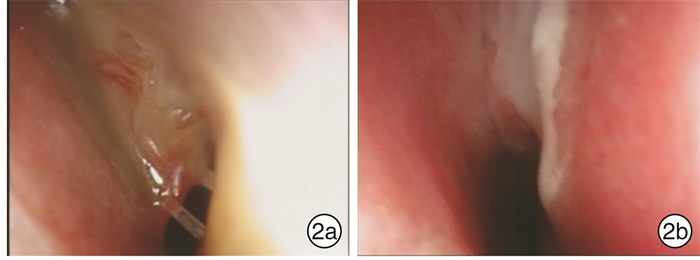
Use of balloon catheter dilation and bioabsorbable steroid-releasing sinus implants in pediatric chronic rhinosinusitis
-
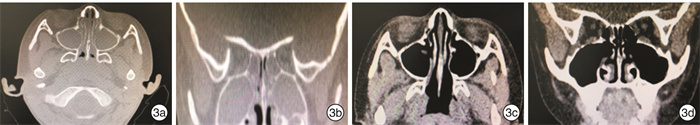
摘要: 目的 探讨鼻窦球囊扩张结合全降解药物支架治疗儿童慢性鼻窦炎(CRS)的疗效。方法 49例因CRS接受手术的患儿,均行腺样体切除术,77侧鼻窦行上颌窦口球囊扩张,依据是否留置鼻窦支架将患儿分为2组:①球囊组26例,其中16例行双侧上颌窦窦口球囊扩张,10例行单侧上颌窦窦口球囊扩张;②球囊支架组23例,其中12例行双侧上颌窦窦口球囊扩张及支架置入,11例行单侧上颌窦窦口扩张及支架置入。对于患儿的主观症状采用视觉模拟量表(VAS)以及SN-5量表进行评估,由监护人和患儿共同完成。同时行鼻窦CT检查,并进行CT评分(Lund-Mackey评分)。结果 球囊支架组患儿手术均成功,术中、术后未发生严重并发症(眶内、颅内并发症),无鼻腔粘连,无眼部不适;鼻窦支架未发生脱落和移位。球囊支架组VAS评分术前1 d为6.9,术后6个月为2.0;SN-5评分术前1 d为2.397,术后6个月为1.376;术侧CT评分术前为9.628,术后6个月为1.314。术后6个月,球囊支架组患儿的VAS评分、SN-5评分、CT评分均较术前显著下降,VAS评分和SN-5评分的术后缓解率分别为100%和95%;2组术前SN-5评分比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.647),2组SN-5评分下降幅度比较差异有统计学意义(F=6.801,P=0.012);2组术前SN-5评分 < 2.5的患儿SN-5评分比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.199),2组评分下降幅度比较差异无统计学意义(F=2.336,P=0.14);2组术前SN-5评分≥2.5的患者SN-5评分比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.628),2组评分下降幅度比较差异有统计学意义(F=13.861,P=0.001)。2组术前CT 3~8分者,术前CT评分比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.411),CT评分下降幅度差异无统计学意义(F=1.108,P=0.300);2组术前CT 9~12分者,术前CT评分比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.792),CT评分下降幅度差异有统计学意义(F=13.059,P=0.001)。结论 采用鼻窦球囊窦口扩张术结合全降解药物支架置入治疗药物治疗不佳的CRS患儿疗效确切,对于较为严重的CRS患儿,该术式明显优于单纯行鼻窦球囊扩张术。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the effect of use of balloon catheter dilation (BCD) with bioabsorbable steroid-releasing sinus implants in pediatric chronic rhinosinusitis(PCRS).Method A retrospective study was performed of 49 children with failed medical therapy, who underwent surgery, and children all accepted adenoidectomy.77 sides of sinus were performed with balloon catheter dilation sinuplasty. They were divided into two groups: the balloon group and the balloon with implant group. The balloon group included 26 cases, 16 cases of which accepted balloon catheter dilation sinuplasty of both maxillary sinuses, and 10 cases of which accepted one side. The balloon with implant group included 23 cases, 12 cases of which accepted balloon catheter dilation sinuplasty of both maxillary sinuses plus positioning of bioabsorbable steroid-releasing sinus implants, and 11 cases of which accepted one side. VAS and SN-5 scales were completed by children and their parents to evaluate subjective symptoms. Children all accepted CT of sinus and CT score (Lund-Mackey) was completed by a doctor. We use the SPSS 23.0 with the way of Repeated measures ANOVA to analyze the data between two groups, aiming to identify the effect of the operation manners.Result The procedures were successful in all patients in the balloon with implant group. No complications happened. No sinus implants moving and no detachment. In the balloon with implant group, VAS score declined from 6.9 before operation to 2.0 of six months after operation and SN-5 score declined from 2.397 to 1.376 and CT score of one side of operation declined from 9.628 to 1.314. VAS score, SN-5 score and CT score of the balloon with implant group all declined significantly after operation. The remission rate of the VAS and SN-5 score in the balloon with implant group were 100% and 95% respectively. The SN-5 score data of patients in two groups with SN-5 score < 2.5 before operation was analyzed. There was no statistical significance between the data of two groups before operation(P=0.199), and there was no statistical significance between the data decline of SN-5 score of two groups after operation (F=2.336, P=0.14). The data of patients in two groups with SN-5 score ≥2.5 before operation was analyzed. There was no statistical significance between the data of two groups before operation(P=0.628), and, after operation, there was statistical significance between the data decline of SN-5 score of two groups (F=13.861, P=0.001).It meant the balloon with implant group declined more. The CT score data of patients in two groups with CT score (3-8) before operation was analyzed. There was no statistical significance between the data of two groups before operation(P=0.411), and there was no statistical significance between the data decline of CT score of two groups after operation(F=1.108, P=0.300).The data of patients in two groups with CT score (9-12) before operation was analyzed. There was no statistical significance between the data of two groups before operation(P=0.792), and, after operation, there was statistical significance between the data decline of CT score of two groups (F=13.059, P=0.001). It meant the balloon with implant group declined more.Conclusion In our study, the use of balloon catheter dilation (BCD) with bioabsorbable steroid-releasing sinus implants made a clinical curative effect in the treatment of PCRS with failed medical therapy, and it was safety. In severe PCRS patients, balloon catheter dilation (BCD) with bioabsorbable steroid-releasing sinus implants was more effective than the use of balloon catheter sinuplasty (BCS) alone.
-
Key words:
- sinusitis /
- endoscopic surgical procedures /
- balloon dilatation /
- drug stent
-

-
[1] 卢智慧. 儿童慢性鼻窦炎151例临床分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2011, 25(17): 800-801. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201117016.htm
[2] Brietzke SE, Shin JJ, Choi S, et al. Clinical consensus statement: pediatric chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2014, 151(4): 542-553. doi: 10.1177/0194599814549302
[3] 粘家斌, 符徵, 魏欣. 鼻内镜下腺样体切除术治疗儿童慢性鼻窦炎的疗效分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2014, 28(15): 1174-1175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201415026.htm
[4] 王轶, 魏莲枝. 腺样体切除术对儿童慢性鼻窦炎的影响[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2008, (11): 493-494. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH200811009.htm
[5] Brietzke SE, Brigger MT. Adenoidectomy outcomes in pediatric rhinosinusitis: a meta-analysis[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2008, 72(10): 1541-1545. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2008.07.008
[6] Ramadan HH. Safety and feasibility of balloon sinuplasty for treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis in children[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2009, 118(3): 161-165. doi: 10.1177/000348940911800301
[7] Murr AH, Smith TL, Hwang PH, et al. Safety and efficacy of a novel bioabsorbable, steroid-eluting sinus stent[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2011, 1(1): 23-32. doi: 10.1002/alr.20020
[8] Kay DJ, Rosenfeld RM. Quality of life for children with persistent sinonasal symptoms[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2003, 128(1): 17-26. doi: 10.1067/mhn.2003.41
[9] Aitken M, Taylor JA. Prevalence of clinical sinusitis in young children followed up by primary care pediatricians[J]. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med, 1998, 152(3): 244-248.
[10] Ramadan HH, Terrell AM. Balloon catheter sinuplasty and adenoidectomy in children with chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2010, 119(9): 578-582. doi: 10.1177/000348941011900902
[11] Makary CA, Ramadan HH. The role of sinus surgery in children[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123(6): 1348-1352. doi: 10.1002/lary.23961
[12] Liu J, Zhao Z, Chen Y, et al. Clinical curative effect and safety of balloon sinuplasty in children with chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2017, 100: 204-210. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2017.06.026
[13] Forwith KD, Chandra RK, Yun PT, et al. ADVANCE: a multisite trial of bioabsorbable steroid-eluting sinus implants[J]. Laryngoscope, 2011, 121(11): 2473-2480. doi: 10.1002/lary.22228
[14] Marple BF, Smith TL, Han JK, et al. Advance Ⅱ: a prospective, randomized study assessing safety and efficacy of bioabsorbable steroid-releasing sinus implants[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2012, 146(6): 1004-1011. doi: 10.1177/0194599811435968
[15] Levine HL, Sertich AP 2nd, Hoisington DR, et al. Multicenter registry of balloon catheter sinusotomy outcomes for 1, 036 patients[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2008, 117(4): 263-270. doi: 10.1177/000348940811700405
[16] Adriaensen GFJPM, Lim KH, Fokkens WJ. Safety and efficacy of a bioabsorbable fluticasone propionate-eluting sinus dressing in postoperative management of endoscopic sinus surgery: a randomized clinical trial[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2017, 7(8): 813-820. doi: 10.1002/alr.21963
[17] Matheny KE. Bioabsorbable steroid-releasing sinus implants in the frontal and maxillary sinuses: 2-year follow-up[J]. Allergy Rhinol(Providence), 2015, 6(2): 118-121.
[18] Ramadan HH. Revision endoscopic sinus surgery in children: surgical causes of failure[J]. Laryngoscope, 2009, 119(6): 1214-1217. doi: 10.1002/lary.20230
[19] Lee TJ, Liang CW, Chang PH, et al. Risk factors for protracted sinusitis in pediatrics after endoscopic sinus surgery[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2009, 36(6): 655-660. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2009.02.008
[20] Weber R, Keerl R, Radziwill R, et al. Videoendoscopic analysis of nasal steroid distribution[J]. Rhinology, 1999, 37(2): 69-73.
[21] Xu JJ, Busato GM, McKnight C, et al. Absorbable Steroid-Impregnated Spacer After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery to Reduce Synechiae Formation[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2016, 125(3): 195-198. doi: 10.1177/0003489415606446
[22] Li W, Lu H, Wang H, et al. Efficacy and safety of steroid-impregnated implants following sinus surgery: A meta-analysis[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019, 22.
[23] Forwith KD, Han JK, Stolovitzky JP, et al. RESOLVE: bioabsorbable steroid-eluting sinus implants for in-office treatment of recurrent sinonasal polyposis after sinus surgery: 6-month outcomes from a randomized, controlled, blinded study[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2016, 6(6): 573-581. doi: 10.1002/alr.21741
[24] Hwang CS, Al Sharhan SS, Kim BR, et al. Randomized controlled trial of steroid-soaked absorbable calcium alginate nasal packing following endoscopic sinus surgery[J]. Laryngoscope, 2018, 128(2): 311-316. doi: 10.1002/lary.26871
[25] Santarelli GD, Han JK. Evaluation of the PROPEL® mini sinus implant for the treatment of frontal sinus disease[J]. Expert Opin Drug Deliv, 2016, 13(12): 1789-1793. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2016.1250740
[26] Huang Z, Huang Q, Zhou B, et al. Bioabsorbable steroid-eluting sinus stents for patients with refractory frontal diseases undergoing a revision Draf 3 procedure: a case series[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2019, 139(7): 636-642. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2019.1592222
[27] Luong A, Ow RA, Singh A, et al. Safety and Effectiveness of a Bioabsorbable Steroid-Releasing Implant for the Paranasal Sinus Ostia: A Randomized Clinical Trial[J]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2018, 144(1): 28-35.
[28] Minni A, Dragonetti A, Sciuto A, et al. Use of balloon catheter dilation and steroid-eluting stent in light and severe rhinosinusitis of frontal sinus: a multicenter retrospective randomized study[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 22(21): 7482-7491.
-




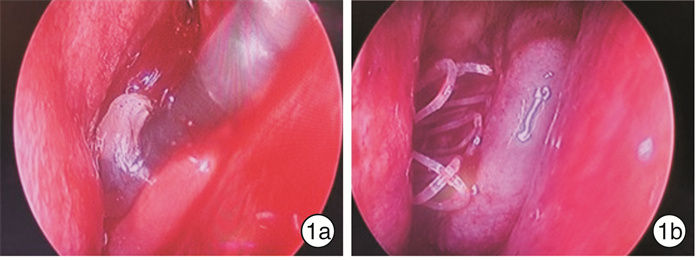
 下载:
下载: