-
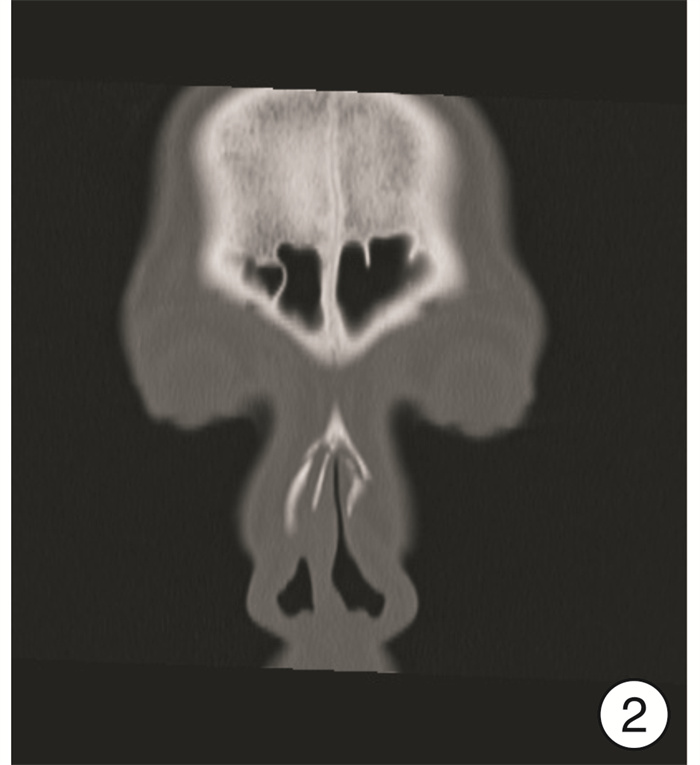
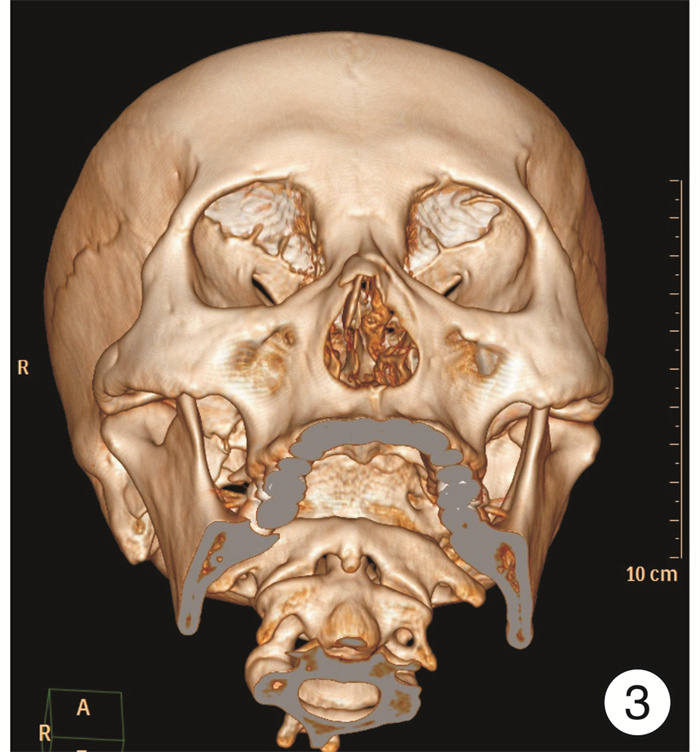
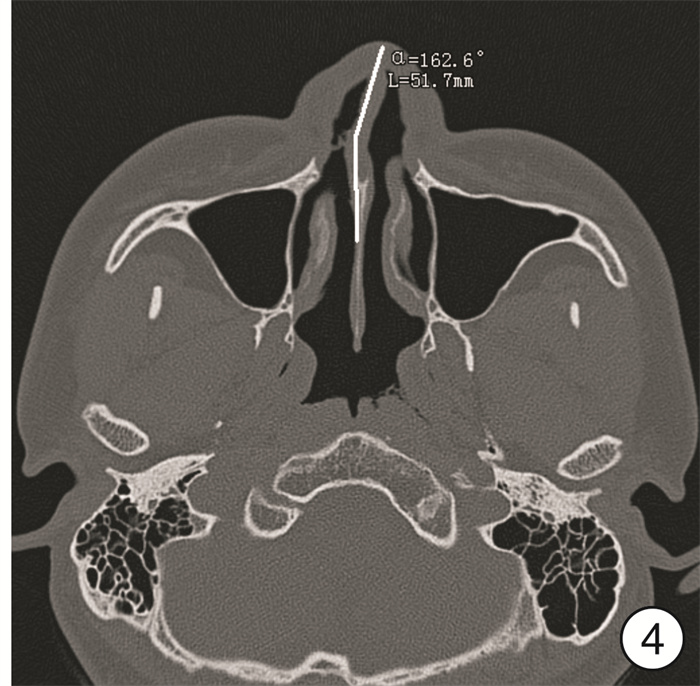
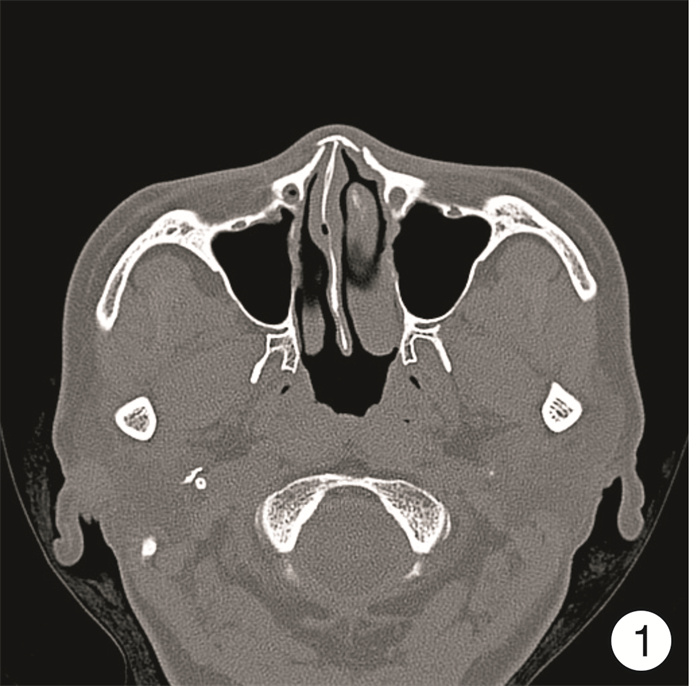
摘要: 探讨鼻外伤后鼻骨骨折的诊断及评估方法,以及三维CT成像技术对治疗的指导意义。方法:鼻骨骨折患者255例,均接受鼻骨CT扫描检查,并在计算机系统上予以三维重建,对重建后的CT图像进行观察、测量及评估,分析鼻骨骨折的形态特点,评估面部其他骨性结构受累情况。结果:255例鼻外伤患者均有外伤性鼻骨骨折,其中单纯鼻骨骨折71例(27.8%),伴外伤性鼻中隔偏曲143例(56.1%),其他部位骨折41例(16.1%)。外鼻骨折分型:Ⅰ型(单侧鼻骨和/或上颌骨额突骨折)91例(35.7%),Ⅱ型(双侧鼻骨和/或上颌骨额突骨折)21例(8.2 %),Ⅲ型(伴外伤性鼻中隔偏曲)143例(56.1%)。选择手术治疗的患者214例(83.9%),采用局部麻醉鼻内镜下鼻骨骨折复位术,同时行鼻中隔手术者77例(30.2%)。结论:CT三维成像技术可以清晰显示鼻骨骨折的部位、骨折线的走形、骨折形成的碎片数量等信息,并对畸形予以定量分析,在鼻骨骨折的诊断及治疗中起着重要作用。Abstract: Objective To investigate the diagnosis and evaluation methods of nasal bone fractures after nasal trauma, and the guiding significance of three-dimensional CT imaging technology for its treatment.Method A total of 255 patients with nasal bone fractures were randomly selected from our hospital. All patients underwent CT scan of the nasal bones and reconstructed on a computer system. The reconstructed CT images were observed, measured and evaluated. Analyze the morphological characteristics of nasal bone fractures and evaluate the involvement of other facial structures.Result Among 255 patients with nasal trauma, there were traumatic nasal bone fractures, including 71 cases(27.8%) with simple nasal bone fractures, 143 cases(56.1%) with traumatic nasal septum deviation, and 41 cases(16.1%) with other fractures. External nasal fracture classification: type Ⅰ(unilateral nasal bone or maxillary frontal fracture) 91 cases(35.7%), type Ⅱ(bilateral nasal bone or fracture) 21 cases(8.2%), type Ⅲ(with trauma Nasal septum deviation) 143 cases(56.1%). A total of 214 patients(83.9%) underwent surgical treatment, and underwent nasal endoscopic reduction of nasal bone fractures under local anesthesia, and 77 patients(30.2%) underwent nasal septum surgery.Conclusion CT three-dimensional imaging technology can clearly display the location of the nasal bone fracture, the shape of the fracture line, the number of fragments formed by the fracture, and quantitative analysis of the deformity caused by it, which plays an important role in its diagnosis and treatment.
-
Key words:
- nasal bone fracture /
- computer tomography /
- three-dimensional imaging
-

-
[1] 赵宇, 朱丽, 马芙蓉, 等. 外鼻骨折分型及骨折部位对鼻中隔影响的CT分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2014, 28(8): 527-530. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201408006.htm
[2] Hwang K, You SH. Analysis of facial bone fractures: An 11-year study of 2094 patients[J]. Indian J Plast Surg, 2010, 43(1): 42-48. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1699402
[3] 苏雪娟, 李运奇, 马文伟, 等. 多层螺旋CT后处理技术及新分型对鼻骨骨折法医鉴定的价值[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2015, 26(6): 443-446. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYYX201506022.htm
[4] 张英. 鼻骨骨折的影像学诊断[J]. 中国中西医结合耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2007, 15(1): 51-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4856.2007.01.017
[5] 吴健, 廖华蓉, 周林, 等. 鼻骨骨折的诊断与整复[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2008, 22(11): 856-857. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNZD200811031.htm
[6] 张艾红. 鼻骨骨折的影像学检查比较[J]. 中国实用医药, 2011, 11(32): 80-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7555.2011.32.050
[7] Hwang K, You SH, Kim SG, et al. Analysis of nasal bone fractures: a six-year study of 503 patients[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2006, 17(2): 261-264. doi: 10.1097/00001665-200603000-00010
[8] Hung T, Chang W, Vlantis AC, et al. Patient satisfaction after closed reduction of nasal fractures[J]. Arch Facial Plast Surg, 2007, 9(1): 40-43 doi: 10.1001/archfaci.9.1.40
-

| 引用本文: | 武勇进, 王鹏, 韩晓东, 等. 鼻骨CT三维成像技术辅助鼻骨骨折的诊断研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(5): 452-454. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.05.016 |
| Citation: | WU Yongjin, WANG Peng, HAN Xiaodong, et al. Three-dimension CT assisted treatment of nasal fracture[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2020, 34(5): 452-454. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.05.016 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.



 下载:
下载: