The value of turbo spin-echo diffusion weighted imaging in the diagnosis of temporal bone cholesteatoma
-
摘要: 目的 评价快速自旋回波弥散加权成像(TSE-DWI)在诊断颞骨胆脂瘤中的应用价值。方法 对76例初步考虑为颞骨胆脂瘤患者,分别运用Philips Ingenia 3.0T超导型磁共振扫描仪和32通道头线圈进行TSE-DWI序列及常规磁共振平扫,并在其随后2周内进行手术治疗,以病理结果为“金标准”,将影像学诊断、术中所见及病理结果进行对比,计算TSE-DWI序列对颞骨胆脂瘤患者诊断的准确率、灵敏度、特异度、阳性预测值及阴性预测值。结果 76例疑似颞骨胆脂瘤患者中,行TSE-DWI扫描,拟诊断胆脂瘤患者44例,非胆脂瘤32例,最终经手术及病理确诊胆脂瘤患者46例,非胆脂瘤30例。TSE-DWI诊断颞骨胆脂瘤的准确率、灵敏度、特异度、阳性预测值和阴性预测值分别为89.47%、89.13%、90.00%、93.18%、84.38%。其中假阴性3例,假阳性5例。结论 TSE-DWI序列成像图像信噪比高,诊断颞骨胆脂瘤敏感性高、特异性强,对临床诊断及治疗有较高的应用价值。Abstract: Objective The aim of this study is to evaluate the diagnostic value of turbo spin-echo(TSE) diffusion weighted imaging(DWI) in temporal bone cholesteatoma.Method A prospective evaluated of 76 patients with suspected sacral cholesteatoma was performed using a Philips Ingenia 3.0T superconducting magnetic resonance scanner and a 32-channel head coil with turbo spin-echo diffusion weighted imaging(TSE-DWI) sequence and conventional magnetic resonance scan, and underwent surgery within the next two weeks. The pathological result is the gold standard, and the imaging diagnosis and surgery are performed. The intraoperative observation and pathological results were compared. The diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of TSE-DWI sequence in the diagnosis of temporal bone cholesteatoma were calculated.Result Of the 76 patients with suspected temporal bone cholesteatoma, TSE-DWI scan was performed, 44 cases were diagnosed as cholesteatoma and 32 cases were non-cholesteatoma. Based on the pathology results, 46 cases were diagnosed as cholesteatoma, 30 cases were non-cholesteatoma. The accuracy of TSW-DWI sequence in the diagnosis of cholesteatoma was 89.47%, 3 cases were false negative and 5 cases was false positive. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of TSE-DWI in the diagnosis of temporal bone cholesteatoma were 89.13%, 90.00%, 93.18%, and 84.38%, respectively.Conclusion The TSE-DWI sequence has high signal-to-noise ratio and can improve the diagnostic accuracy and specificity. TSE-DWI sequence is of great value in clinical diagnosis and treatment.
-
Key words:
- cholesteatoma /
- turbo spin-echo /
- diffusion weighted imaging
-

-
表 1 患者临床资料
n=76,例(%) 项目 例(%) 胆脂瘤组 非胆脂瘤组 P 耳内流脓间隔 0.369 间歇性 55(72.4) 35(63.6) 20(36.4) 持续性 21(27.6) 11(52.4) 10(47.6) 分泌物性质 黏稠 29(38.2) 18(62.1) 11(37.9) 0.829 有臭味 33(43.4) 19(57.6) 14(42.4) 0.645 混血丝 39(51.3) 24(61.5) 15(38.5) 0.853 鼓室导抗图 0.248 As型 4(5.3) 3(75.0) 1(25.0) B型 67(88.2) 42(62.7) 25(37.3) C型 4(5.3) 1(25.0) 3(75.0) 未引出 1(1.3) 0(0) 1(100.0) 听力损失 0.231 传导性聋 40(52.6) 23(57.5) 17(42.5) 混合性聋 31(40.8) 19(61.3) 12(38.7) 全聋 4(5.3) 4(100.0) 0(0) 重度感音神经性聋 1(1.3) 0(0) 1(100.0) 鼓膜穿孔 28(36.8) 16(57.1) 12(42.9) 0.645 -
[1] Fukuda A, Morita S, Harada T, et al. Value of T1-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Cholesteatoma Detection[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2017, 38(10): 1440-1444. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001558
[2] Rogha M, Hashemi SM, Mokhtarinejad F, et al. Comparison of Preoperative Temporal Bone CT with Intraoperative Findings in Patients with Cholesteatoma[J]. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol, 2014, 26(74): 7-12.
[3] Widmann G, Henninger B, Kremser C, et al. MRI Sequences in Head & Neck Radiology-State of the Art[J]. Rofo, 2017, 189(5): 413-422. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-103280
[4] van Egmond SL, Stegeman I, Grolman W, et al. A Systematic Review of Non-Echo Planar Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Detection of Primary and Postoperative Cholesteatoma[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2016, 154(2): 233-240. doi: 10.1177/0194599815613073
[5] Garrido L, Cenjor C, Montoya J, et al. Diagnostic capacity of non-echo planar diffusion-weighted MRI in the detection of primary and recurrent cholesteatoma[J]. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp, 2015, 66(4): 199-204. doi: 10.1016/j.otorri.2014.07.006
[6] Muzaffar J, Metcalfe C, Colley S, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for residual and recurrent cholesteatoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2017, 42(3): 536-543. doi: 10.1111/coa.12762
[7] Lingam RK, Bassett P. A Meta-Analysis on the Diagnostic Performance of Non-Echoplanar Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Detecting Middle Ear Cholesteatoma: 10 Years On[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2017, 38(4): 521-528. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001353
[8] Migirov L, Wolf M, Greenberg G, et al. Non-EPI DW MRI in planning the surgical approach to primary and recurrent cholesteatoma[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2014, 35(1): 121-125. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000000234
[9] Akkari M, Gabrillargues J, Saroul N, et al. Contribution of magnetic resonance imaging to the diagnosis of middle ear cholesteatoma: analysis of a series of 97 cases[J]. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, 2014, 131(3): 153-158. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2013.08.002
[10] Garcia-Iza L, Guisasola A, Ugarte A, et al. Utility of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of cholesteatoma and the influence of the learning curve[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 275(9): 2227-2235. doi: 10.1007/s00405-018-5074-5
[11] Laske RD, Roth TN, Baráth K, et al. The Role of Non-Echoplanar Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Diagnosis of Primary Cholesteatoma and Cholesteatoma Recidivism as an Adjunct to Clinical Evaluation[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2018, 127(12): 919-925. doi: 10.1177/0003489418800833
[12] Nash R, Lingam RK, Chandrasekharan D, et al. Does non-echo-planar diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging have a role in assisting the clinical diagnosis of cholesteatoma in selected cases?[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2018, 132(3): 207-213. doi: 10.1017/S0022215118000087
[13] Karandikar A, Loke SC, Goh J, et al. Evaluation of cholesteatoma: our experience with DW Propeller imaging[J]. Acta Radiol, 2015, 56(9): 1108-1112. doi: 10.1177/0284185114549568
[14] Saat R, Laulajainen-Hongisto AH, Mahmood G, et al. MR imaging features of acute mastoiditis and their clinical relevance[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2015, 36: 361-367. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4120
[15] Velthuis S, van Everdingen KJ, Quak JJ, et al. The value of non echo planar, diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for the detection of residual or recurrent middle-ear cholesteatoma[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2014, 128(7): 599-603. doi: 10.1017/S0022215114001418
[16] Patel B, Hall A, Lingam R, et al. Using Non-Echoplanar Diffusion Weighted MRI in Detecting Cholesteatoma Following Canal Wall Down Mastoidectomy-Our Experience with 20 Patient Episodes[J]. J Int Adv Otol, 2018, 14: 263-266. doi: 10.5152/iao.2018.5033
-




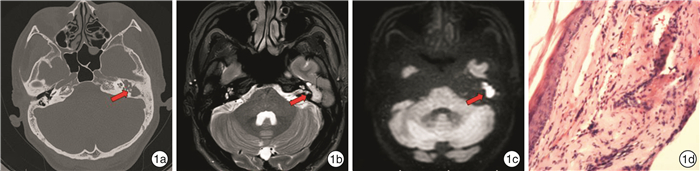
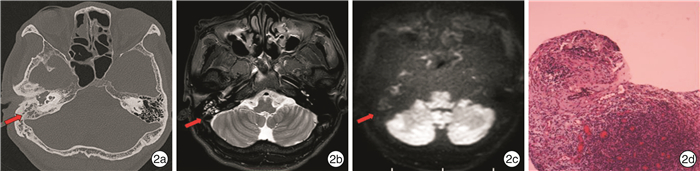
 下载:
下载: