Surgical efficacy analysis of venous pulsatile tinnitus related to sigmoid sinus diverticulum
-
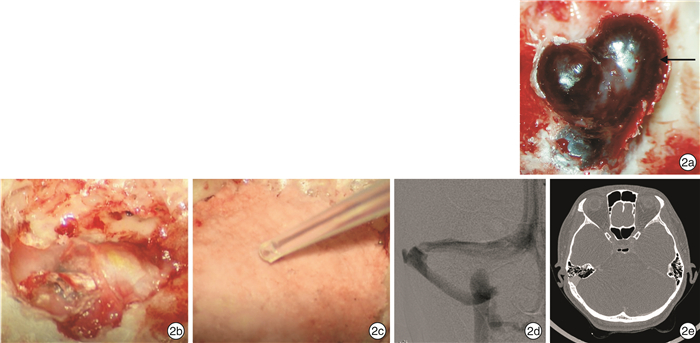
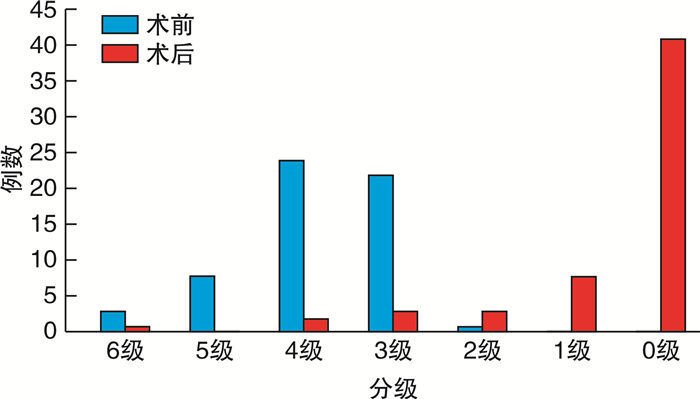
摘要: 目的 探讨乙状窦憩室引起静脉源性搏动性耳鸣的手术疗效。方法 对58例单侧乙状窦憩室致静脉源性搏动性耳鸣患者的耳鸣情况进行分级后行乙状窦骨壁重建术,对其中28例患者行乙状窦憩室缺损最大横截面面积测量。术后随访3~44个月,统计分析术后耳鸣的改善程度,乙状窦憩室缺损最大横截面面积大小与病程长短及耳鸣程度的关系。结果 术后耳鸣痊愈41例(70.69%),显效10例(17.24%),有效3例(5.17%),无效4例(6.90%)。患者手术前和手术后的耳鸣程度分级差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。对28例患者行乙状窦憩室缺损最大横截面面积测量,Pearson相关分析发现乙状窦憩室缺损最大横截面面积大小与耳鸣程度及病程长短均无明显相关性(P>0.05)。结论 乙状窦骨壁重建术能够在保证患者安全的情况下,有效地缓解乙状窦憩室相关静脉源性搏动性耳鸣。Abstract: Objective To discuss the outcomes of the surgical treatment of venous pulsatile tinnitus caused by sigmoid sinus diverticulum.Method Fifty-eight patients with venous pulsatile tinnitus caused by unilateral sigmoid sinus diverticulum were admitted. The patients' tinnitus was graded and treated by sigmoid sinus bone wall reconstruction. The maximum cross-sectional area of sigmoid sinus diverticulum defect was measured in 28 patientsc. All the patients were followed up for 3 to 44 months after operation to analyze the improvement of postoperative tinnitus, the relationship between the size of the sigmoid sinus cross-sectional area and the degree of tinnitus and length of disease statistically.Result Postoperative tinnitus was cured in 41 cases(70.69%), markedly effective in 10 cases(17.24%), effective in 3 cases(5.17%) and ineffective in 4 cases(6.90%). There was a statistically significant difference in the degree of tinnitus before and after surgery (P < 0.05). Pearson correlation analysis showed thatthe maximum cross-sectional area of the sigmoid sinus diverticulum defect was not significantly correlated with the degree of tinnitus and the length of the disease in 28 patients (P>0.05).Conclusion The sigmoid sinus bone wall reconstruction can effectively relieve venous pulsatile tinnitus related to sigmoid sinus diverticulum while ensuring patient safety.
-

-
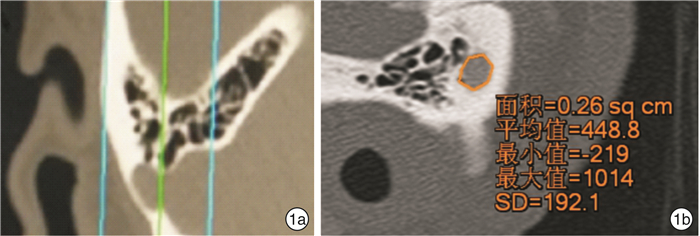
表 1 28例患者乙状窦憩室缺损面积大小、术前耳鸣程度及耳鸣时间
术前耳鸣程度分级 例数 乙状窦憩室缺损面积平均值/cm2 耳鸣平均时间/年 6级 3 0.67 6.0 5级 5 0.50 3.6 4级 9 0.64 5.8 3级 10 0.67 7.0 2级 1 0.47 0.5 -
[1] 曹向宇, 张荣举, 王君, 等. 源于乙状窦憩室搏动性耳鸣的血管内治疗[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2017, 19(2): 134-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNXG201702006.htm
[2] Biehl R, Boecking B, Brueggemann P, et al. Personality Traits, Perceived Stress, and Tinnitus-Related Distress in Patients With Chronic Tinnitus: Support for a Vulnerability-Stress Model[J]. Front Psychol, 2019, 10: 3093. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.03093
[3] Handscomb L, Shorter GW, Hoare DJ, et al. Evaluation of a Cognitive Behavioral Model of Tinnitus Distress: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Structural Equation Modeling[J]. Ear Hear, 2020, 41(4): 1028-1039. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000826
[4] Wang GP, Zeng R, Ma XB, et al. Surgical treatment of pulsatile tinnitus caused by the sigmoid sinus diverticuluma preliminary study[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2015, 94(21): e882.
[5] 彭佳丽, 赵蓉, 李格飞, 等. 乙状窦憩室致搏动性耳鸣的介入治疗成功案例报道[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2016, 36(12): 1820-1822. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2016.12.029
[6] Ding H, Zhao P, Lv H, et al. Temporal bone contrast-enhanced high-resolution CT evaluation of pulsatile tinnitus after sigmoid sinus wall reconstruction[J]. Acta Radiol, 2019, 60(1): 54-60. doi: 10.1177/0284185118773509
[7] Reardon MA, Raghavan P. Venous Abnormalities Leading to Tinnitus: Imaging Evaluation[J]. Neuroimaging Clin N Am, 2016, 26(2): 237-245. doi: 10.1016/j.nic.2015.12.006
[8] 刘蓬. 耳鸣程度分级与疗效评定标准的探讨[J]. 中国中西医结合耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2004, 12(4): 181-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYJH200404004.htm
[9] Truesdale CM, El-Kashlan HK. Pulsatile tinnitus with imaging[J]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2018, 144(5): 451-452. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2018.0014
[10] Zeng R, Wang GP, Liu ZH, et al. Sigmoid sinus wall reconstruction for pulsatile tinnitus caused by sigmoid sinus wall dehiscence: a singlecenter experience[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(10): e0164728. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164728
[11] 孙兴旺, 崔豹, 徐卫峰, 等. 搏动性耳鸣乙状窦骨壁缺损与病程相关性研究[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2017, 27(6): 1032-1035. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYXZ201706010.htm
[12] 龚树生, 曾嵘, 王国鹏. 重视乙状窦相关病变致搏动性耳鸣的诊治[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 29(8): 677-680. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201508001.htm
[13] Berguer R, Nowak P. Treatment of venous pulsatile tinnitus in younger women[J]. Ann Vasc Surg, 2015, 29(4): 650-653. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2014.12.039
[14] Ding H, Zhao P, Lv H, et al. Temporal bone contrast-enhanced high-resolution CT evaluation of pulsatile tinnitus after sigmoid sinus wall reconstruction[J]. Acta Radiol, 2019, 60(1): 54-60. doi: 10.1177/0284185118773509
[15] Liu GS, Boursiquot BC, Blevins NH, et al. Systematic Review of Temporal Bone-Resurfacing Techniques for Pulsatile Tinnitus Associated with Vascular Wall Anomalies[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 160(5): 749-761. doi: 10.1177/0194599818823205
-




 下载:
下载: