Clinical value of upper airway MSCT measurement in adult male patients with moderate to severe OSA
-
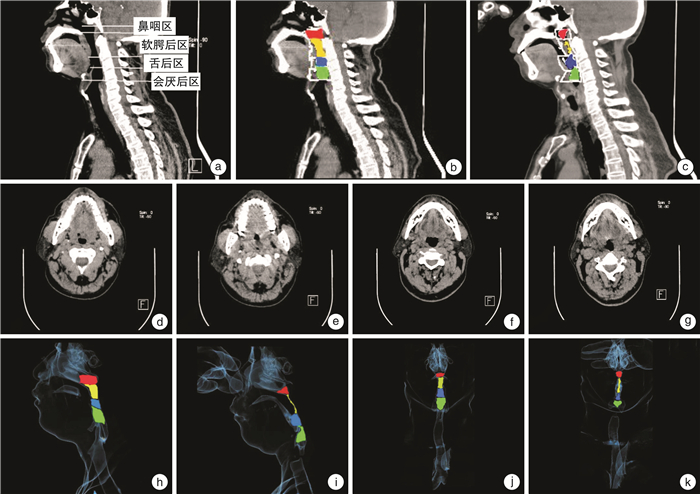
摘要: 目的 通过128层螺旋CT测量中重度阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停(OSA)成年男性患者在不同呼吸时相上气道解剖结构的变化,探讨与OSA相关的发病机制,优化OSA患者的治疗选择。方法 应用128层螺旋CT对52例中重度OSA成年男性患者(OSA组)和20例正常对照组(正常组)分别在平静呼吸及Müller动作2种不同呼吸状态下进行上气道扫描,测量上气道各区域平面径线长度、面积大小,软腭长度、厚度、气道体积、气道长度、咽侧壁总厚度,并计算出咽腔顺应性包括咽侧壁顺应性、咽前后壁顺应性及总咽壁顺应性,将各测量结果进行相互比较并与相关参数进行相关性分析。结果 OSA组平静呼吸时气道各区(除会厌后区外)最小平面的径线长度及面积均显著大于Müller动作(P < 0.05),OSA组平静呼吸时的软腭长度、厚度显著大于正常组(P < 0.01),OSA组Müller动作软腭区和舌后区咽侧壁总厚度显著大于平静呼吸状态(P < 0.01),OSA组平静呼吸时鼻咽区、会厌后区体积、气道长度显著大于正常组(P < 0.01),OSA组Müller动作时软腭后区和舌后区体积以及气道总体积均显著小于平静呼吸状态(P < 0.01),OSA组咽腔顺应性均显著大于正常组(P < 0.05),OSA组软腭后区咽侧壁顺应性显著大于咽前后壁顺应性,而舌后区咽前后壁顺应性显著大于咽侧壁顺应性(P < 0.05)。OSA患者的BMI与AHI呈正相关(P < 0.05)。结论 通过MSCT对中重度OSA成年男性患者上气道的测量,能直观地观察上气道形态结构和顺应性的变化,精准评估上气道狭窄程度和狭窄部位,同时结合测量指标与相关参数的相关性能够优化临床上OSA成年男性患者的治疗选择。
-
关键词:
- 睡眠呼吸暂停, 阻塞性 /
- 咽侧壁总厚度 /
- 成年男性 /
- 气道塌陷
Abstract: Objective To investigate the pathogenesis of OSA-related through 128-slice spiral CT measurements of adult male patients with moderate to severe OSA at different respiratory phases, and to optimize treatment options for patients with OSA.Method 128-slice spiral CT was used to scan the upper airway in 52 adult male patients with moderate to severe OSA and 20 normal controls under two different breathing states: calm breathing and Müller maneuver. The plane diameter and length of each area of the upper airway were measured. Area size, soft palate length, thickness, airway volume, airway length, total thickness of the pharyngeal wall, and calculate the compliance of the pharyngeal cavity, including the compliance of the pharyngeal wall, the compliance of the anterior and posterior pharyngeal wall, and the total pharyngeal compliance. Comparison of measurement results and correlation analysis with related parameters.Result In the OSA group, the length and area of the smallest plane of each airway area(except the posterior epiglottic area) during calm breathing are greater than Müller's movement, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05). The soft palate length and thickness of the OSA group during calm breathing were significantly larger than those of the normal group, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.01), In the OSA group, the total thickness of the soft palate region and the posterior lingual area of the pharyngeal wall in the Müller group was significantly greater than the calm breathing state, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.01). The volume of the nasopharynx, posterior epiglottic area and airway length in the OSA group during calm breathing were significantly larger than those in the normal group, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.01). The compliance of the pharyngeal cavity in the OSA group was greater than that in the normal group, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05). In the OSA group, the volume of the posterior soft palate, posterior tongue, and total airway volume during Müller movement were significantly smaller than those of calm breathing, and the differences were statistically significant(P < 0.01). In the OSA group, the compliance of the pharyngeal wall in the posterior region of the soft palate was greater than the compliance of the anterior and posterior wall of the pharynx, while the compliance of the posterior region of the pharynx in the posterior region of the pharynx was greater than the compliance of the pharynx. There was a significant positive correlation between BMI and AHI in OSA patients(P < 0.05), which was statistically significant.Conclusion Through MSCT measurement of the upper airways of adult male patients with moderate to severe OSA, the morphological structure and compliance of the upper airways can be observed intuitively, and the degree and location of upper airway stenosis can be accurately assessed, and the measurement indicators and related parameters can be combined. The correlation can optimize the clinical treatment options for adult male patients with OSA. -

-
表 1 2组平静呼吸时的软腭长度、软腭厚度比较
mm,x±s 测量指标 OSA组 正常组 t值 P值 软腭厚度 11.02±0.94 8.10±0.85 12.01 < 0.01 软腭长度 50.32±3.02 37.85±1.09 17.95 < 0.01 表 2 OSA组Müller动作与平静呼吸状态下气道各区咽侧壁总厚度比较
x±s 测量指标 Müller动作 平静呼吸状态 t值 P值 软腭后区咽侧壁总厚度/mm 28.52±2.33 23.38±1.952 -13.450 < 0.01 舌后区咽侧壁总厚度/mm 28.56±4.175 19.73±2.613 -11.010 < 0.01 会厌后区咽侧壁总厚度/mm 14.31±2.540 15.67±2.332 2.754 0.08 表 3 OSA组平静呼吸时与正常组气道各区体积、长度比较
x±s 测量指标 OSA组 正常组 t值 P值 鼻咽区体积/cm3 4.22±0.393 3.92±0.315 3.081 < 0.01 软腭后区体积/cm3 3.54±0.362 3.79±0.312 -2.081 0.06 舌后区体积/cm3 3.62±0.369 3.89±0.39 -2.668 0.09 会厌后区体积/cm3 7.32±0.831 4.20±1.187 12.584 < 0.01 气道总体积/cm3 18.69±1.422 15.80±1.567 7.529 < 0.01 气道总长度/cm 8.89±0.516 7.03±0.499 13.728 < 0.01 表 4 OSA组Müller动作与平静呼吸状态气道体积、气道长度比较
x±s 测量指标 Müller动作 平静呼吸状态 t值 P值 鼻咽区体积/cm3 4.14±0.445 4.18±0.448 5.560 0.56 软腭后区体积/cm3 1.24±0.494 3.61±0.349 19.607 < 0.01 舌后区体积/cm3 2.25±1.012 3.63±0.432 6.305 < 0.01 会厌后区体积/cm3 7.30±1.058 6.97±0.514 1.531 0.28 气道总体积/cm3 11.24±1.078 18.74±1.791 18.335 < 0.01 气道总长度/cm 8.61±0.449 8.76±0.516 0.994 0.33 表 5 OSA组Müller动作与平静呼吸状态上气道各区最小平面的径线长度和截面积比较
x±s 测量指标 Müller动作 平静呼吸状态 t值 P值 鼻咽区截面积/cm2 2.14±0.359 2.46±0.412 4.690 < 0.01 软腭后区截面积/cm2 0.02±0.030 10.08±0.327 22.891 < 0.01 舌后区截面积/cm2 0.22±0.069 1.07±0.227 25.414 < 0.01 会厌后区截面积/cm2 2.28±0.372 2.33±0.426 0.556 0.58 鼻咽区前后径/cm 1.48±0.179 1.59±0.169 3.060 < 0.01 鼻咽区左右径/cm 1.44±0.193 1.54±0.181 3.904 < 0.01 软腭后区前后径/cm 0.18±0.067 1.03±0.225 22.908 < 0.01 软腭后区左右径/cm 0.15±0.059 1.04±0.166 35.131 < 0.01 舌后区前后径/cm 0.44±0.103 1.11±0.100 44.099 < 0.01 舌后区左右径/cm 0.52±0.113 0.96±0.160 16.143 < 0.01 会厌后区前后径/cm 1.50±0.169 1.51±0.163 0.524 0.60 会厌后区左右径/cm 1.52±0.162 1.53±0.168 0.209 0.84 表 6 OSA组与正常组咽腔顺应性比较
x±s 测量指标 OSA组 正常组 t值 P值 软腭后区 咽侧壁顺应性 0.84±0.077 0.27±0.124 28.851 < 0.01 咽前后壁顺应性 0.81±0.107 0.27±0.093 28.865 < 0.01 总咽壁顺应性 0.96±0.033 0.45±0.121 29.637 < 0.01 舌后区 咽侧壁顺应性 0.44±0.147 0.13±0.879 12.703 < 0.01 咽前后壁顺应性 0.61±0.819 0.21±0.061 24.905 < 0.01 总咽壁顺应性 0.77±0.468 0.32±0.851 23.207 < 0.01 会厌后区 咽侧壁顺应性 0.18±0.081 0.09±0.038 7.382 < 0.01 咽前后壁顺应性 0.12±0.057 0.09±0.026 3.150 < 0.01 总咽壁顺应性 0.22±0.778 0.18±0.548 4.110 < 0.01 表 7 OSA组软腭后区和舌后区的咽侧壁顺应性与咽前后壁顺应性比较
x±s 测量指标 咽侧壁顺应性 咽前后壁顺应性 t值 P值 软腭后区 0.84±0.776 0.807±0.108 2.243 0.02 舌后区 0.45±0.147 0.60±0.082 -7.384 < 0.01 表 8 OSA组气道各区咽侧壁总厚度与BMI的相关性分析
测量指标 平静呼吸状态r值 平静呼吸状态P值 Müller动作r值 Müller动作P值 软腭后区咽侧壁总厚度/mm 0.275 0.049 0.037 0.79 舌后区咽侧壁总厚度/mm 0.307 0.027 0.329 0.02 会厌后区咽侧壁总厚度/mm 0.029 0.836 -0.263 0.06 -
[1] 陈桂, 廖雯静, 张孝文. 会厌塌陷引起阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征的研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(2): 186-189. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201902024.htm
[2] Laratta CR, Ayas NT, Povitz M, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in adults[J]. CMAJ, 2017, 189(48): E1481-E1488. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.170296
[3] Jung AR, Koh TK, Kim SJ, et al. Comparison of level and degree of upper airway obstruction by Müller's maneuver and drug-induced sleep endoscopy in obstructive sleep apnea patients[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2017, 44(5): 571-575. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2016.10.012
[4] 杨阳, 刁楠, 史河水, 等. OSAHS患者上气道形态与顺应性改变的MSCT研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(3): 246-250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201903016.htm
[5] Askar SM, Quriba AS, Hassan EM, et al. Positional Awake Endoscopy Versus DISE in Assessment of OSA: A Comparative Study[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019. [online ahead of print]
[6] Ravesloot MJ, de Vries N. One hundred consecutive patients undergoing drug-induced sleep endoscopy: results and evaluation[J]. Laryngoscope, 2011, 121(12): 2710-2716. doi: 10.1002/lary.22369
[7] 詹善强, 倪宝良, 胡伟, 等. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征患者上气道CT测量研究[J]. 中国医学创新, 2015, 12(29): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2015.29.001
[8] Paje DT, Kremer MJ. The perioperative implications of obstructive sleep apnea[J]. Orthop Nurs, 2006, 25(5): 291-7;quiz 298-299.
[9] 吕丹, 孙铭宏, 于雪莹, 等. 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征患者CPAP治疗前后上气道顺应性的CT改变[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报, 2020, 34(1): 46-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYU202001011.htm
[10] 郑哲, 刘洪, 刘东旭. OSAHS患者上气道流固耦合模型中软组织生物力学参数的研究进展[J]. 中华口腔正畸学杂志, 2017, 24(1): 42-46. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-5760.2017.01.009
[11] 陆立彦, 张宇宁, 郭宇峰, 等. OSAHS患者上气道流体动力学模型的建立与应用[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2012, 10(5): 397-402. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKQ201205018.htm
[12] 白春杰, 李淑芝, 刘子晔, 等. 体质量指数和阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征的相关性研究[J]. 重庆医学, 2019, 48(22): 3811-3814. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2019.22.008
[13] 吴绯红, 彭德昌, 苏筱芮, 等. 128层螺旋CT对阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征咽旁间隙脂肪及颌下脂肪的研究[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2016, 24(4): 253-255, 260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5185.2016.04.004
-




 下载:
下载: