Analysis of efficacy of coblation assisted endoscope system for the treatment of parapharyngeal space tumors with transoral approach
-
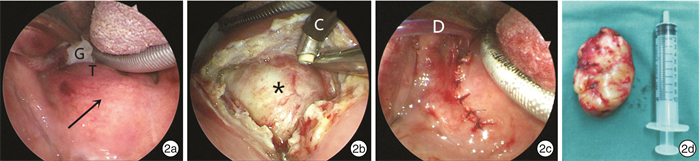
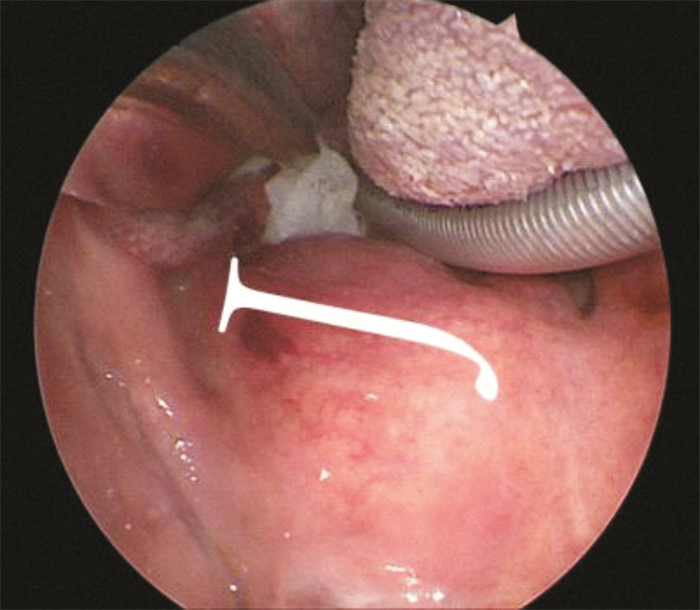
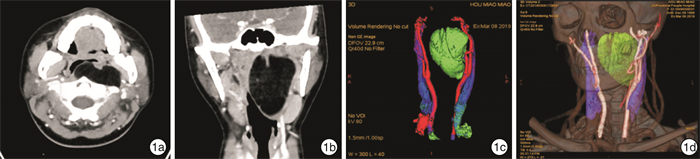
摘要: 目的 探讨在等离子及内镜系统的辅助下口内径路咽旁间隙肿瘤手术的可行性、安全性及有效性。 方法 回顾性分析20例咽旁间隙肿瘤患者的临床资料,术前均行CT和(或)MRI检查,均在等离子及内镜系统辅助下进行口内径路手术。术后密切随访,随访时间为8~56个月,中位随访时间为28个月。 结果 20例患者中良性肿瘤共18例(90%),恶性肿瘤2例(10%),肿瘤最大直径(4.4±1.6) cm,手术时间(79.00 ± 30.03) min,术中出血量(23.63 ± 22.20) mL,术后疼痛VAS评分2.8±1.4。17例完整切除,3例术后复发,包括1例滑膜肉瘤远处转移后死亡患者。2例出现术后并发症,1例神经纤维瘤出现声音嘶哑,1例神经鞘瘤出现伸舌偏斜。 结论 等离子及内镜系统辅助下口内径路治疗咽旁间隙肿瘤具有颈部不留瘢痕、患者易于接受、术中出血少、手术时间短、术后反应轻、恢复快等特点。但对原发恶性病变,广泛或高度血管化的病变,肿瘤位于颈内动脉外侧、上极与颅底距离小于2 cm或向外侧侵犯腮腺深叶,术前或术中考虑多形性腺瘤较大无法完整切除时,仍建议行外部入路手术。Abstract: Objective To summarize and analyze the feasibility, safety and efficacy of parapharyngeal space surgery assisted by coblation and endoscopic system with transoral approach. Methods The data of 20 patients with parapharyngeal space tumors were retrospectively analyzed. All the patients underwent CT and/or MRI examination before surgery, and all underwent transoral approach assisted by coblation and endoscopic systems. The patients were followed up strictly after the operation, with a follow-up time of 8-56 months and the median follow-up time of 28 months. Results Among the 20 patients, 18 (90%) were pathologically benign tumors and 2 (10%) were malignant tumors. The maximum tumor diameter was (4.4±1.6) cm, the operative time was (79.00±30.03) min, the intraoperative blood loss was (23.63±22.20) mL, and the postoperative pain VAS score was 2.8±1.4. There were 17 cases complete resection, and 3 cases of relapse, including 1 patient who died after distant metastasis of synovial sarcoma postoperative complications occurred in 2 cases, hoarseness in 1 case of neurofibroma and tongue extension deflection in 1 case of schwannoma. Conclusion Coblation assisted endoscopic system for the treatment of parapharyngeal space tumors with transoral approach has no cervical scar, which is a satisfaction for the patients, less intraoperative bleeding, short operative time, mild postoperative reaction and quick recovery. However, external approach is still recommended for primary malignant lesions, extensive or highly vascularized lesions, tumors located on the lateral side of the internal carotid artery, less than 2 cm from the skull base, or lateral invasion of the deep lobe of the parotid gland, or a pleomorphic adenoma is considered or is found to be too large to be completely resected preoperatively or intraoperatively.
-
Key words:
- parapharyngeal space tumor /
- transoral approach /
- coblation /
- endoscopic system
-

-
[1] Riffat F, Dwivedi RC, Palme C, et al. A systematic review of 1143 parapharyngeal space tumors reported over 20 years[J]. Oral Oncol, 2014, 50(5): 421-430. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2014.02.007
[2] Bradley PJ, Bradley PT, Olsen KD. Update on the management of parapharyngeal tumours[J]. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2011, 19(2): 92-98. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0b013e328342b9b4
[3] Dallan I, Fiacchini G, Turri-Zanoni M, et al. Endoscopic-assisted transoral-transpharyngeal approach to parapharyngeal space and infratemporal fossa: focus on feasibility and lessons learned[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 273(11): 3965-3972. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4074-6
[4] Unsaler S, BaȘaran B, DeȘer K. A giant mixed tumor originating from the parapharyngeal space[J]. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg, 2012, 22(3): 186-187.
[5] Infante-Cossio P, Gonzalez-Cardero E, Gonzalez-Perez LM, et al. Management of parapharyngeal giant pleomorphic adenoma[J]. Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2011, 15(4): 211-216. doi: 10.1007/s10006-011-0289-2
[6] Dimitrijevic MV, Jesic SD, Mikic AA, et al. Parapharyngeal space tumors: 61 case reviews[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2010, 39(10): 983-989. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2010.06.005
[7] Mondal P, Basu N, Gupta SS, et al. Fine needle aspiration cytology of parapharyngeal tumors[J]. J Cytol, 2009, 26(3): 102-104. doi: 10.4103/0970-9371.59395
[8] Matsuki T, Miura K, Tada Y, et al. Classification of tumors by imaging diagnosis and preoperative fine-needle aspiration cytology in 120 patients with tumors in the parapharyngeal space[J]. Head Neck, 2019, 41(5): 1277-1281. doi: 10.1002/hed.25552
[9] Lee HS, Kim J, Lee HJ, et al. Transoral robotic surgery for neurogenic tumors of the prestyloid parapharyngeal space[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2012, 39(4): 434-437. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2011.10.021
[10] Ducic Y, Oxford L, Pontius AT. Transoral approach to the superomedial parapharyngeal space[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2006, 134(3): 466-470. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2005.10.003
[11] Shirakura S, Tsunoda A, Akita K, et al. Parapharyngeal space tumors: anatomical and image analysis findings[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2010, 37(5): 621-625. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2010.01.003
[12] Boyce BJ, Curry JM, Luginbuhl A, et al. Transoral robotic approach to parapharyngeal space tumors: Case series and technical limitations[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126(8): 1776-1782. doi: 10.1002/lary.25929
[13] Goodwin WJ Jr, Chandler JR. Transoral excision of lateral parapharyngeal space tumors presenting intraorally[J]. Laryngoscope, 1988, 98(3): 266-269.
[14] 何龙, 谢景华, 高雄辉. 内镜辅助下经口径路咽旁间隙肿瘤切除术临床分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(9): 824-827, 835. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202009013.htm
[15] 陶磊, 石小玲, 李筱明, 等. 188例咽旁间隙肿瘤的回顾性分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(2): 129-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201802013.htm
[16] Castelnuovo P, Battaglia P, Bignami M, et al. Endoscopic transnasal resection of anterior skull base malignancy with a novel 3D endoscope and neuronavigation[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2012, 32(3): 189-91.
[17] 杨党卫, 周华磊, 李建兴, 等. 内镜下经口入路咽旁间隙手术的解剖标志[J]. 局解手术学杂志, 2016, 25(6): 391-394. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJXZ201606002.htm
[18] Utley DS, Goode RL, Hakim I. Radiofrequency energy tissue ablation for the treatment of nasal obstruction secondary to turbinate hypertrophy[J]. Laryngoscope, 1999, 109(5): 683-686. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199905000-00001
[19] 李五一, 刘建汉, 杨大海, 等. 经口低温等离子辅助显微外科治疗头颈肿瘤的初步效果[J]. 协和医学杂志, 2012, 3(2): 143-147. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XHYX201202008.htm
[20] Carney AS, Timms MS, Marnane CN, et al. Radiofrequency coblation for the resection of head and neck malignancies[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2008, 138(1): 81-85. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2007.08.022
[21] De Virgilio A, Park YM, Kim WS, et al. Transoral robotic surgery for the resection of parapharyngeal tumour: our experience in ten patients[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2012, 37(6): 483-488. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-4486.2012.02525.x
[22] Ansarin M, Tagliabue M, Chu F, et al. Transoral robotic surgery in retrostyloid parapharyngeal space schwannomas[J]. Case Rep Otolaryngol, 2014, 2014: 296025.
[23] Panda S, Sikka K, Thakar A, et al. Transoral robotic surgery for the parapharyngeal space: expanding the transoral corridor[J]. J Robot Surg, 2020, 14(1): 61-67. doi: 10.1007/s11701-019-00932-3
-




 下载:
下载: