Study of ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo associated with Meniere's disease
-
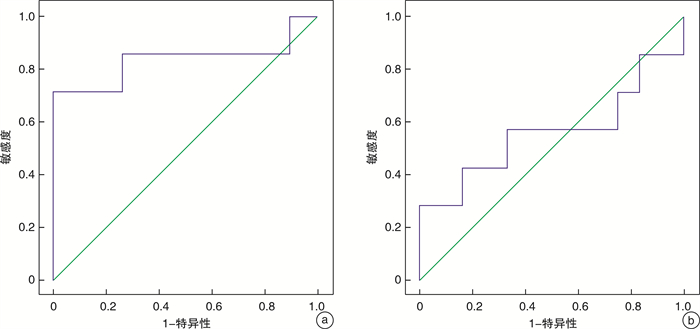
摘要: 目的 通过分析梅尼埃病合并良性阵发性位置性眩晕(BPPV-MD)患者的眼肌前庭诱发肌源性电位(oVEMP)特征, 探讨oVEMP频率振幅比(FAR)的临床特性。方法 选取2016年1月-2019年4月期间门诊确诊的单侧MD患者41例, 其中15例BPPV-MD患者设为BPPV-MD组, 26例单侧MD患者设为MD组; 同期选取30例(60耳)年龄和性别相匹配的健康志愿者作为对照组。分别以500、1000 Hz气导短纯音作为刺激声, 对三组受试者进行oVEMP和cVEMP检测。应用SPSS 20.0软件对BPPV-MD组和MD组患耳与对照组右耳oVEMP和cVEMP的引出率, N1、P1波潜伏期、振幅以及1000/500 Hz FAR进行对比分析, 并对FAR进行受试者工作特征曲线分析。结果 500 Hz刺激下BPPV-MD组、MD组患耳与对照组右耳的oVEMP引出率分别为46.67%(7/15)、46.15%(12/26)及76.67%(23/30);1000 Hz刺激下引出率分别为53.33%(8/15)、46.15%(12/26)及63.33%(19/30)。500 Hz下BPPV-MD组患耳oVEMP的N1、P1波潜伏期较MD组和对照组右耳延长(P < 0.05);1000 Hz下BPPV-MD组和MD组患耳oVEMP的N1、P1波潜伏期较对照组右耳延长(P < 0.05)。500 Hz下BPPV-MD组和MD组患耳oVEMP振幅较对照组右耳降低(P < 0.05);1000 Hz下BPPV-MD组、MD组患耳与对照组右耳比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。BPPV-MD组和MD组患耳oVEMP的FAR较对照组右耳高(P < 0.05);BPPV-MD组和MD组患耳之间FAR比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 BPPV-MD的oVEMP具有频率调谐的特性, 当FAR大于0.84时, 表明患者内耳存在膜迷路积水的病理学改变; 当FAR大于1.79时, 表明膜迷路积水引起椭圆囊囊斑耳石膜受损, 因此FAR可作为评价椭圆囊功能的指标之一。Abstract: Objective The aim of this study is to explore the characteristics of ocular muscle vestibular evoked myogenic potential (oVEMP) in patients with Meniere's disease and benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV-MD), and to explore the clinical characteristics of oVEMP frequency amplitude ratio (FAR).Methods Forty-one patients with unilateral MD diagnosed in the outpatient clinic from January 2016 to April 2019 were selected, of which 15 patients with BPPV-MD were set as BPPV-MD group, and 26 patients with unilateral MD were set as MD group. During the same period, 30 healthy volunteers matched in age and gender were selected as the control group. All the individuals underwent oVEMP and cVEMP recording for 500 Hz and 1000 Hz tone burst. The oVEMP and cVEMP response rate, N1 and P1 waves latency, N1-P1 wave amplitude and 1000/500 Hz FAR of the affected and contralateral ears of the three groups were compared and analyzed by SPSS 20.0 software. The receiver operating characteristics curves were obtained for finding out the criterion point, sensitivity, and specificity of 1000/500 Hz FAR for the diagnosis of BPPV-MD.Results In response to 500 Hz tone burst, oVEMP response rates in the affected lateral ears of BPPV-MD group, MD group and right ears of control group were 46.67%, 46.15% and 76.67%, respectively; the rates for the 1000 Hz-oVEMP of the three groups were 53.33%, 46.15% and 63.33%, respectively. By the 500 Hz air-conducted tone-burst stimulus, the oVEMP N1 and P1 latency of the affected ears in the BPPV-MD group was longer than that in the MD group and the control group(P < 0.05). By the stimulus of 1000 Hz tone burst, the oVEMP N1 and P1 latency of the affected ears in BPPV-MD group and MD group was longer than that in control group(P < 0.05). At 500 Hz, the oVEMP amplitude of the affected ears in BPPV-MD group and MD group was lower than that in the right ears of the control group(P < 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in the N1-P1 amplitudes of oVEMP in the three groups under the stimulation of 1000 Hz tone burst(P>0.05). The FAR for 1000/500 Hz of the affected ears in BPPV-MD group and MD group was higher than that in control group(P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference between BPPV-MD group and MD group(P>0.05).Conclusion When FAR is greater than 0.84, which indicates that the pathophysiologic factor is accumulation of excessive amounts of endolymph; when FAR is greater than 1.79, which suggests that the otolitic membrane of the elliptic cyst is damaged by the hydrops of the labyrinthus. The FAR of BPPV-MD can be used as one of the indicators to evaluate the function of the utricle.
-
Key words:
- Meniere's disease /
- vertigo /
- vestibular evoked myogenic potential /
- frequency tuning
-

-
表 1 三组患者在500、1000 Hz短纯音刺激下VEMP引出率比较
组别 例数 oVEMP(500 Hz) oVEMP(1000 Hz) cVEMP(500 Hz) cVEMP(1000 Hz) 患耳 健耳 患耳 健耳 患耳 健耳 患耳 健耳 BPPV-MD组 15 7(46.67) 11(73.33) 8(53.33) 10(66.67) 9(60.00) 11(73.33) 10(66.67) 12(80.00) MD组 26 12(46.15) 18(69.23) 12(46.15) 17(65.38) 16(61.54) 23(88.46) 17(65.38) 23(88.46) 对照组 30 23(76.67) 22(73.33) 19(63.33) 24(80.00) 26(86.67) 28(93.33) 25(83.33) 27(90.00) P < 0.05 >0.05 >0.05 >0.05 < 0.05 >0.05 >0.05 >0.05 表 2 三组患者在500 Hz短纯音刺激下VEMP N1、P1波潜伏期比较
ms 组别 例数 oVEMP(500 Hz) cVEMP(500 Hz) 患耳 健耳 患耳 健耳 N1波 P1波 N1波 P1波 N1波 P1波 N1波 P1波 BPPV-MD组 15 12.45±1.62 17.71±1.59 11.74±2.19 16.77±1.78 15.91±3.38 24.89±3.44 15.17±2.13 24.71±4.25 MD组 26 11.03±0.80 16.12±1.06 11.13±1.27 16.39±1.33 15.87±2.02 24.74±2.07 15.06±2.61 24.31±3.04 对照组 30 10.87±1.60 15.33±1.18 10.78±1.24 15.50±1.22 14.23±1.13 24.41±1.64 14.87±1.03 24.20±2.49 P < 0.05 < 0.05 >0.05 < 0.05 < 0.05 >0.05 >0.05 >0.05 表 3 三组患者在1000 Hz短纯音刺激下VEMP N1、P1波潜伏期比较
ms 组别 例数 oVEMP(1000 Hz) cVEMP(1000 Hz) 患耳 健耳 患耳 健耳 N1波 P1波 N1波 P1波 N1波 P1波 N1波 P1波 BPPV-MD组 15 11.87±1.52 16.79±1.77 10.59±0.88 16.13±3.06 14.53±3.02 23.35±3.24 13.57±1.91 23.42±1.18 MD组 26 11.68±1.25 16.72±1.4 6 11.21±1.15 16.08±1.09 14.84±1.91 22.92±1.85 14.18±2.47 22.75±2.72 对照组 30 10.70±1.24 15.11±1.15 11.32±1.63 15.69±1.05 13.40±1.04 23.47±1.51 13.69±0.95 23.28±2.29 P < 0.05 < 0.05 >0.05 >0.05 < 0.05 >0.05 >0.05 >0.05 表 4 三组患者在500、1000 Hz短纯音刺激下oVEMP振幅及FAR比较
组别 例数 患耳 健耳 500 Hz/μV 1000 Hz/μV FAR 500 Hz/μV 1000 Hz/μV FAR BPPV-MD组 15 4.07±1.29 4.53±1.39 1.29±0.71 5.59±1.32 4.61±1.30 0.86±0.35 MD组 26 4.16±0.85 4.62±0.79 1.16±0.33 5.66±1.02 4.64±1.19 0.86±0.26 对照组 30 5.99±0.72 4.24±0.45 0.72±0.09 5.83±0.81 4.41±0.58 0.77±0.13 P < 0.05 >0.05 < 0.05 >0.05 >0.05 >0.05 表 5 三组患者在500、1000 Hz短纯音刺激下cVEMP振幅及FAR比较
组别 例数 患耳 健耳 500 Hz/μV 1000 Hz/μV FAR 500 Hz/μV 1000 Hz/μV FAR BPPV-MD组 15 43.32±11.03 47.86±11.90 1.08±0.32 50.30±11.19 42.56±8.40 0.88±0.23 MD组 26 42.64±5.99 46.18±8.33 1.06±0.19 51.89±12.75 47.94±7.18 0.92±0.35 对照组 30 51.95±10.82 43.11±7.53 0.84±0.21 52.46±14.62 45.76±10.17 0.87±0.31 P >0.05 < 0.05 < 0.05 >0.05 >0.05 >0.05 -
[1] 赵鹏鹏, 徐先荣, 金占国, 等. 继发性良性阵发性位置性眩晕的临床特征分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(3): 220-224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201903009.htm
[2] 张青, 宋辉, 胡娟, 等. 气导短纯音诱发的眼肌前庭诱发肌源性电位在健康青年人群中的波形特征[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2012, 47(1): 15-18. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2012.01.005
[3] Winters SM, Campschroer T, Grolman W, et al. Ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in response to air-conducted sound in Ménière's disease[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2011, 32(8): 1273-1280. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e31822e5ac9
[4] Perez N, Martin E, Zubieta JL, et al. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in patients with Ménière's disease treated with intratympanic gentamycin[J]. Laryngoscope, 2002, 112(6): 1104-1109. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200206000-00031
[5] Gross EM, Ress BD, Viirre ES, et al. Intractable benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in patients with Meniere's disease[J]. Laryngoscope, 2000, 110(4): 655-659. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200004000-00022
[6] Paparella MM, Mancini F. Trauma and Meniere's syndrome[J]. Laryngoscope, 1983, 93(8): 1004-1012.
[7] Seo T, Saka N, Ohta S, et al. Detection of utricular dysfunction using ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potential in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2013, 550: 12-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.06.041
[8] Singh NK, Barman A. Characterizing the frequency tuning properties of air-conduction ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in healthy individuals[J]. Int J Audiol, 2013, 52(12): 849-854. doi: 10.3109/14992027.2013.822994
[9] Sandhu JS, Low R, Rea PA, et al. Altered frequency dynamics of cervical and ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in patients with Ménière's disease[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2012, 33(3): 444-449. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e3182488046
[10] Wen MH, Cheng PW, Young YH. Augmentation of ocular vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials via bone-conducted vibration stimuli in Ménière disease[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2012, 146(5): 797-803. doi: 10.1177/0194599811433982
[11] Winters SM, Berg IT, Grolman W, et al. Ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials: frequency tuning to air-conducted acoustic stimuli in healthy subjects and Ménière's disease[J]. Audiol Neurootol, 2012, 17(1): 12-19. doi: 10.1159/000324858
[12] Singh NK, Barman A. Frequency-Amplitude Ratio of Ocular Vestibular-Evoked Myogenic Potentials for Detecting Meniere's Disease: A Preliminary Investigation[J]. Ear Hear, 2016, 37(3): 365-373. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000263
[13] Singh NK, Barman A. Utility of the Frequency Tuning Measure of oVEMP in Differentiating Meniere's Disease from BPPV[J]. J Am Acad Audiol, 2016, 27(9): 764-777. doi: 10.3766/jaaa.15141
[14] Okuno T, Sando I. Localization, frequency, and severity of endolymphatic hydrops and the pathology of the labyrinthine membrane in Menière's disease[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 1987, 96(4): 438-445. doi: 10.1177/000348948709600418
[15] Morita N, Kariya S, Farajzadeh Deroee A, et al. Membranous labyrinth volumes in normal ears and Ménière disease: a three-dimensional reconstruction study[J]. Laryngoscope, 2009, 119(11): 2216-2220. doi: 10.1002/lary.20723
[16] Todd NP, Rosengren SM, Govender S, et al. Low-frequency tuning in the human vestibular-ocular projection is determined by both peripheral and central mechanisms[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2009, 458(1): 43-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.04.014
[17] Uzun-Coruhlu H, Curthoys IS, Jones AS. Attachment of the utricular and saccular maculae to the temporal bone[J]. Hear Res, 2007, 233(1/2): 77-85.
[18] von Brevern M, Schmidt T, Schönfeld U, et al. Utricular dysfunction in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2006, 27(1): 92-96. doi: 10.1097/01.mao.0000187238.56583.9b
[19] Singh NK, Barman A. Inter-frequency amplitude ratio of oVEMP for differentiating Meniere's disease from BPPV: clinical validation using a double-blind approach[J]. Int J Audiol, 2019, 58(1): 21-28. doi: 10.1080/14992027.2018.1529440
-




 下载:
下载: