) 4(2, 5) 0.787 流涕a) - 2.37(2, 3) 2.31(2, 3) 0.799 头痛a) - 1.56(0, 2) 0.82(0, 2) 0.014 面部疼痛a) - 0.67(0, 1) 0.23(0, 0) 0.058 嗅觉障碍a) - 3.84(3, 5) 1.28(0, 2) 0.001 总体评分a) - 3.72(3, 4) 2.44(2, 3) 0.001 PEAC /(×109·L-1) 0.09(0.04, 0.15) 0.22(0.15, 0.34) 0.1(0.05, 0.23) 0.002 4 外周血嗜酸粒细胞/% 1.9(1.08, 3.43) 3.8(1.8, 5.2) 3(1, 4.8) 0.586 nNO水平/(×10-9) 361(273, 427.5) 133(37, 230) 226(171, 316) 0.000 3 注: a)为平均值(25,75)。 表 2 CRSwNP分型相关因素的单变量Logistic回归分析
相关因素 P OR 95%CI 年龄 0.112 1.03 0.993~1.067 性别 0.679 0.82 0.319~2.104 吸烟史 0.01 0.23 0.075~0.703 PEAC 0.002 0.003 0~0.118 外周血嗜酸粒细胞百分比 0.462 0.935 0.783~1.118 Lund-Mackay评分 0.346 0.971 0.912~1.033 Lund-Kennedy评分 0.085 0.835 0.680~1.025 E/M比值 0.886 1.011 0.866~1.181 VAS总体评分 0.000 0.169 0.085~0.339 nNO值 0.001 1.007 1.003~1.011 表 3 CRSwNP分型相关因素的多变量Logistic回归分析
P OR 95%CI PEAC 0.040 0.005 0~0.792 VAS总体评分 0.000 0.158 0.068~0.367 nNO值 0.002 1.010 1.003~1.016 表 4 ROC曲线评价nNO的诊断价值
AUC 临界值/(×10-9) 敏感度 特异度 P 阳性预测值 阴性预测值 约登指数 对照组vs病例组 对照组vs Eos CRSwNP组 0.939 231 76.74 96.67 < 0.001 97.10 76.3 0.76 对照组vs non-Eos CRSwNP组 0.830 334 63.33 89.74 < 0.001 86.40 76.6 0.56 Eos CRSwNP组vs non-Eos CRSwNP组 0.710 158 76.92 60.47 0.001 65.20 75.0 0.40 特应性vs非特应性 特应性Eos CRSwNP和特应性non-Eos CRSwNP vs非特应性Eos CRSwNP 0.844 216 76.32 90.91 0.001 96.80 55.6 0.70 特应性Eos CRSwNP和特应性non-Eos CRSwNP vs非特应性non-Eos CRSwNP 0.707 158 65.79 72.73 0.003 74.30 66.7 0.41 非特应性Eos CRSwNP vs非特应性non-Eos CRSwNP 0.794 162 72.73 81.25 < 0.001 3.88 0.34 0.54 -
[1] Maniscalco M, Bianco A, Mazzarella G, et al. Recent Advances on Nitric Oxide in the Upper Airways[J]. Curr Med Chem, 2016, 23(24): 2736-2745. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666160627115335
[2] Ren L, Zhang W, Zhang Y, et al. Nasal Nitric Oxide Is Correlated With Nasal Patency and Nasal Symptoms[J]. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res, 2019, 11(3): 367-380. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.3.367
[3] Wang X, Zhang N, Bo M, et al. Diversity of TH cytokine profiles in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: A multicenter study in Europe, Asia, and Oceania[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2016, 138(5): 1344-1353. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.05.041
[4] 杜艳玲, 孔慧, 于博, 等. 改良鼻内镜评分及ELR值与慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉亚分型的相关性分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(4): 306-310. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202004005.htm
[5] Hauser LJ, Chandra RK, Li P, et al. Role of tissue eosinophils in chronic rhinosinusitis-associated olfactory loss[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2017, 7(10): 957-962. doi: 10.1002/alr.21994
[6] Grayson JW, Li W, Ho J, et al. Topography of polyp recurrence in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2020, 10(5): 604-609. doi: 10.1002/alr.22529
[7] Lou H, Meng Y, Piao Y, et al. Predictive significance of tissue eosinophilia for nasal polyp recurrence in the Chinese population[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2015, 29(5): 350-356. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2015.29.4231
[8] Liao B, Liu JX, Li ZY, et al. Multidimensional endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis and their association with treatment outcomes[J]. Allergy, 2018, 73(7): 1459-1469. doi: 10.1111/all.13411
[9] Brescia G, Zanotti C, Parrino D, et al. Nasal polyposis pathophysiology: Endotype and phenotype open issues[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2018, 39(4): 441-444. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2018.03.020
[10] Meng Y, Lou H, Wang C, et al. Predictive significance of computed tomography in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2016, 6(8): 812-819. doi: 10.1002/alr.21749
[11] Kambara R, Minami T, Akazawa H, et al. Lower Airway Inflammation in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis as Determined by Exhaled Nitric Oxide[J]. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2017, 173(4): 225-232. doi: 10.1159/000479387
[12] Yoshida K, Takabayashi T, Imoto Y, et al. Reduced nasal nitric oxide levels in patients with eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Allergol Int, 2019, 68(2): 225-232. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2018.09.005
[13] Nakayama T, Yoshikawa M, Asaka D, et al. Mucosal eosinophilia and recurrence of nasal polyps-new classification of chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Rhinology, 2011, 49(4): 392-396. doi: 10.4193/Rhino10.261
[14] Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, et al. Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2009, 124(3): 478-484, 484. e1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.05.017
[15] Mahdavinia M, Suh LA, Carter RG, et al. Increased noneosinophilic nasal polyps in chronic rhinosinusitis in US second-generation Asians suggest genetic regulation of eosinophilia[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2015, 135(2): 576-579. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.08.031
[16] Song J, Liu Z, Wang Z, et al. Ectopic lymphoid tissues support local immunoglobulin production in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2018, 141(3): 927-937. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.10.014
[17] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组. 中国慢性鼻窦炎诊断和治疗指南(2018)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 54(2): 81-100. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2019.02.001
[18] Dweik RA, Boggs PB, Erzurum SC, et al. An official ATS clinical practice guideline: interpretation of exhaled nitric oxide levels(FENO)for clinical applications[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2011, 184(5): 602-615. doi: 10.1164/rccm.9120-11ST
[19] Hu Y, Cao PP, Liang GT, et al. Diagnostic significance of blood eosinophil count in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in Chinese adults[J]. Laryngoscope, 2012, 122(3): 498-503. doi: 10.1002/lary.22507
[20] Honma A, Takagi D, Nakamaru Y, et al. Reduction of blood eosinophil counts in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis after surgery[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2016, 130(12): 1147-1152. doi: 10.1017/S0022215116009324
[21] Yao Y, Wang ZC, Liu JX, et al. Increased expression of TIPE2 in alternatively activated macrophages is associated with eosinophilic inflammation and disease severity in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2017, 7(10): 963-972. doi: 10.1002/alr.21984
[22] Yoshimura K, Kawata R, Haruna S, et al. Clinical epidemiological study of 553 patients with chronic rhinosinusitis in Japan[J]. Allergol Int, 2011, 60(4): 491-496. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.10-OA-0234
[23] Wang ET, Zheng Y, Liu PF, et al. Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in East Asians[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2014, 2(12): 873-882. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i12.873
[24] Meng Y, Zhang L, Lou H, et al. Predictive value of computed tomography in the recurrence of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2019, 9(11): 1236-1243. doi: 10.1002/alr.22355
[25] Ambrosino P, Molino A, Spedicato GA, et al. Nasal Nitric Oxide in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with or without Nasal Polyps: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9(1): 200-200. doi: 10.3390/jcm9010200
[26] Colantonio D, Brouillette L, Parikh A, et al. Paradoxical low nasal nitric oxide in nasal polyposis[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2002, 32(5): 698-701. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.2002.01379.x
[27] Noda N, Takeno S, Fukuiri T, et al. Monitoring of oral and nasal exhaled nitric oxide in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis: a prospective study[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2012, 26(4): 255-259. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2012.26.3772
[28] Berlyne GS, Parameswaran K, Kamada D, et al. A comparison of exhaled nitric oxide and induced sputum as markers of airway inflammation[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2000, 106(4): 638-644. doi: 10.1067/mai.2000.109622
[29] Payne DN, Adcock IM, Wilson NM, et al. Relationship between exhaled nitric oxide and mucosal eosinophilic inflammation in children with difficult asthma, after treatment with oral prednisolone[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2001, 164(8 Pt 1): 1376-1381.
[30] Warke TJ, Fitch PS, Brown V, et al. Exhaled nitric oxide correlates with airway eosinophils in childhood asthma[J]. Thorax, 2002, 57(5): 383-387. doi: 10.1136/thorax.57.5.383
[31] Nonaka M, Pawankar R, Fukumoto A, et al. Heterogeneous response of nasal and lung fibroblasts to transforming growth factor-beta 1[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2008, 38(5): 812-821. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.02959.x
[32] Liu C, Zheng K, Liu X, et al. Use of Nasal Nitric Oxide in the Diagnosis of Allergic Rhinitis and Nonallergic Rhinitis in Patients with and without Sinus Inflammation[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract, 2020, 8(5): 1574-1581. e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2019.12.017
[33] Takahara D, Kono T, Takeno S, et al. Nasal nitric oxide in the inferior turbinate surface decreases with intranasal steroids in allergic rhinitis: A prospective study[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2019, 46(4): 507-512. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2018.11.005
[34] Liu C, Zheng M, He F, et al. Role of exhaled nasal nitric oxide in distinguishing between chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2017, 31(6): 389-394. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2017.31.4480
[35] Jeong JH, Yoo HS, Lee SH, et al. Nasal and exhaled nitric oxide in chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2014, 28(1): e11-16. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2014.28.3984
[36] Suojalehto H, Vehmas T, Lindström I, et al. Nasal nitric oxide is dependent on sinus obstruction in allergic rhinitis[J]. Laryngoscope, 2014, 124(6): E213-218. doi: 10.1002/lary.24590
-




 下载:
下载: