-
摘要: 目的 通过临床病例资料分析了解儿童腮腺区病损的疾病谱,明确现有治疗方法下疾病的转归和预后。方法 分析170例腮腺区病损患儿的基础资料、入院临床症状、诊断结果、治疗方法、预后及随访情况。结果 170例腮腺区病损患儿中,先天性疾病83例(48.82%),脉管性肿物62例(36.47%),良恶性肿瘤17例(10.00%),炎性病变8例(4.71%);108例患儿接受手术治疗,34例患儿接受局部博来霉素注射治疗,28例患儿接受手术和局部博来霉素注射治疗。2例患儿术后复发经再次手术治愈;1例患儿出现面瘫,随访3个月后恢复。结论 儿童腮腺区病损最为常见的疾病是先天性疾病和脉管性肿物。手术结合博来霉素局部治疗是主要治疗手段且取得了显著的疗效。口服普萘洛尔对于腮腺区血管瘤有一定的治疗作用。Abstract: Objective To observe the disease spectrum of the parotid region lesions in children, and clarify the outcome and prognosis of the disease by analyzing of clinical data.Method The basic information, clinical symptoms, diagnosis results, treatment, prognosis and follow-up of 170 cases with parotid region lesions were analyzed.Result Among 170 cases of the parotid region lesions, 83 cases(48.82%) were congenital disease, 62 cases(36.47%) were vascular mass, 17 cases(10.00%) were benign or malignant tumor, and 8 cases(4.71%) were infectious disease; 108 cases of the patients were treated with surgery, 34 of them were treated with local bleomycin injection while 28 cases were treated with both surgery and local bleomycin injection. Two cases was cured by reoperation after recurrence and 1 case had facial paralysis but recovered after 3 months of follow-up.Conclusion The most common diseases of parotid region lesions in children were congenital disease and vascular mass. Surgery combined with bleomycin local treatment is the main therapy in parotid area and has achieved remarkable results. Oral propranolol has certain therapeutic value for parotid region hemangioma.
-
Key words:
- child /
- parotid diseases /
- surgical procedures, operative
-

-
[1] 尹德佩, 窦训武, 杨素娜, 等. 儿童腮腺区脉管瘤的外科治疗[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2010, 37(6): 659-660. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5749.2010.06.011
[2] 刘宇楠, 刘宇. 婴幼儿腮腺区血管瘤治疗的研究进展[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2012, 39(4): 487-490. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5749.2012.04.019
[3] 李思源, 郭雪生, 单小峰, 等. 177例儿童口腔颌面部恶性肿瘤临床病理分析[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2016, 14(2): 134-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKQ201602014.htm
[4] 李万鹏, 赵利敏, 徐宏鸣, 等. 婴儿颈部巨大囊性淋巴管瘤3例治疗体会[J]. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志, 2017, 17(5): 345-347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YRBH201705010.htm
[5] 杨学芳, 王亚娟, 丁翎君, 等. 新生儿化脓性腮腺炎13例临床分析[J]. 中华新生儿科杂志, 2018, 33(1): 56-58. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2096-2932.2018.01.014
[6] Arnot RS. Defects of the first branchial cleft[J]. S Afr J Surg, 1971, 9(2): 93-98. doi: 10.1097/00006534-196301000-00011
[7] Shinn JR, Purcell PL, Horn DL, et al. First branchial cleft anomalies: otologic manifestations and treatment outcomes[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2015, 152(3): 506-512. doi: 10.1177/0194599814562773
[8] Li W, Xu H, Zhao L, et al. Branchial anomalies in children: A report of 105 surgical cases[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 104: 14-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2017.10.035
[9] Teo NW, Ibrahim SI, Tan KK. Distribution of branchial anomalies in a paediatric Asian population[J]. Singapore Med J, 2015, 56(4): 203-207. doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015060
[10] Inarejos CE, Navallas M, Tolend M, et al. Imaging Evaluation of Pediatric Parotid Gland Abnormalities[J]. Radiographics, 2018, 38(5): 1552-1575. doi: 10.1148/rg.2018170011
[11] Ren W, Li S, Gao L, et al. Low-dose propranolol for infantile hemangioma of the head and neck: Analysis of 23 consecutive patients[J]. Pediatr Int, 2017, 59(2): 213-217. doi: 10.1111/ped.13109
[12] 顾美珍, 吴佳欐, 赵利敏, 等. 婴幼儿腮腺血管瘤口服盐酸普萘洛尔片治疗体会[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2013, 48(9): 769-770. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2013.09.016
[13] Mirza B, Ijaz L, Saleem M, et al. Cystic hygroma: an overview[J]. J Cutan Aesthet Surg, 2010, 3(3): 139-144. doi: 10.4103/0974-2077.74488
[14] Ghritlaharey RK. Management of giant cystic lymphangioma in an infant[J]. J Clin Diagn Res, 2013, 7(8): 1755-1756. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2013/5418.3256
[15] Gontarz M, Wyszynska-Pawelec G, Zapala J. Primary epithelial salivary gland tumours in children and adolescents[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2018, 47(1): 11-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2017.06.004
[16] Mehta D, Willging JP. Pediatric salivary gland lesions[J]. Semin Pediatr Surg, 2006, 15(2): 76-84. doi: 10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2006.02.004
[17] Tilaveridis I, Kalaitsidou I, Pastelli N, et al. Lipoma of Parotid Gland: Report of Two Cases[J]. J Maxillofac Oral Surg, 2018, 17(4): 453-457. doi: 10.1007/s12663-018-1080-9
[18] Starkman SJ, Olsen SM, Lewis JE, et al. Lipomatous lesions of the parotid gland: analysis of 70 cases[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123(3): 651-656. doi: 10.1002/lary.23723
[19] 张敏, 贾志宇, 刘树妍, 等. 腮腺良性肿瘤浅叶部分切除术与浅叶切除术的循证医学分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(9): 875-882. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201909019.htm
[20] Tanaka A, Moriyama M, Nakashima H, et al. Th2 and regulatory immune reactions contribute to IgG4 production and the initiation of Mikulicz disease[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2012, 64(1): 254-263. doi: 10.1002/art.33320
[21] Rhee F V, Stone K, Szmania S, et al. Castleman disease in the 21st century: An update on diagnosis, assessment, and therapy[J]. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol, 2010, 8(7): 486-498. http://med.wanfangdata.com.cn/Paper/Detail/PeriodicalPaper_PM20864917
[22] Munshi N, Mehra M, van de Velde H, et al. Use of a claims database to characterize and estimate the incidence rate for Castleman disease[J]. Leuk Lymphoma, 2015, 56(5): 1252-1260. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2014.953145
[23] 马欣, 王永功. 腮腺区包块的临床诊断与治疗分析[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2012, 28(9): 918-919. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KQYZ201209024.htm
[24] 李晓娜. 高频彩色多普勒超声诊断腮腺区肿块的临床价值[J]. 中国社区医师(医学专业), 2012, 14(7): 240-241. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2012.07.237
[25] Tian X, Eldadah M, Cheng W. Neonatal Suppurative Parotitis: Two Cases[J]. Pediatr Infect Dis J, 2016, 35(7): 823-824. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000001177
-

| 引用本文: | 徐宏鸣, 郑阳阳, 陈芳, 等. 儿童腮腺区病损的诊疗特点[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(10): 941-944. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.10.017 |
| Citation: | XU Hongming, ZHENG Yangyang, CHEN Fang, et al. Diagnosis and characteristics of parotid region lesions in children[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2020, 34(10): 941-944. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.10.017 |
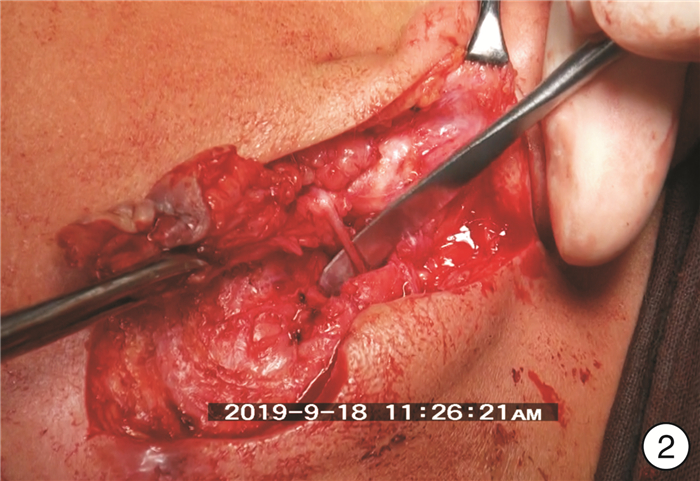
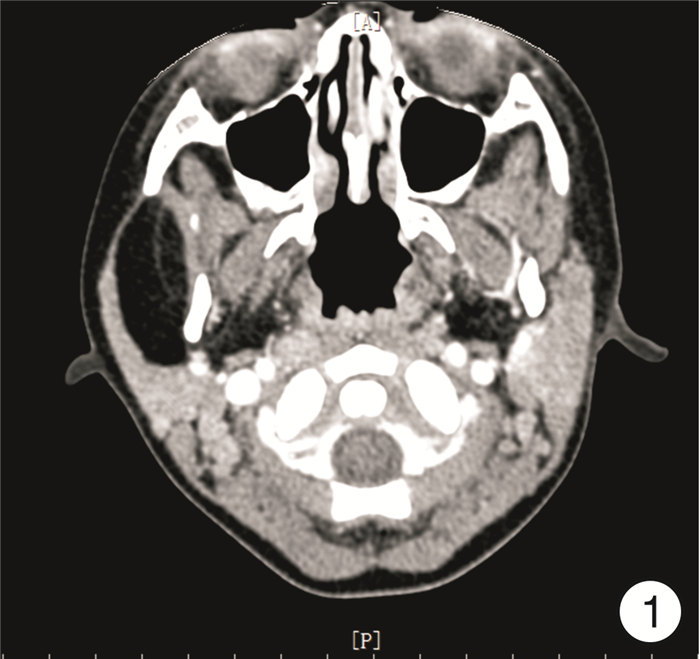
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
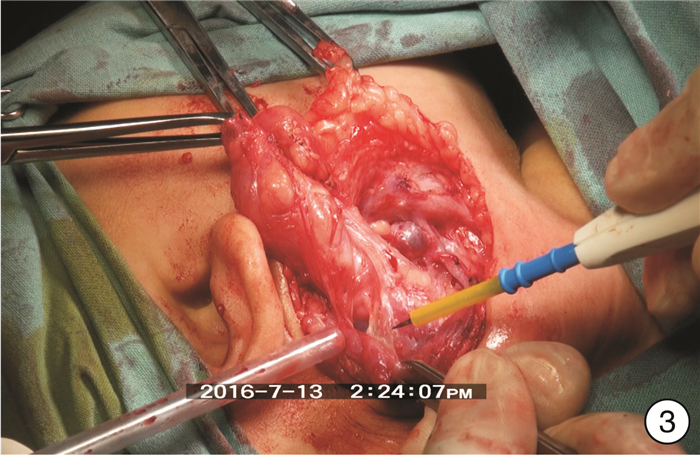
- Figure 3.



 下载:
下载: