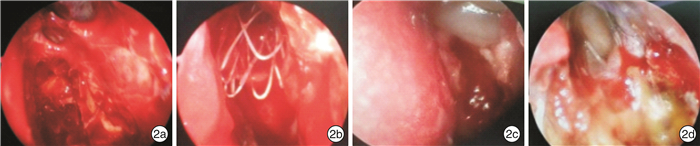
Efficacy analysis of use of absorbable sinus drug stents in functional endoscopic sinus surgery
-
摘要: 目的 探讨功能性内镜鼻窦手术(FESS)术中置入可吸收鼻窦药物支架治疗慢性鼻窦炎的疗效。方法 将107例拟行FESS的慢性鼻窦炎患者分成支架组58例和非支架组49例,支架组术中使用鼻窦药物支架;非支架组术中未使用鼻窦药物支架。2组接受相同的术后治疗。术后随访1个月,术后3个月复查。疗效主要通过内镜检查评估,评估指标包括鼻窦黏膜是否充血水肿、中鼻甲有无黏连、有无囊泡或息肉样变黏膜形成、窦口有无狭窄或再次闭塞、鼻窦黏膜是否上皮化和术后是否干预6项。结果 支架组58例患者成功植入支架。术后1个月上述6项指标在支架组与非支架组之间的差异均有统计学意义,支架组术后并发症发生率及术后干预率均明显低于非支架组(均P < 0.01),支架组鼻窦黏膜上皮化发生率明显高于非支架组(P < 0.01)。术后3个月复查2组均全部完成鼻窦黏膜上皮化,而支架组术后并发症发生率及术后干预率仍均明显低于非支架组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。结论 FESS术中置入可吸收鼻窦药物支架治疗慢性鼻窦炎效果安全理想,在有效缓解鼻窦炎患者临床症状的同时能进一步控制并发症的产生。Abstract: Objective To explore the efficacy of functional endoscopic sinus surgery(FESS) with an absorbable sinus drug stent in the treatment of chronic sinusitis.Method 107 patients with chronic sinusitis who underwent FESS were divided into two groups: 58 patients were set as stent group who were treated with sinus drug elution during surgery; 49 patients who did not receive a sinus drug stent were included in the non-stent group. The same postoperative treatment were used in the two groups. The patients were followed up for 1 month and reviewed 3 months after surgery. Efficacy is mainly evaluated by endoscopy. The evaluation indicators include whether the sinus mucosa is congested and edema, whether there is adhesion in the middle turbinate, whether vesicles or polyp-like mucosa are formed, whether the sinus mouth is stenosed or reoccluded, whether the sinus mucosa is epithelialized, and whether the patient had intervention after surgery.Result Stents were successfully implanted in 58 patients in the stent group. The difference of the above six indexes between the stent group and the non-stent group was statistically significant at 1 month after operation. The postoperative complication rate and postoperative intervention rate were significantly lower in the stent group than in the control group(P < 0.01), the incidence of sinus mucosal epithelialization in the stent group was significantly higher than that in the non-stent group(P < 0.01). The sinus mucosal epithelialization were all completed in both groups after 3 months of surgery. The postoperative complication rate and postoperative intervention rate were significantly lower in the stent group than in the non-stent group(P < 0.05 or P < 0.01).Conclusion FESS combined with the absorption of sinus drug stents for the treatment of chronic sinusitis is safe and effective which can control the complications further after surgery while relieving the clinical symptoms of patients with sinusitis effectively.
-
Key words:
- sinusitis /
- endoscopy /
- absorbable sinus drug stent
-

-
表 1 支架组和非支架组术后并发症的发生情况比较
组别 例数 黏膜充血水肿状态 有无黏连 有无囊泡或息肉样变黏膜 1个月 3个月 1个月 3个月 1个月 3个月 支架组 58 29(50.0) 0 3(5.2) 2(3.4) 14(24.1) 0 非支架组 49 38(77.6) 0 14(28.6) 8(16.3) 33(67.3) 0 χ2 - 8.612 9 - 10.882 1 5.066 8 24.021 4 - P - 0.003 3 - 0.001 0 0.024 4 < 0.000 1 - 组别 例数 窦口有无狭窄或再次闭塞 鼻窦黏膜上皮化程度 术后干预情况 1个月 3个月 1个月 3个月 1个月 3个月 支架组 58 2(3.4) 0 28(48.3) 58(100.0) 14(24.1) 2(3.4) 非支架组 49 13(26.5) 8(16.3) 11(22.4) 49(100.0) 33(67.3) 18(36.7) χ2 - 11.740 5 10.234 6 7.648 5 - 20.132 9 19.363 9 P - 0.000 6 0.001 4 0.005 7 - 0.000 1 < 0.000 1 -
[1] Sedaghat AR. Chronic Rhinosinusitis[J]. Am Fam Physician, 2017, 96(8): 500-506.
[2] Campbell RG, Kennedy DW. What is new and promising with drug-eluting stents in sinus surgery?[J]. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2014, 22(1): 2-7. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0000000000000012
[3] Taulu R, Bizaki AJ, Numminen J, et al. A prospective, randomized clinical study comparing drug eluting stent therapy and intranasal corticoid steroid therapy in the treatment of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Rhinology, 2017, 55(3): 218-226. doi: 10.4193/Rhino16.070
[4] Hauser LJ, Turner JH, Chandra RK. Trends in the Use of Stents and Drug-Eluting Stents in Sinus Surgery[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2017, 50(3): 565-571. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2017.01.007
[5] Yaniv D, Shlossberg L, Yaniv E. A Prospective Study on the Safety and Effectiveness of a Composite Sinus Stent for Use After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2019, 33(1): 17-25. doi: 10.1177/1945892418803101
[6] Jankowski R, Gallet P, Nguyen DT, et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis of adults: new definition, new diagnosis[J]. Rev Prat, 2019, 69(3): 274-278.
[7] Jankowski R, Nguyen DT, Russel A, et al. Chronic nasal dysfunction[J]. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, 2018, 135(1): 41-49. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2017.11.006
[8] Levine CG, Casiano RR. Revision Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2017, 50(1): 143-164. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2016.08.012
[9] Alsharif S, Jonstam K, van Zele T, et al. Endoscopic Sinus Surgery for Type-2 CRS wNP: An Endotype-Based Retrospective Study[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019, 129(6): 1286-1292. doi: 10.1002/lary.27815
[10] Akiyama K, Makihara S, Uraguchi K, et al. Impact of Preoperative Systemic Corticosteroids on the Histology and Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis[J]. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2019, 179(2): 81-88. doi: 10.1159/000496437
[11] Tajudeen BA, Ganti A, Kuhar HN, et al. The presence of eosinophil aggregates correlates with increased postoperative prednisone requirement[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019, 129(4): 794-799. doi: 10.1002/lary.27693
[12] Hopkins C. Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 381(1): 55-63. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1800215
[13] Adriaensen GFJPM, Lim KH, Fokkens WJ. Safety and efficacy of a bioabsorbable fluticasone propionate-eluting sinus dressing in postoperative management of endoscopic sinus surgery: a randomized clinical trial[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2017, 7(8): 813-820. doi: 10.1002/alr.21963
[14] Luk LJ, DelGaudio JM. Topical Drug Therapies for Chronic Rhinosinusitis[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2017, 50(3): 533-543. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2017.01.005
[15] Bassiouni A, Chen PG, Naidoo Y, et al. Clinical significance of middle turbinate lateralization after endoscopic sinus surgery[J]. Laryngoscope, 2015, 125(1): 36-41. doi: 10.1002/lary.24858
[16] Chaaban MR, Baillargeon JG, Baillargeon G, et al. Use of balloon sinuplasty in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis in the United States[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2017, 7(6): 600-608. doi: 10.1002/alr.21939
[17] Chaaban MR, Rana N, Baillargeon J, et al. Outcomes and Complications of Balloon and Conventional Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2018, 32(5): 388-396. doi: 10.1177/1945892418782248
[18] Huang Z, Huang Q, Zhou B, et al. Bioabsorbable steroid-eluting sinus stents for patients with refractory frontal diseases undergoing a revision Draf 3 procedure: a case series[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2019, 139(7): 636-642. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2019.1592222
[19] Han JK, Kern RC. Topical therapies for management of chronic rhinosinusitis: steroid implants[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2019, 9(S1): S22-S26. doi: 10.1002/alr.22344
-





 下载:
下载: