-
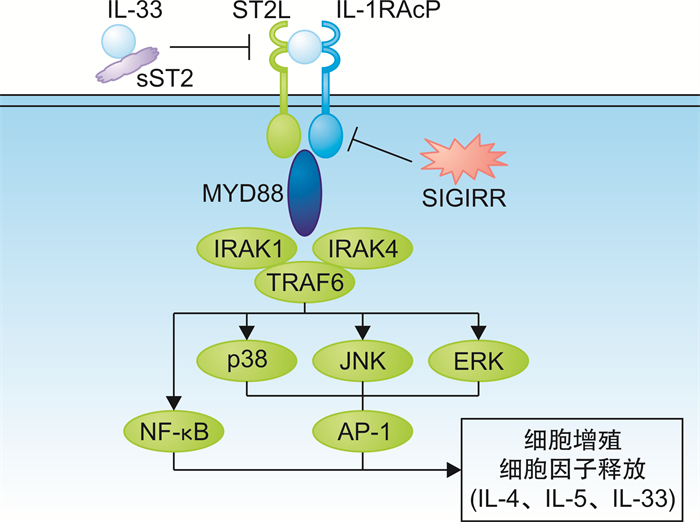
Abstract: Interleukin-33 that binds to the membrane receptor ST2L, can not only regulate mast cells, eosinophils, and group 2 innate lymphoid cells(ILC2s), but also affect the function of regulatory T cells(Treg) and Follicular helper T cells(Tfh). Interleukin-33 can activate the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways of the above cells, then participates in allergic immunity reaction. IL-33/ST2 signaling pathway is closely related to the allergic rhinitis(AR). IL-33 has been used as a new biomarker to evaluate the effect of AR treatment. At the same time, antagonizing IL-33 is also expected to become a new treatment. This article reviewed the latest research of IL-33/ST2 signaling pathway in the field of AR.
-
Key words:
- rhinitis, allergic /
- Interleukin-33 /
- ST2 /
- signaling pathway
-

-
[1] Drake LY, Kita H. IL-33: biological properties, functions, and roles in airway disease[J]. Immunol Rev, 2017, 278(1): 173-184. doi: 10.1111/imr.12552
[2] 杜云艳, 罗英, 杨春平, 等. IL-33及其受体ST2与变应性鼻炎发病机制的相关性探讨[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 29(9): 811-814. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201509010.htm
[3] Liew FY, Girard JP, Turnquist HR. Interleukin-33 in health and disease[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2016, 16(11): 676-689. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.95
[4] Vasanthakumar A, Moro K, Xin A, et al. The transcriptional regulators IRF4, BATF and IL-33 orchestrate development and maintenance of adipose tissue-resident regulatory T cells[J]. Nat Immunol, 2015, 16(3): 276-285. doi: 10.1038/ni.3085
[5] Bonilla WV, Frohlich A, SENN K, et al. The alarmin interleukin-33 drives protective antiviral CD8(+)T cell responses[J]. Science, 2012, 335(6071): 984-989. doi: 10.1126/science.1215418
[6] Baumann C, Bonilla WV, Frohlich A, et al. T-bet-and STAT4-dependent IL-33 receptor expression directly promotes antiviral Th1 cell responses[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2015, 112(13): 4056-4061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1418549112
[7] Gautier V, Cayrol C, Farache D, et al. Extracellular IL-33 cytokine, but not endogenous nuclear IL-33, regulates protein expression in endothelial cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 34255. doi: 10.1038/srep34255
[8] Bulek K, Swaidani S, Qin J, et al. The essential role of single Ig IL-1 receptor-related molecule/Toll IL-1R8 in regulation of Th2 immune response[J]. J Immunol, 2009, 182(5): 2601-2609. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802729
[9] Zhao J, Wei J, Mialki RK, et al. F-box protein FBXL19-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of the receptor for IL-33 limits pulmonary inflammation[J]. Nat Immunol, 2012, 13(7): 651-658. doi: 10.1038/ni.2341
[10] Cavagnero K, Doherty TA. Cytokine and Lipid Mediator Regulation of Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells(ILC2s)in Human Allergic Airway Disease[J]. J Cytokine Biol, 2017, 2(2): 116-116.
[11] Kabata H, Moro K, Koyasu S. The group 2 innate lymphoid cell(ILC2) regulatory network and its underlying mechanisms[J]. Immunol Rev, 2018, 286(1): 37-52. doi: 10.1111/imr.12706
[12] Nagashima H, Okuyama Y, Fujita T, et al. GITR cosignal in ILC2s controls allergic lung inflammation[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2018, 141(5): 1939-1943. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.01.028
[13] Stier MT, Zhang J, Goleniewska K, et al. IL-33 promotes the egress of group 2 innate lymphoid cells from the bone marrow[J]. J Exp Med, 2018, 215(1): 263-281. doi: 10.1084/jem.20170449
[14] Johansson K, Malmhall C, Ramos-ramirez P, et al. Bone marrow type 2 innate lymphoid cells: a local source of interleukin-5 in interleukin-33-driven eosinophilia[J]. Immunology, 2018, 153(2): 268-278. doi: 10.1111/imm.12842
[15] Schroder PC, Casaca VI, Illi S, et al. IL-33 polymorphisms are associated with increased risk of hay fever and reduced regulatory T cells in a birth cohort[J]. Pediatr Allergy Immunol, 2016, 27(7): 687-695. doi: 10.1111/pai.12597
[16] Chen CC, Kobayashi T, Iijima K, et al. IL-33 dysregulates regulatory T cells and impairs established immunologic tolerance in the lungs[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2017, 140(5): 1351-1363. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.01.015
[17] Arpaia N, Green JA, Moltedo B, et al. A Distinct Function of Regulatory T Cells in Tissue Protection[J]. Cell, 2015, 162(5): 1078-1089. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.021
[18] Bird L. Regulatory T cells: Ageing muscles lose T Reg-eneration[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2016, 16(4): 204-204. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.30
[19] Kubo M. T follicular helper and TH2 cells in allergic responses[J]. Allergol Int, 2017, 66(3): 377-381. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2017.04.006
[20] Kobayashi T, Iijima K, Dent AL, et al. Follicular helper T cells mediate IgE antibody response to airborne allergens[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2017, 139(1): 300-313. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.04.021
[21] Zhao PW, Shi X, Li C, et al. IL-33 Enhances Humoral Immunity Against Chronic HBV Infection Through Activating CD4(+)CXCR5(+)TFH Cells[J]. J Interferon Cytokine Res, 2015, 35(6): 454-463. doi: 10.1089/jir.2013.0122
[22] Leaker BR, Malkov VA, Mogg R, et al. The nasal mucosal late allergic reaction to grass pollen involves type 2 inflammation(IL-5 and IL-13), the inflammasome(IL-1beta), and complement[J]. Mucosal Immunol, 2017, 10(2): 408-420. doi: 10.1038/mi.2016.74
[23] Gluck J, Rymarczyk B, Rogala B. Serum IL-33 but not ST2 level is elevated in intermittent allergic rhinitis and is a marker of the disease severity[J]. Inflamm Res, 2012, 61(6): 547-550. doi: 10.1007/s00011-012-0443-9
[24] Kim JH, Yoon MG, Seo DH, et al. Detection of Allergen Specific Antibodies From Nasal Secretion of Allergic Rhinitis Patients[J]. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res, 2016, 8(4): 329-337. doi: 10.4168/aair.2016.8.4.329
[25] 樊华, 覃泰杰, 叶林松, 等. 接受免疫治疗的变应性鼻炎儿童患者外周血中IL-25、IL-33的表达和EOS计数及意义[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(6): 443-446. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201806011.htm
[26] Iinuma T, Okamoto Y, Morimoto Y, et al. Pathogenicity of memory Th2 cells is linked to stage of allergic rhinitis[J]. Allergy, 2018, 73(2): 479-489. doi: 10.1111/all.13295
[27] Fan D, Wang X, Wang M, et al. Allergen-Dependent Differences in ILC2s Frequencies in Patients With Allergic Rhinitis[J]. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res, 2016, 8(3): 216-222. doi: 10.4168/aair.2016.8.3.216
[28] Haenuki Y, Matsushita K, Futatsugi-yumikura S, et al. A critical role of IL-33 in experimental allergic rhinitis[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2012, 130(1): 184-194. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.02.013
[29] Akasaki S, Matsushita K, Kato Y, et al. Murine allergic rhinitis and nasal Th2 activation are mediated via TSLP-and IL-33-signaling pathways[J]. Int Immunol, 2016, 28(2): 65-76.
[30] Nakanishi W, Yamaguchi S, Matsuda A, et al. IL-33, but not IL-25, is crucial for the development of house dust mite antigen-induced allergic rhinitis[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(10): e78099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078099
[31] Wang Y, Li C, Xu Y, et al. Sublingual Immunotherapy Decreases Expression of Interleukin-33 in Children with Allergic Rhinitis[J]. Indian J Pediatr, 2018, 85(10): 872-876. doi: 10.1007/s12098-018-2703-3
[32] Nasr WF, Sorour SS, El BA, et al. The Role of the Level of Interleukin-33 in the Therapeutic Outcomes of Immunotherapy in Patients with Allergic Rhinitis[J]. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 22(2): 152-156. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1605596
[33] Park CS, Jang TY, Heo MJ, et al. Antiallergic effects of anti-interleukin-33 are associated with suppression of immunoglobulin light chain and inducible nitric oxide synthase[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2016, 30(1): 17-22. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2015.29.4251
[34] Kim YH, Yang TY, Park CS, et al. Anti-IL-33 antibody has a therapeutic effect in a murine model of allergic rhinitis[J]. Allergy, 2012, 67(2): 183-190. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02735.x
-

| 引用本文: | 刘果, 刘锋. IL-33/ST2信号通路在变应性鼻炎中的研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(6): 565-568. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.06.020 |
| Citation: | LIU Guo, LIU Feng. Advances of IL-33/ST2 signaling pathway in allergic rhinitis[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2020, 34(6): 565-568. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.06.020 |
- Figure 1.



 下载:
下载: