-
摘要: 目的 探讨女性喉接触性肉芽肿的临床特点、诊断及治疗方法。方法 对2011-03-2018-10期间诊治的46例女性喉接触性肉芽肿患者的临床资料进行回顾分析。结果 46例患者,插管后33例,咽喉反流8例,慢性咳嗽2例,咽喉反流合并慢性咳嗽2例,用声过度及过分清理喉咙1例。所有患者至少随访半年以上,全部治愈,6例病变较大行手术治疗的患者3个月内复发3例,复发后质子泵抑制剂治疗2~6个月,随访至今未见再次复发,疗程(1.67±2.34)个月; 11例糖皮质激素注射患者全部痊愈,注射1~7次,疗程(2.64±1.69)个月; 13例口服抑酸药物患者全部治愈,疗程(4.15±2.76)个月; 16例定期观察下保守治疗患者随访至今未见复发,疗程(5.88±3.76)个月。干预组(30例)与观察组(16例)的治愈时间差异有统计学意义,干预组治愈时间短于观察组(H=11.902,P=0.008)。结论 女性喉接触肉芽肿病患者常见于插管后,各种治疗或保守观察均能取得较好效果,治疗干预可能缩短治愈时间。Abstract: Objective To investigate the clinical characteristics, diagnosis and treatment of female laryngeal contact granuloma.Method The clinical data of 46 female patients with laryngeal contact granuloma diagnosed and treated by our clinical team from March 2011 to October 2018 were retrospectively analyzed.Result The age of the 46 patients ranged from 5 to 58 years old, with an average age of 36.76 years old. The causes of the contact granulomas historically may be the result of intubation in 33 cases, laryngopharyngeal reflux in 8 cases, chronic cough in 2 cases, laryngopharyngeal reflux combined with chronic cough in 2 cases, and voice abuse and excessive clearing of the throat in one case. All patients were followed up for at least half a year, and all of them were cured. Among the 6 patients with large lesions who underwent surgical treatment, 3 relapsed within 3 months, PPI treatment was performed for 2 to 6 months after recurrence, and no recurrence was observed during follow-up, with an average course of treatment of (1.67±2.34) months. All the 11 patients who received corticosteroid injections recovered after 1 to 7 injections, with a median of 3 injections, and an average course of treatment of (2.64±1.69) months. All the 13 patients with oral PPI were cured, with an average course of treatment of (4.15±2.76)months; No recurrence was found in the follow-up of 16 patients with conservative treatment under regular observation, with an average course of treatment of (5.88±3.76) months. The difference in cure time between the intervention group (30 cases) and the observation group (16 cases) was statistically significant, and the cure time of the intervention group was shorter than that of the observation group (H=11.902, P=0.008).Conclusion Female patients with laryngeal contact granuloma are common after intubation, and various treatments or conservative observation can achieve good results, and treatment intervention may shorten the cure time.
-
Key words:
- granuloma, laryngeal /
- woman /
- diagnosis /
- treatment
-

-
[1] Wani MK, Woodson GE. Laryngeal contact granuloma[J]. Laryngoscope, 1999, 109(10): 1589-1593. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199910000-00008
[2] 郑美君, 杨慧, 吕丹, 等. 喉接触性肉芽肿18例临床治疗分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 31(3): 230-232. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201703016.htm
[3] Ylitalo R, Lindestad PA. Laryngeal findings in patients with contact granuloma: a long-term follow-up study[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2000, 120(5): 655-659. doi: 10.1080/000164800750000504
[4] Jaroma M, Pakarinen L, Nuutinen J. Treatment of vocal cord granuloma[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 1989, 107(3/4): 296-299.
[5] Ylitalo R, Lindestad PA. A retrospective study of contact granuloma[J]. Laryngoscope, 1999, 109(3): 433-436. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199903000-00017
[6] 柯朝阳, 罗树青, 刘明, 等. 18例喉接触性肉芽肿的临床病理分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2007, 21(12): 545-547. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH200712006.htm
[7] Snow JC, Hirano M, Balogh K. Post-intubation granuloma of the larynx[J]. Anesth Analg, 1966, 45: 425-429.
[8] Pontes P, Kyrillos L, De Biase N, et al. Importance of glottic configuration in the development of posterior laryngeal granuloma[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2001, 110(8): 765-769. doi: 10.1177/000348940111000812
[9] Havas TE, Priestley J, Lowinger DS. A management strategy for vocal process granulomas[J]. Laryngoscope, 1999, 109(2 Pt 1): 301-306.
[10] Hoffman HT, Overholt E, Karnell M, et al. Vocal process granuloma[J]. Head Neck, 2001, 23(12): 1061-1074. doi: 10.1002/hed.10014
[11] Shimazu R, Kuratomi Y, Aoki S, et al. Laryngeal granuloma in experimental rats with gastroesophageal reflux disease and mechanically injured vocal cord mucosa[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2014, 123(4): 247-251. doi: 10.1177/0003489414525018
[12] 中华医学会呼吸病学会哮喘学组. 咳嗽的诊断与治疗指南[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2016, 39(5): 323-340. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-0939.2016.05.003
[13] Koufman JA. The otolaryngologic manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease(GERD): a clinical investigation of 225 patients using ambulatory 24-hour pH monitoring and an experimental investigation of the role of acid and pepsin in the development of laryngeal injury[J]. Laryngoscope, 1991, 101(4 Pt 2 Suppl 53): 1-78.
[14] 刘晖, 王晋平, 杨颖, 等. 喉接触性肉芽肿15例诊治分析[J]. 中国临床医学, 2012, 19(6): 672-673. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6358.2012.06.035
[15] 夏兵华, 蒋明. 治疗喉接触性肉芽肿19例的疗效观察[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2011, 27(22): 3365-3366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYWS201122003.htm
[16] Rimoli CF, Martins RHG, Cataneo DC, et al. Treatment of post-intubation laryngeal granulomas: systematic review and proportional meta-analysis[J]. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 84(6): 781-789. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2018.03.003
[17] 田师宇, 李进让. 喉接触性肉芽肿的治疗现状[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 31(15): 1217-1220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201715022.htm
-

| 引用本文: | 张冉, 李进让, 聂倩, 等. 女性喉接触性肉芽肿46例临床分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(4): 360-363. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.04.018 |
| Citation: | ZHANG Ran, LI Jinrang, NIE Qian, et al. Clinical analysis of 46 cases of female laryngeal contact granuloma[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2020, 34(4): 360-363. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.04.018 |
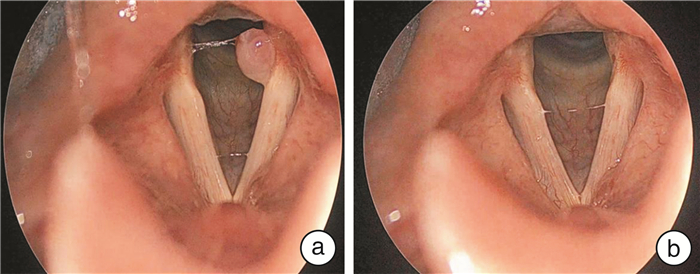
- Figure 1.



 下载:
下载: