Characterization of otorhinolaryngologic manifestations in children with mucopolysaccharide storage disease typeⅠand type Ⅱ
-
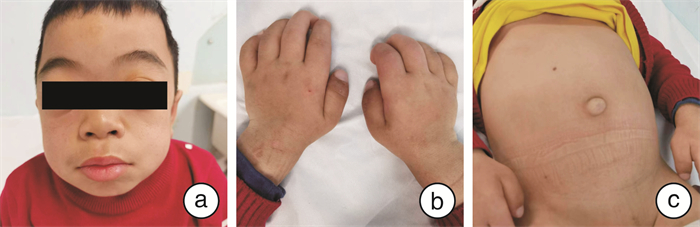
摘要: 目的 分析黏多糖贮积症(mucopolysaccharidosis,MPS)Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型患儿临床表现的特点,以提高耳鼻喉科医生对该病的认识。方法 回顾性分析55例MPSⅠ型和Ⅱ型患儿的相关临床资料,探讨MPS在耳鼻喉科的临床表现。结果 40例(72.72%)的MPS患者在病程中均至少出现了一种耳鼻喉科症状,其中95%的患者在确诊MPS前出现耳鼻喉科症状;上气道阻塞为最常见的耳鼻喉科症状(34例,85.00%),反复上呼吸道感染次之(23例,57.50%),最后为听力下降(11例,27.50%);26例患者至少接受过1次外科手术,其中15例(57.69%)接受过耳鼻喉科手术,这些患者均在确诊前接受耳鼻喉科手术。最常见的耳鼻喉科手术是腺样体切除术。结论 MPS患者早期临床表现不典型,但耳鼻喉科症状出现早期且普遍,提高耳鼻喉科医生对该病的认识对MPS预后有着积极的意义。Abstract: Objective To analyze the characteristics of otorhinolaryngological clinical manifestations in children with Mucopolysaccharide(MPS) type Ⅰ and type Ⅱ in order to improve the knowledge of otorhinolaryngologists about this disease.Methods Clinical data related to 55 children with MPS type Ⅰ and type Ⅱ were retrospectively analyzed to investigate the clinical manifestations of MPS in ENT.Results All 40 patients(72.72%) with MPS had at least one ENT symptom during the course of the disease, with 95% of them having an ENT symptom prior to the diagnosis of MPS; upper airway obstruction was the most common ENT symptom(34, 85.00%), followed by recurrent upper respiratory tract infections(23, 57.50%), and lastly, hearing loss(11, 27.50%); all 26 patients had undergone at least one surgical procedure, of which 15(57.69%) had undergone ENT surgery, and all of these patients underwent ENT surgery before diagnosis. The most common ENT surgery was adenoidectomy.Conclusion Early clinical manifestations of MPS patients are atypical, but the early and prevalent appearance of otolaryngologic symptoms and increased awareness of the disease among otolaryngologists has a positive impact on the prognosis of MPS.
-

-
[1] Wraith JE. The mucopolysaccharidoses: a clinical review and guide to management[J]. Arch Dis Child, 1995, 72(3): 263-267. doi: 10.1136/adc.72.3.263
[2] Arunkumar N, Langan TJ, Stapleton M, et al. Newborn screening of mucopolysaccharidoses: past, present, and future[J]. J Hum Genet, 2020, 65(7): 557-567. doi: 10.1038/s10038-020-0744-8
[3] Khan SA, Peracha H, Ballhausen D, et al. Epidemiology of mucopolysaccharidoses[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2017, 121(3): 227-240. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2017.05.016
[4] Murgasova L, Jurovcik M, Jesina P, et al. Otorhinolaryngological manifestations in 61 patients with mucopolysaccharidosis[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 135: 110137. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110137
[5] Lee CL, Lee KS, Chuang CK, et al. Otorhinolaryngological Management in Taiwanese Patients with Mucopolysaccharidoses[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2021, 18(15): 3373-3379. doi: 10.7150/ijms.61827
[6] Peracha H, Sawamoto K, Averill L, et al. Molecular genetics and metabolism, special edition: Diagnosis, diagnosis and prognosis of Mucopolysaccharidosis IVA[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2018, 125(1-2): 18-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2018.05.004
[7] Kiely BT, Kohler JL, Coletti HY, et al. Early disease progression of Hurler syndrome[J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2017, 12(1): 32. doi: 10.1186/s13023-017-0583-7
[8] Torres DA, Barth AL, Valente M, et al. Otolaryngologists and the Early Diagnosis of Mucopolysaccharidoses: A Cross-Sectional Study[J]. Diagnostics(Basel), 2019, 9(4): 187.
[9] Hashimoto A, Kumagai T, Mineta H. Hunter Syndrome Diagnosed by Otorhinolaryngologist[J]. Case Rep Otolaryngol, 2018, 2018: 4252696.
[10] Pires de Mello P, Lopes Barth A, de Araujo Torres D, et al. Laryngeal, Tracheal, and Bronchial Disease in the Mucopolysaccharidoses: Endoscopic Study[J]. Diagnostics(Basel), 2020, 10(1): 37.
[11] Muhlebach MS, Shaffer CB, Georges L, et al. Bronchoscopy and airway management in patients with mucopolysaccharidoses(MPS)[J]. Pediatr Pulmonol, 2013, 48(6): 601-607. doi: 10.1002/ppul.22629
[12] Karl R, Carola S, Regina E, et al. Tracheobronchial stents in mucopolysaccharidosis[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 83: 187-192. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.02.015
[13] Muhlebach MS, Wooten W, Muenzer J. Respiratory manifestations in mucopolysaccharidoses[J]. Paediatr Respir Rev, 2011, 12(2): 133-138. doi: 10.1016/j.prrv.2010.10.005
[14] Gönüldaş B, Yılmaz T, Sivri HS, et al. Mucopolysaccharidosis: Otolaryngologic findings, obstructive sleep apnea and accumulation of glucosaminoglycans in lymphatic tissue of the upper airway[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2014, 78(6): 944-949. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2014.03.021
[15] Wold SM, Derkay CS, Darrow DH, et al. Role of the pediatric otolaryngologist in diagnosis and management of children with mucopolysaccharidoses[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2010, 74(1): 27-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2009.09.042
[16] Keilmann A, Läßig AK, Pollak-Hainz A, et al. Adenoids of patients with mucopolysaccharidoses demonstrate typical alterations[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2015, 79(2): 115-118. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2014.11.014
[17] Harrison R, Schaefer S, Warner L, et al. Transnasal adenoidectomy in mucopolysaccharidosis[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 111: 149-152. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.04.028
[18] Bianchi PM, Gaini R, Vitale S. ENT and mucopolysaccharidoses[J]. Ital J Pediatr, 2018, 44(Suppl 2): 127.
[19] Dohrmann T, Muschol NM, Sehner S, et al. Airway management and perioperative adverse events in children with mucopolysaccharidoses and mucolipidoses: A retrospective cohort study[J]. Paediatr Anaesth, 2020, 30(2): 181-190. doi: 10.1111/pan.13787
[20] Clark BM, Sprung J, Weingarten TN, et al. Anesthesia for patients with mucopolysaccharidoses: Comprehensive review of the literature with emphasis on airway management[J]. Bosn J Basic Med Sci, 2018, 18(1): 1-7. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2017.2201
[21] Mesolella M, Cimmino M, Cantone E, et al. Management of otolaryngological manifestations in mucopolysaccharidoses: our experience[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2013, 33(4): 267-272.
[22] Bicalho CG, de Araújo Leão E, de Andrade ÁM, et al. Hearing Loss in Mucopolysaccharidosis[J]. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2021, 25(3): e386-e391. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1712107
[23] Wolfberg J, Chintalapati K, Tomatsu S, et al. Hearing Loss in Mucopolysaccharidoses: Current Knowledge and Future Directions[J]. Diagnostics(Basel), 2020, 10(8): 554.
[24] Lin HY, Shih SC, Chuang CK, et al. Assessment of hearing loss by pure-tone audiometry in patients with mucopolysaccharidoses[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2014, 111(4): 533-538. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.02.003
[25] Ahn J, Lee JJ, Park SI, et al. Auditory Characteristics in Patients With Mucopolysaccharidosis[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2019, 40(10): e955-e961. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002422
[26] 周玉晨, 陆玲, 赵宁, 等. 儿童分泌性中耳炎与学习困难的相关性研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(3): 222-224. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.03.013
[27] Bicalho CG, Rezende MM, Nogueira AMCM, et al. A importância da avaliação otorrinolaringológica de pacientes com mucopolissacaridose[J]. Arquivos Internacionais de Otorrinolaringologia(Impresso), 2011, 15(3): 290-294. doi: 10.1590/S1809-48722011000300004
-




 下载:
下载: