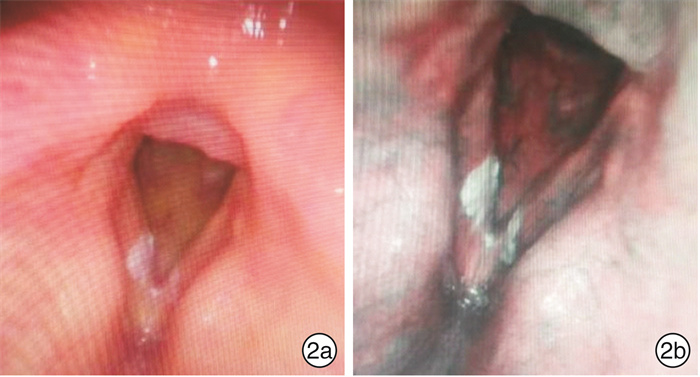
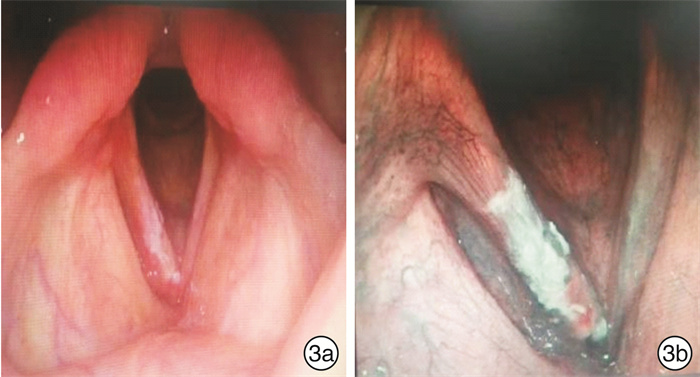
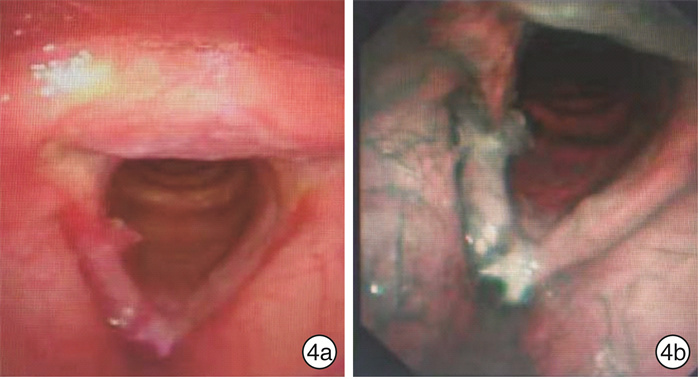
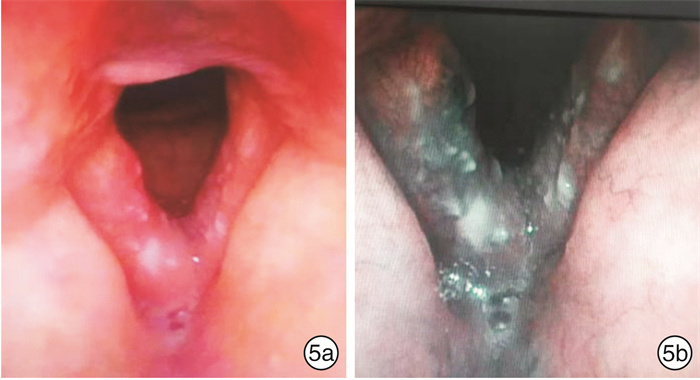
-
摘要: 目的 分析声带白斑的临床特征及常见病因,探讨其治疗原则。方法 选取157例声带白斑患者,常规行白光喉镜、窄带成像内镜(NBI)、频闪喉镜以及咽喉反流体征评分量表(RFS)、反流症状指数量表(RSI)评估,予以戒烟酒、抑酸、休声等保守治疗和(或)手术治疗。结果 157例声带白斑患者中109例(69.4%)经保守治疗后白斑基本减退或消失,48例行手术治疗,术后病理诊断分别为轻度不典型增生2例(1.3%)、中度不典型增生15例(9.6%)、重度不典型增生或原位癌19例(12.1%)、浸润癌12例(7.6%)。结论 声带白斑经NBI、频闪喉镜检查大多数未见有恶性体征不符合手术适应证,经保守治疗后有效,仅少部分患者有病理组织活检或手术治疗指征,而且大部分患者伴有咽喉反流,抑酸治疗有效,也是治疗的重要环节。Abstract: Objective To study the clinical characteristics and common etiology of vocal cord leukoplakia, and explore the treatment principle.Method One hundred and fifty-seven patients with vocal cord leukoplakia were recruited in this study. They were assessed by routine laryngoscope, narrow band imaging (NBI), stroboscope, reflux finding score (RFs) and reflux symptom index (RSI), and given conservative treatment (smoking cessation, alcohol, acid suppression, sound cessation, etc.) and/or surgical treatment.Result Among 157 patients with leukoplakia of vocal cord, 109 (69.4%) had basically improved or cured after conservative treatment. Forty-eight cases underwent operation. The postoperative pathological diagnosis was mild dysplasia in 2 cases (1.3%), moderate dysplasia in 15 cases (9.6%), severe dysplasia or carcinoma in situ in 19 cases (12.1%), and invasive carcinoma in 12 cases (7.6%).Conclusion NBI and stroboscopic laryngoscopy showed that most of the leukoplakia of vocal cord was non-malignant in nature, which was not in accordance with the indication of operation. Conservative treatment is effective. Biopsy or operation was indicated in only a few patients. Moreover, most of the patients are accompanied by laryngopharyngeal reflux, and the treatment of acid suppression is effective.
-

-
[1] 崔卫新, 徐文, 杨庆文, 等. 声带白斑临床病理特征及复发癌变的影响因素[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 30(24): 1926-1931. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201624007.htm
[2] Rzepakowska A, Sobol M, Sielska-Badurek E, et al. Morphology, Vibratory Function, and Vascular Pattern for Predicting Malignancy in Vocal Fold Leukoplakia[J]. J Voice, 2019, S0892-1997(19)30001-3.
[3] Ni XG, He S, Xu ZG, et al. Endoscopic diagnosis of laryngeal cancer and precancerous lesions by narrow band imaging[J]. Laryngol Otol, 2011, 125(3): 288-296. doi: 10.1017/S0022215110002033
[4] Chen M, Cheng L, Li CJ, et al. Nonsurgical Treatment for Vocal Fold Leukoplakia: An Analysis of 178 Cases[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2017, 2017: 6958250.
[5] 徐文. 声带白斑的诊断与治疗[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 50(12): 1049-1052. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2015.12.021
[6] Koufman JA, Amin MR, Panetti M. Prevalence of reflux in 113 consecutive patients with laryngeal and voice disorders[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2000, 123(4): 0-388.
[7] Lechien JR, Huet K, Finck C, et al. Clinical and Acoustical Voice Quality Evolutions Throughout Empirical Treatment for Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease According to Gender: A Preliminary Study[J]. Folia Phoniatr Logop, 2019, 27: 1-10.
[8] Zhukhovitskaya A, Battaglia D, Khosla SM, et al. Gender and age in benign vocal fold lesions[J]. Laryngoscope, 2015, 125(1): 191-196. doi: 10.1002/lary.24911
[9] Van Houtte E, Van Lierde K, Claeys S. Pathophysiology and treatment of muscle tension dysphonia: a review of the current knowledge[J]. J Voice, 2011, 25(2): 202-207. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2009.10.009
[10] Lechien JR, Saussez S, Harmegnies B, et al. Laryngopharyngeal Reflux and Voice Disorders: A Multifactorial Model of Etiology and Pathophysiology[J]. J Voice, 2017, 31(6): 733-752. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2017.03.015
[11] Yamauchi A, Yokonishi H, Imagawa H, et al. Age-and gender-related difference of vocal fold vibration and glottal configuration in normalspeakers: analysis with glottal area waveform[J]. J Voice, 2014, 28(5): 525-531. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2014.01.016
[12] Yoon YH, Park KW, Lee SH, et al. Efficacy of three proton-pump inhibitor therapeutic strategies on laryngopharyngeal reflux disease; a prospective randomized double-blind study[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2019, 44(4): 612-618. doi: 10.1111/coa.13345
[13] Karkos PD, Wilson JA. Empiric treatment of laryngopharyngeal reflux with proton pump inhibitors: a systematic review[J]. Laryngoscope, 2006, 116(1): 144-148. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000191463.67692.36
[14] 齐智伟, 陆鸿略, 张洁, 等. 奥美拉唑治疗反流性咽喉炎不同疗程的疗效评价[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(9): 693-697. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201809013.htm
[15] 李进让, 肖水芳, 李湘平, 等. 咽喉反流性疾病诊断与治疗专家共识(2015年)解读[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 51(5): 327-332. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2016.05.003
[16] He C, Yu J, Huang F, et al. The utility of narrow band imaging in endoscopic diagnosis of laryngopharyngeal reflux[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2019, 40(5): 715-719. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2019.06.009
[17] Luers JC, Sircar K, Drebber U, et al. The impact of laryngeal dysplasia on the development of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2014, 271(3): 539-545. doi: 10.1007/s00405-013-2670-2
-

| 引用本文: | 宋晓霞, 张森, 皇甫辉, 等. 157例声带白斑的临床诊治研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(6): 528-531. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.06.012 |
| Citation: | SONG Xiaoxia, ZHANG Sen, HUANG FU Hui, et al. Clinical diagnosis and treatment of 157 cases of vocal leukoplakia[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2020, 34(6): 528-531. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.06.012 |
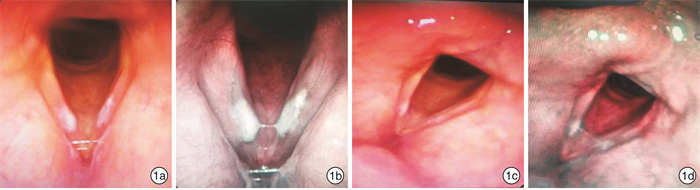
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.
- Figure 5.
- Figure 6.
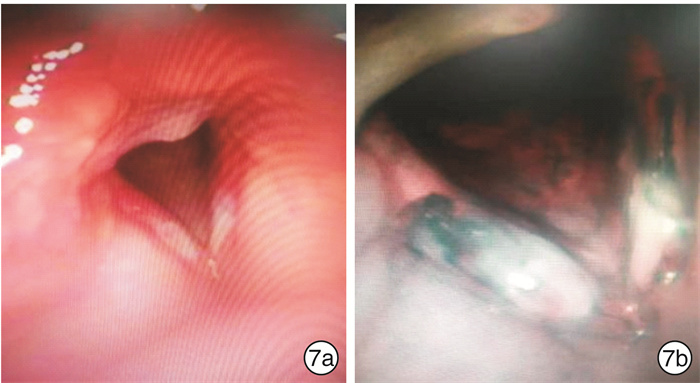
- Figure 7.



 下载:
下载: