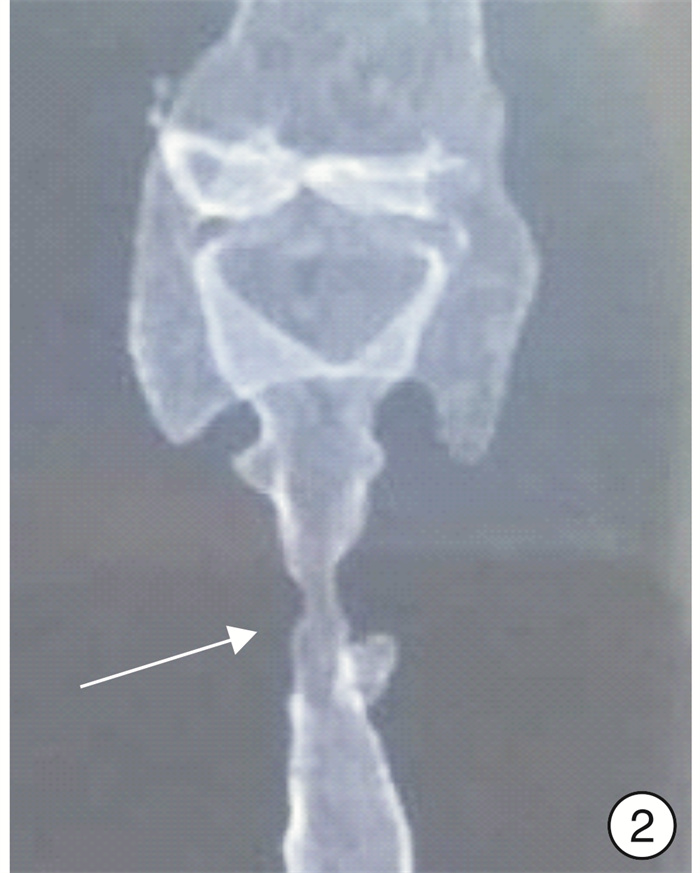
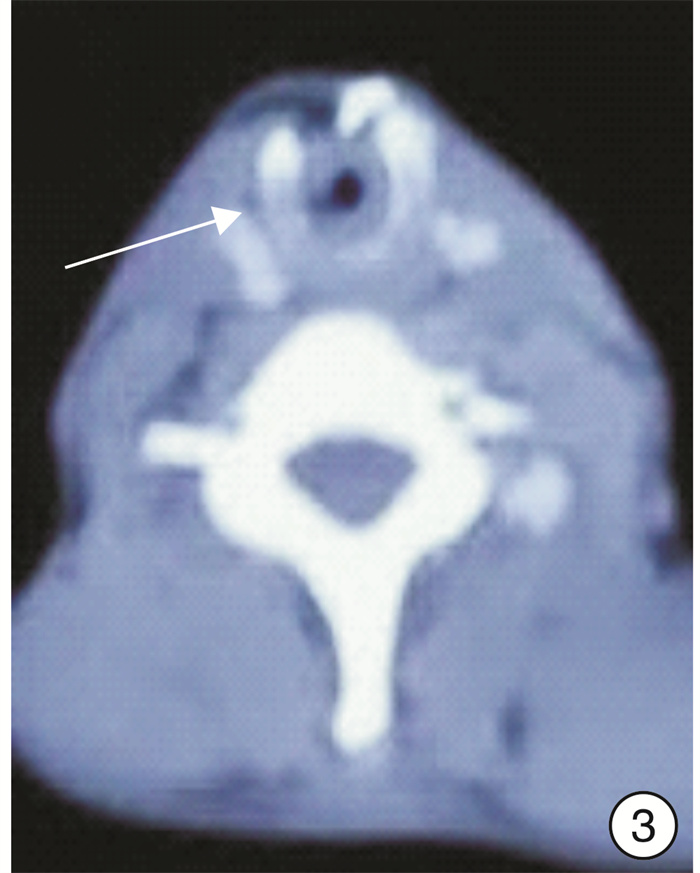
Diagnosis and treatment of laryngotracheal stenosis induced by relapsing polychondritis
-
摘要: 目的 探讨复发性多软骨炎(RP)导致的喉气管狭窄的诊断、治疗特点及预后。方法 回顾性分析11例RP并发喉气管狭窄患者的临床资料。狭窄程度按照Myer-Cotton法分类:Ⅱ度4例,Ⅲ度3例,Ⅳ度4例。结果 1例胸段气管狭窄T型管长期置入,1例经2次球囊扩张后成功拔管,9例应用胸骨舌骨肌皮瓣或肋软骨加宽行喉气管重建术,手术成功,效果巩固。结论 由RP导致的喉气管狭窄治疗棘手。选择恰当的手术时机及适当的手术方法,效果满意。Abstract: Objective To investigate the clinical characteristics, management and prognosis of laryngotracheal stenosis induced by relapsing polychondritis.Method A retrospective analysis was performed of 11 patients with laryngotracheal stenosis induced by relapsing polychondritis. Stenosis was classified as Myer and Cotton grade Ⅱ in 4 patients, grade Ⅲ in 3 and grade Ⅳin 4.Result Long-term T-tube implantation of thoracic tracheal stenosis was performed in 1 patient, and one patient who had underwent 2 dilations was decannulated, and the tube was successfully extubated in 9 cases who had underwent laryngotracheal reconstruction with sternohyoid myocutaneous flap or costal cartilage.Conclusion Treatment of laryngotracheal stenosis induced by relapsing polychondritis is challenging. If the surgical intervention was selected properly on an individual basis, favorable clinical outcome can be obtained.
-
Key words:
- laryngotracheal stenosis /
- polychondritis, relapsing /
- surgery
-

-
表 1 患者的临床资料
例序 性别 年龄/岁 Myer-Cotton分级 并发症 来院是否行气管切开 结果 随访时间 1 女 45 Ⅱ 无 否 拔管 2年 2 女 41 Ⅱ 胸段气管狭窄 是 拔管 3年 3 女 48 Ⅲ 耳廓畸形 是 拔管 7年 4 女 47 Ⅳ 耳廓畸形 否 拔管 4年 5 男 25 Ⅱ 鼻梁塌陷 是 拔管 5年 6 男 40 Ⅳ 胸段气管狭窄 是 长期佩戴T型管 3年 7 女 35 Ⅱ 鼻梁塌陷 是 拔管 4年 8 男 21 Ⅳ 同时伴随鼻梁塌陷及耳廓畸形 是 拔管 5年 9 女 51 Ⅲ 无 是 拔管 3.5年 10 男 19 Ⅲ 鼻梁塌陷 是 拔管 4年 11 男 24 Ⅳ 同时伴随鼻梁塌陷及耳廓畸形 是 拔管 1年 -
[1] 中华医学会风湿病学分会. 复发性多软骨炎诊治指南(草案)[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2004, 8(4): 251-253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSBZ200404023.htm
[2] 孟莉. 复发性多软骨炎的诊断和治疗[J]. 医学综述, 2009, 15(3): 415-417. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXZS200903033.htm
[3] Lin DF, Yang WQ, Zhang PP, et al. Clinical and prognostic characteristics of 158 cases of relapsing polychondritis in China and review of the literature[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2016, 36(7): 1003-1009. doi: 10.1007/s00296-016-3449-8
[4] Vitale A, Sota J, Rigante D, et al. Relapsing Polychondritis: an Update on Pathogenesis, Clinical Features, Diagnostic Tools, and Therapeutic Perspectives[J]. Curr Rheumatol Rep, 2016, 18(1): 3-3. doi: 10.1007/s11926-015-0549-5
[5] Lei W, Zeng DX, Chen T, et al. FDG PET-CT combined with TBNA for the diagnosis of atypical relapsing polychondritis: report of 2 cases and a literature review[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2014, 6(9): 1285-1292.
[6] Yamashita H, Takahashi H, Kubota K, et al. Utility of fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography for earlydiagnosis and evaluation of disease activity of relapsing polychondritis: a case series and literature review[J]. Rheumatology(Oxford), 2014, 53(8): 1482-1490. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu147
[7] Bayer G, Diot E, Erra B. Utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT in relapsing polychondritis[J]. QJM, 2015, 108(4): 339-340. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcu187
[8] Lei W, Zeng H, Zeng DX, et al. (18) F-FDG PET-CT: a powerful tool for the diagnosis and treatment of relapsing polychondritis[J]. Br J Radiol, 2016, 89(1057): 20150695. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20150695
[9] 沈慧, 沈策. 复发性多软骨炎的诊治进展[J]. 国外医学呼吸系统分册, 2005, 25(5): 384-385. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWHX20050500O.htm
[10] Woodbury K, Smith LJ. Relapsing polychondritis: a rare etiology of dysphonia and novel approach to treatment[J]. Laryngoscope, 2011, 121(5): 1006-1008. doi: 10.1002/lary.21452
[11] Hazra N, Dregan A, Charlton J, et al. Incidence and mortality of relapsing polychondritis in the UK: a population-based cohort study[J]. Rheumatology(Oxford), 2015, 54(12): 2181-2187.
[12] Ernst A, Rafeq S, Boiselle P, et al. Relapsing polychondritis and airway involvement[J]. Chest, 2009, 135(4): 1024-1030. doi: 10.1378/chest.08-1180
[13] Vitale A, Sota J, Rigante D, et al. Relapsing Polychondritis: an Update on Pathogenesis, Clinical Features, Diagnostic Tools, and Therapeutic Perspectives[J]. Curr Rheumatol Rep, 2016, 18(1): 3-3. doi: 10.1007/s11926-015-0549-5
[14] Xie C, Shah N, Shah PL, et al. Laryngotracheal reconstruction for relapsing polychondritis: case report and review of the literature[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2013, 127(9): 932-935. doi: 10.1017/S0022215113001746
[15] Lekpa FK, Chevalier X. Refractory relapsing polychondritis: challenges and solutions[J]. Open Access Rheumatol, 2018, 10: 1-11. doi: 10.2147/OARRR.S142892
[16] Jeong N, Jang HJ, Lee JH, et al. A case of tracheobronchomalacia due to relapsing polychondritis treated with Montgomery T-tube[J]. SAGE Open Med Case Rep, 2019, 7: 1-4.
[17] 张志丽, 王洪武, 张楠, 等. 气道内支架在复发性多软骨炎中的应用[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2013, 18(3): 566-567. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFK201303098.htm
-





 下载:
下载: