Analysis of follow-up results of neonatal congenital auricle deformity after noninvasive correction
-
摘要: 目的 对不同类型的耳廓畸形患儿无创矫正后的随访结果进行分析, 了解患儿矫正后的反弹率, 为提高患儿耳廓的矫正效果提供相应指导。方法 矫正期间通过微信, 每日随访1次, 矫正结束后2 d随访1次, 持续1周; 若无变化, 1个月后进行最后一次随访。结果 对33例耳廓畸形患儿进行矫正, 6例隐耳, 4例杯状耳, 9例耳轮畸形, 4例垂耳, 4例环缩耳, 3例招风耳, 1例隐耳+环缩耳, 2例隐耳+耳轮畸形。年龄7 d~9个月, 均应用爱韦尔无创矫正器矫正, 矫正时间为3周~6个月。隐耳畸形患儿矫正对年龄的要求较为宽松, 1岁以内可进行矫正, 矫正时间约为1个月, 配合家长良好的矫正后护理, 反弹率几乎为0;环缩耳畸形患儿对年龄要求较高, 矫正时间较长, 最长可达6个月, 反弹率与矫正时间呈反比。结论 耳轮畸形、垂耳患儿矫正时间与患儿年龄大小成反比。良好的护理可以降低耳廓畸形患儿的反弹率, 提高矫治效果。Abstract: Objective To analyze the follow-up results of children with different types of auricle deformities after non-invasive correction, to understand the rebound rate of the children after correction, so as to provide corresponding guidance for improving the correction effect of the children's auricle.Methods During the correction period, follow up once a day through WeChat, and once every 2 days after the correction, lasting 1 week, and if there was no change, the last follow-up was carried out after 1 month.Results Thirty-three cases with ear deformities were corrected, 6 cases of cryptotia, 4 cases of cup ear, 9 cases of ear tubercle malformation, 4 cases of lope ear, 4 cases of constricted ear, 3 cases of prominent ear, 1 case of cryptotia mixed constricted ear, 2 cases of cryptotia mixed prominent ear. The age of 7 d to 9 months, all were corrected with EarWell non-invasive corrective system, correction duration time was 3 weeks to 6 months.Conclusion The age requirements for correction of hidden ear deformities are relatively loose, and they can be corrected within 1 year old, and the correction time is about one month. With good parental post-correction care, the rebound rate is almost 0; children with ring-shaped ear deformities, Requires higher age, longer correction time, up to 6 months, rebound rate is inversely proportional to correction time. The correction time of children with helix deformity and lop ears is inversely proportional to the age of the children. Good nursing can reduce the rebound rate of auricle deformity and improve the correction effect.
-
Key words:
- newborn /
- ear malformation /
- noninvasive correction
-
新生儿耳廓畸形是临床上较常见的头面部先天畸形,分为结构畸形和形态畸形,前者是指耳廓皮肤及软骨缺损导致的发育不全,后者则是耳廓发育完整但形态异常变化[1]。国外学者将其称为耳发育异常和耳变形[2],其发病率约为11.5/10 000[3]。吴胜林等[1]调查珠三角地区耳形态畸形发生率为43.46%,其发生率明显高于国人认知;尽管有研究表明耳廓形态畸形对患儿听力损失无直接影响[4],但其美学形态上的不足,容易对患儿身心的健康发育造成不良影响。对于耳廓结构畸形以传统手术治疗为主要手段[5]。而形态畸形国内尚未系统地进行耳廓畸形非手术矫正的临床应用。周智英等[6]报道应用矫正模型对小儿先天性耳廓畸形的矫正效果显著,但随着患儿年龄增大,矫正效果下降,并发症的发生率升高。因此,为防止小儿先天性耳廓畸形的并发症,并提高矫正效果,我院2017年5月-2019年6月采用无创矫正方式对33例耳廓形态畸形的患儿进行治疗,并通过微信回访和指导,对结果进行分析,现报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料
选取2017年5月—2019年6月在我院采用无创矫正方式进行治疗的33例先天性耳廓畸形患儿,年龄7 d~9个月,平均(78±25) d。均应用爱韦尔无创矫正器矫正,矫正时间为3周~6个月。其中隐耳6例,杯状耳4例,耳轮畸形9例,垂耳4例,环缩耳4例,招风耳3例,隐耳+环缩耳1例,隐耳+耳轮畸形2例。
1.2 矫正方法
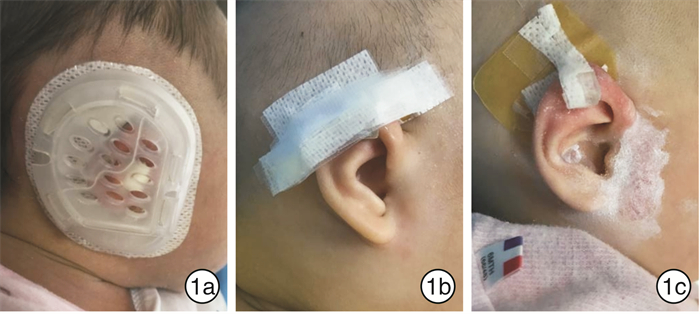
① 矫正器:矫正器由基座、耳轮牵引器、耳甲腔矫治器以及带孔前盖构成,按正常流程进行矫正并进行信息存档;②矫正器+3M胶:前期运用矫正器,后期用3M胶+耳轮牵引器;③3M胶+人工皮:对于隐耳畸形及轻度耳轮畸形患儿,以人工皮为基座贴于颞骨皮肤,3M分别贴于人工皮及耳廓背侧,外用牵引器进行必要的耳轮固定。矫正方法见图 1。
1.3 矫正后回访及指导方法
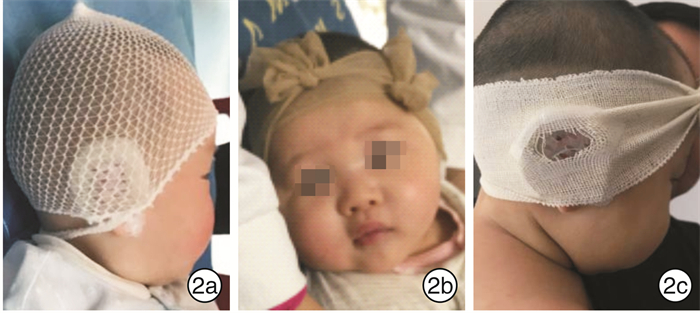
矫正器安装后拍照留档,与家属建立患儿沟通微信群,编辑照片(圈出本次主要受力部位),将照片发送至沟通群,告知患儿家属相关注意事项:①每日固定一个时段拍照1次,发送给微信群;②指导家属在家观察患儿耳廓受力的位置(如皮肤有无发白、发红、发紫);③时常透过耳窗闻看有无腥臭味;回访医护人员每日观察图片,若发现问题及时予以回复,对家属反映的问题提供相应线上指导。每周门诊复诊,提供各种加固措施:丝袜、头帽、绷带等,加强基座的稳定性(见图 2)。
2. 结果
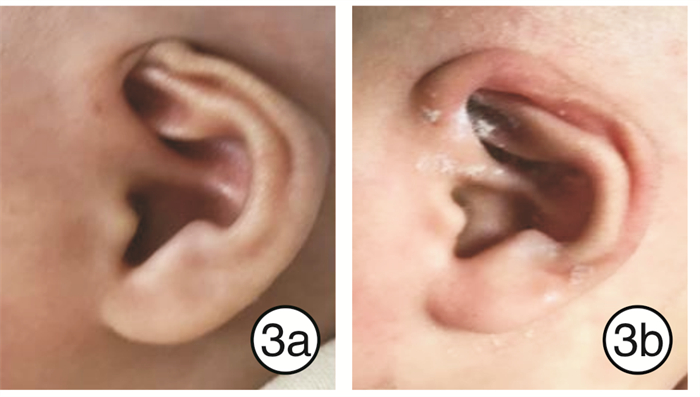
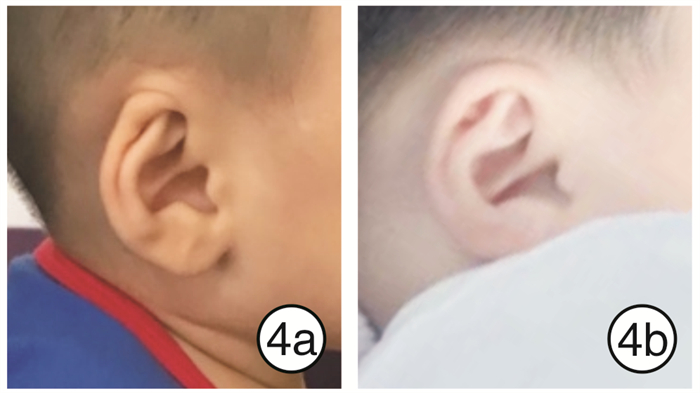
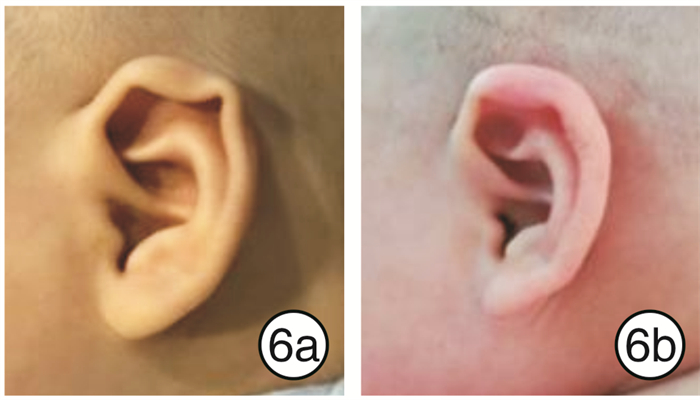
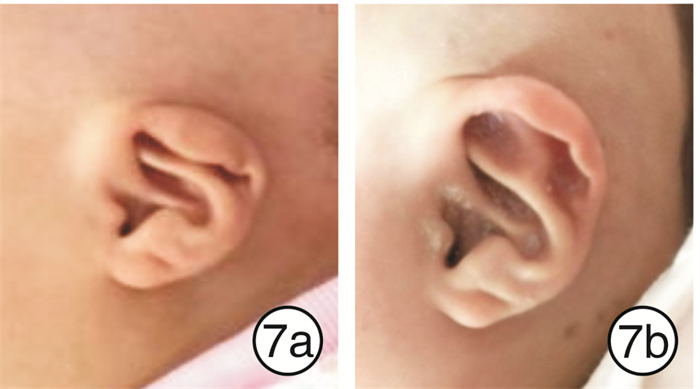
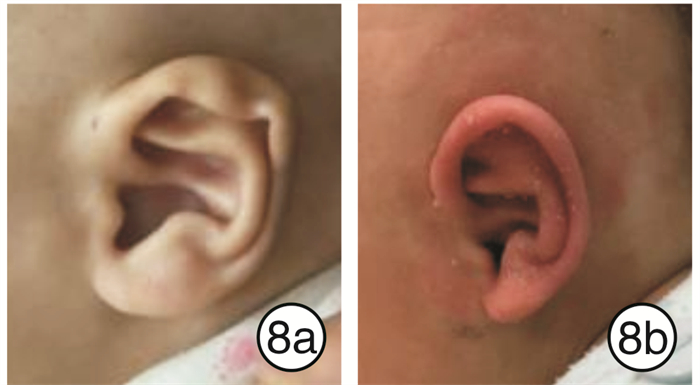
33例患儿矫正效果均达到满意。临床中发现隐耳畸形矫正对年龄的要求较为宽松,提前与家长做好沟通,1岁以内的患儿均可进行矫正,矫正时间为4~6周,畸形矫正前后对比见图 3~5;对于环缩耳畸形矫正,其有效率最低,反弹率最高,而患儿矫正后的反弹率与矫正时间呈反比,因此对患儿年龄要求较高,建议新生儿期完成,有条件的情况下,维持矫正至6个月,矫正时间为3~6个月;对于耳轮、垂耳畸形矫正,患儿年龄要求适中,出生1~8周均可,越早越好,矫正的时间与患儿年龄呈反比,治疗时间为4~6周(见图 6~8)。对于不同类型的耳廓畸形选用不同的治疗方案(如矫正器、3M胶、人工皮等基座固定方式);根据患儿的年龄大小定制不同的矫正时间,新生儿期矫正时间为4~6周,1~3个月的患儿矫正时间为2~3个月。
3. 讨论
新生儿先天性耳廓畸形传统治疗方法为手术治疗,不同耳廓畸形的手术方式不同。研究发现新生儿体内含有大量的产妇雌激素,雌激素在出生后72 h内达到一个明显的高峰,在6周后回到正常水平,透明质酸是耳软骨的重要组成成分,其含量受到产妇雌激素浓度的影响,雌激素浓度越高,透明质酸的含量也就越高,进而增加了耳廓软骨的延展性和可塑性[7]。出生后3 d~6周的时间为矫正窗口期,耳廓畸形可通过力学矫正的方式进行矫正。周婕等[8]报道在窗口期行无创矫正,治疗满意度较高,同时也可以减少相应的并发症。
国内陆续开展的耳廓畸形窗口期无创矫正中,环缩耳矫正后反弹率较高。如单纯的环缩耳或混合型环缩耳畸形(如环缩耳+隐耳),2~4周可见到明显的矫正效果,往往在矫正后2周可见环缩的外耳轮可以得到较好的舒展,但是这种舒展往往仅能维持数小时,然后外耳轮慢慢地向内复原。本研究从一开始的矫正时间2~4周,到6周到最后的维持矫正6个月,随着矫正时间的逐渐延长,患儿矫正后的反弹程度逐渐下降。由此得知,患儿环缩耳矫正后效果与矫正时间相关,矫正开始的时间越早,矫正时间越长,反弹越低。
对于年龄>3个月或矫正治疗无效、复发的耳廓畸形患儿,目前的治疗方法通常是在学龄期采取手术治疗[9]。Tanzer(1975)将环缩耳分为3型,而环缩耳畸形的矫正手术方法较多,尚无完全合适的术式,因此在窗口期行无创矫正显得尤为重要。
本研究中隐耳畸形的患儿年龄为9个月,已过了窗口期,矫正时间增加到2个月,仍然得到较好的疗效(矫正结束后半年回访结果),见图 4。隐于颞前皮下的耳轮软骨被完全牵引出来,也形成了较好的颅耳沟,矫正后半年未见反弹。Leclère等[10]采用激光配合胶带矫正成年人招风耳取得较好疗效,虽然并未得到广泛使用,但仍不失为一个有效的治疗方案,有助于推进无创矫治技术在先天性耳廓畸形治疗中非窗口期的应用。
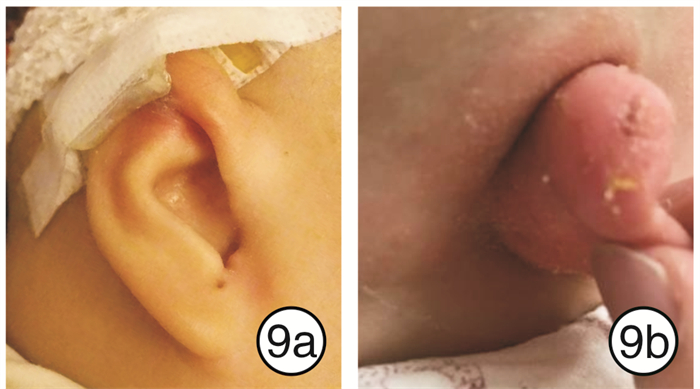
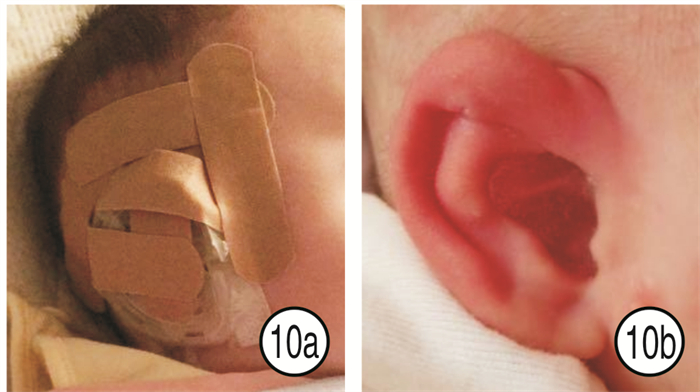
为了防止反弹,减少并发症的发生,孙美华等(2020)运用安普贴薄膜对耳轮畸形的塑型、预防无创耳矫正术中的压力性损伤、对受压部位的治疗均取得较好的效果。而本研究则是选择非刺激性、柔软且有足够的牵引力、稳定性强、性价比高的辅助材料(如人工皮、3M胶、头帽、丝袜等),疗效满意。利用人工皮对皮肤的保湿、无害性,将人工皮按照耳后沟形态修剪,行常规备皮、去脂处理后,以人工皮充当基座,贴于耳后,持久性强于3M胶,最长可持续3周;当然运用3M胶进行外固定的时间长短与家长护理有密切关系,如果护理不当,会导致3M胶易脱落现象;如患儿所处的外在环境温度过高,底胶受温度影响,会出现脱胶现象;母乳喂养时,未做好防护,残余奶汁流至3M胶上,导致脱胶、发臭,长时间不进行处理会发生感染;患儿长时间哭闹,皮肤出汗,底胶受汗渍影响,会出现脱胶现象;3M胶因脱落移动,牵引器也随之移位;运用3M胶外固定,缺少了起缓冲支撑作用的矫正器基座,牵引器直接作用于耳廓后皮肤,导致耳廓后皮肤过度受压易出现皮肤破损问题(图 9)。上述因素都会延长矫正时间,降低矫正效果。当然基座脱胶、耳廓皮肤损伤在运用矫正器、3M胶、人工皮等材料时均会出现,因此线上回访与家长及时沟通,对家长进行指导在矫正过程中占有重要地位。医护回访需要根据患儿家长提供的实时照片,及时进行正确指导,避免患儿出现不良反应及严重并发症,见图 10。同时,应对矫正后的患儿家长提出不同的护理要求,也有利于矫正治疗的预后。
-
[1] 吴胜林, 齐向东, 赵卉, 等. 新生儿耳廓形态学分型的初步研究[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志, 2013, 31(4): 384-388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLJZ201304006.htm
[2] Byrd HS, Langevin CJ, Ghidoni LA. Ear molding in newborn infants with auricular deformities[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2010, 126(4): 1191-1200. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181e617bb
[3] Anstadt EE, Johns DN, Kwok AC, et al. Neonatal Ear Molding: Timing and Technique[J]. Pediatrics, 2016, 137(3): e20152831. doi: 10.1542/peds.2015-2831
[4] 田野, 王芳, 於娟娟, 等. 先天性耳廓畸形筛查及无创矫正效果分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(3): 259-261. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201903019.htm
[5] 毕晔, 林琳, 宋宇鹏, 等. 先天性复合耳廓畸形的类型与临床治疗[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2013, 11(4): 481-484. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2013.04.002
[6] 周智英, 付勇, 毕静, 等. 耳矫正模型对小儿先天性耳廓畸形的近期应用研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 31(12): 949-952. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201712013.htm
[7] Leonardi A, Bianca C, Basile E, et al. Neonatal molding in deformational auricolar anomalies[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2012, 16(11): 1554-1558.
[8] 周婕, 齐向东, 陈建武. 先天耳廓畸形的无创矫正方法[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2017, 33(15): 2489-2492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2017.15.016
[9] 张天宇, 陈颖. 先天性外中耳畸形综合征的诊治原则[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(12): 883-885. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201812002.htm
[10] Leclère FM, Mordon S, Alcolea J, et al. 1064-nm Nd: YAG laser-assisted cartilage reshaping for treating ear protrusions[J]. Laryngoscope, 2015, 125(11): 2461-2467. doi: 10.1002/lary.25294
期刊类型引用(14)
1. 王施梦,米彦芳,张慧,陈莹,宋云韬,杨瑾. 先天性耳廓形态畸形及其不同分型的危险因素分析. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志. 2024(02): 160-163+167 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 柳燕伟,吴倩. 优质护理在耳模矫正新生儿中的应用效果分析. 中国医刊. 2024(03): 344-347 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张磊,汤顺英,张旭. 外耳矫正器治疗新生儿先天性耳郭畸形疗效探讨. 医学理论与实践. 2023(01): 111-113 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 纪尧峰,张凤飞. 皮肤牵引联合手术矫正儿童隐耳畸形. 中国美容医学. 2023(01): 1-3 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 肖栋,杜晓东,张磊,沈帆,谢晓颖. EarWell耳矫治器对新生儿耳廓畸形的效果及其预后不良影响因素分析. 现代生物医学进展. 2023(06): 1131-1135 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 植良娥,姜振东,何亚,兰发璋,钟诚. 不同类型的先天性耳廓畸形耳模矫正疗效分析. 中华耳科学杂志. 2023(03): 321-325 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 段晓晗 ,张铭 ,林佳华 ,邹艺辉 . 耳廓矫形器适应证拓展研究. 中华耳科学杂志. 2023(03): 350-355 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王晓丽,吴丹,钟启宝,章凤强,赵雅利,贺定华,熊黎黎. 先天性耳廓畸形耳模矫正的疗效分析. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志. 2023(05): 25-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 吴杰,谢晋,陈洪涛,陈洪颖. 耳模矫正在儿童先天性耳廓形态畸形中的应用研究. 现代诊断与治疗. 2023(18): 2770-2772 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 王艳丹,程楠,史保院,WANG Shujing. 无创耳模矫正技术治疗小儿先天性耳郭畸形的临床研究. 河南大学学报(医学版). 2022(03): 188-193 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 许慧娟,杨海涛,丁韶洸,谢存存,贾晓东,王广科,刘宏建. 超时间窗轻度隐耳畸形无创矫正的疗效分析. 中华耳科学杂志. 2022(04): 581-588 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 林恩润,茅林蔚,胡伟群. 莆田地区新生儿耳郭畸形的发生情况及耳郭无创矫正的效果分析. 中国民间疗法. 2022(19): 100-102 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 杨慧芬,陶跃进,黄彩琴. Earwell耳廓矫形器治疗先天性耳廓形态畸形的临床效果分析. 中国医疗美容. 2021(06): 46-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 仇祥宇,李佳,侯晓英. 产前超声诊断胎儿单侧耳廓畸形1例. 中国优生与遗传杂志. 2021(09): 1313-1314 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)
-




 下载:
下载: