Diagnosis and treatment of tumors involving the root of neck: experience of 73 cases
-
摘要: 目的 研究累及颈根部肿物的临床诊断和外科治疗方法。方法 回顾性分析北京大学第一医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科收治的73例累及颈根部肿物患者的临床资料,总结分析其临床表现、术前影像学评估、手术入路选择、术后病理类型、术后并发症及预后。结果 73例累及颈根部肿物患者临床多表现为颈部无痛性肿物(36例)及吞咽困难(16例)。颈部增强CT或MRI及其三维重建能清楚显示肿块的大小、形态、位置、与周围结构特别是重要血管的关系及继发改变。病理诊断良性37例,恶性36例;良性肿瘤最常见为胸骨后甲状腺肿17例,恶性肿瘤最常见为颈段食管癌15例。手术治疗70例,非手术治疗3例。手术径路选择:颈部入路61例(87.1%),颈胸联合入路9例(12.9%);完整切除肿瘤67例,姑息性切除3例。手术和胸外科合作16例,和骨科合作1例。发生手术并发症16例(22.9%)。73例患者中失访7例,66例随访3个月~15年。35例良性肿瘤随访均未见复发;31例恶性肿瘤患者的3年生存率为48.4%,5年生存率为32.3%。结论 颈根部解剖结构复杂,累及该部位的肿瘤病理类型多样,良性和恶性肿瘤比例相当。手术切除是主要治疗方法,但应根据肿瘤的病理、大小及周围结构关系以及术者的习惯决定手术入路及方式,主要为颈部入路及颈胸联合入路。良性肿瘤多可采取颈部入路切除,颈胸联合入路适用于边界不清和重要血管神经粘连紧密的恶性肿瘤,对于大血管的妥善处理是肿瘤能否完整切除的关键。该部位手术并发症较多,术前需与患者充分沟通,有时需要多学科合作。Abstract: Objective To summarize and analyze the clinical diagnosis and surgical treatment of patients with tumors involving the root of neck.Method We retrospectively analyzed the clinical data of 73 patients with tumors involving the root of neck in Peking University First Hospital Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery department. Data collected included clinical manifestations, preoperative imaging evaluation, surgical approach selection, postoperative pathological types, postoperative complications and prognosis.Result The most frequent symptom was a painless cervical mass(36 cases) and dysphagia(16 cases). All patients underwent preoperative enhanced CT scan or MRI, which would be helpful to evaluate the tumor size, shape, location, relationship with surrounding structures, especially important blood vessels, and secondary changes. The postoperative pathological diagnosis included 37 cases of benign and 36 cases of malignant. The most common benign tumor was retrosternal goiter in 17 cases, and the most common malignant tumor was cervical esophageal cancer in 15 cases. Nonsurgical treatment was performed in 3 cases, while surgical treatment was performed in 70 cases, including 61 cases (87.1%)with cervical approach, 9 cases (12.9%)with combined cervicothoracic approach, 67 cases of complete tumor resection and 3 cases of palliative resection. Sixteen cases cooperated with thoracic surgerons, and 1 case with orthopedic surgerons. Surgical complications occurred in 16 cases (22.9%). Seven patients were lost to follow-up, and 66 patients were followed up for 3 months to 15 years. None of the 35 patients with benign tumors had recurrence, and among the 31 patients with malignant tumors, the 3-year survival rate was 48.4% and the 5-year survival rate was 32.3%.Conclusion Tumors involving the root of neck are challenging to diagnose and treat due to the complex regional anatomy and a variety of pathological types, with comparable proportion of benign and malignant tumors. Surgery is the first choice, but it requires careful preoperative assessment. Surgical approaches include cervical approach and combined cervicothoracic approach, which should be determined according to the pathology, size and surrounding structure of the tumor, as well as the habits of the surgeon. Most benign tumors can be excised by the cervical approach. The combined cervicothoracic approach is suitable for malignant tumors with unclear boundaries and close adhesion of important blood vessels and nerves. Proper treatment of large vessels is the key to complete resection of tumors. There are many complications in the operation of this site, so it is necessary to fully communicate with the patient before operation, and sometimes multidisciplinary cooperation is needed.
-
Key words:
- root of neck neoplasms /
- diagnosis, surgical procedures, operative /
-

-
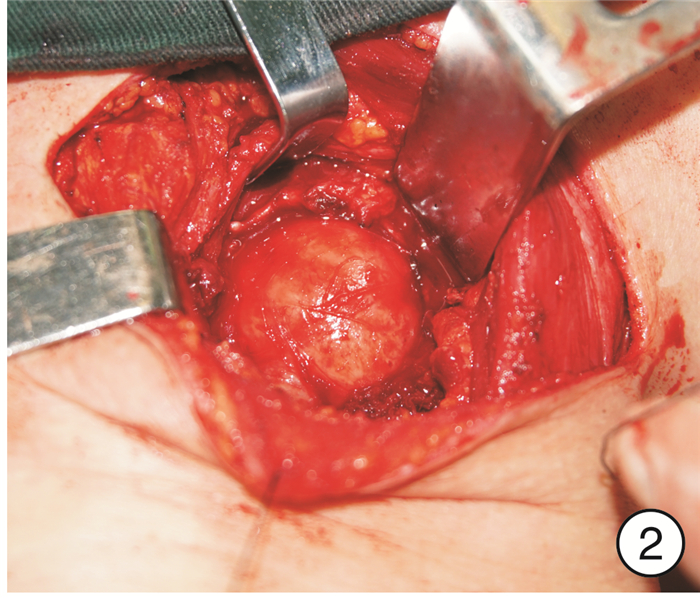
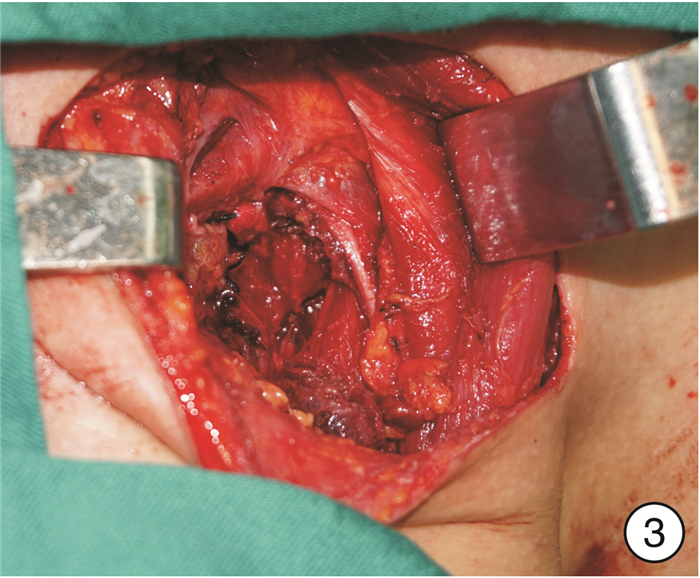
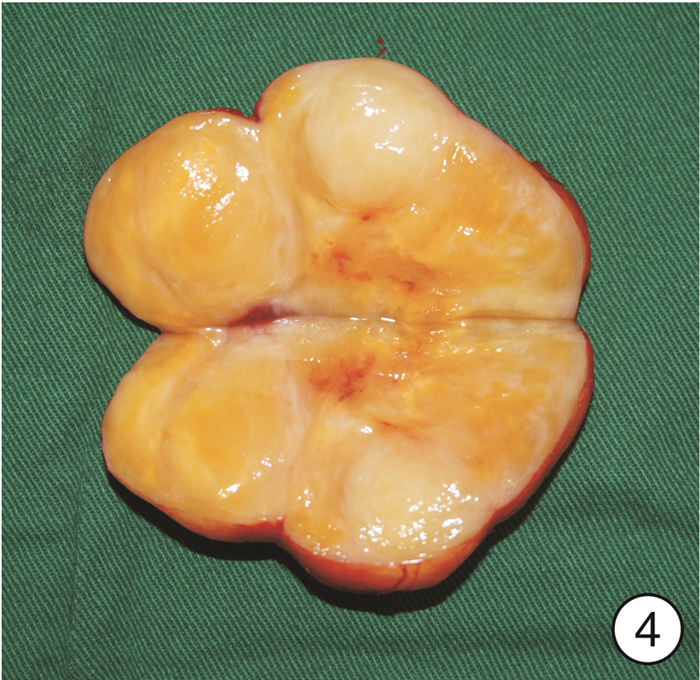
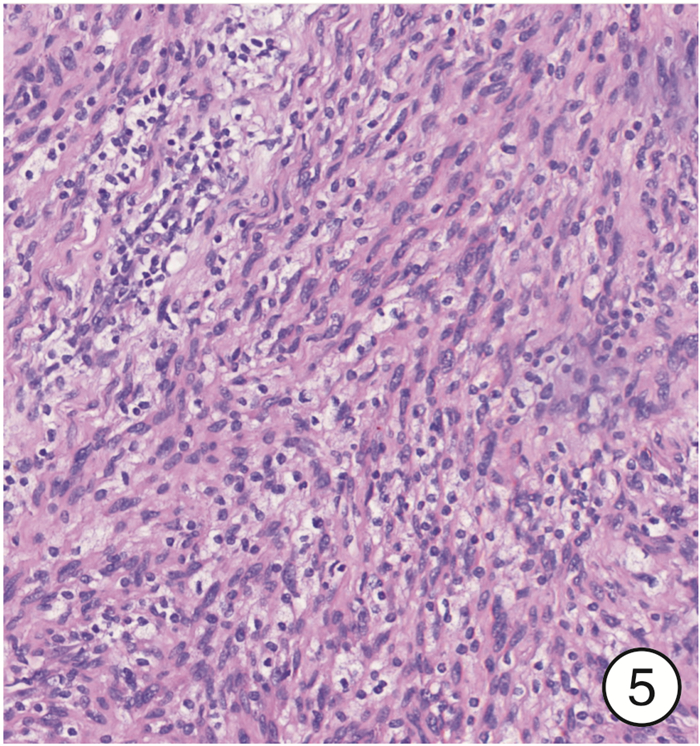
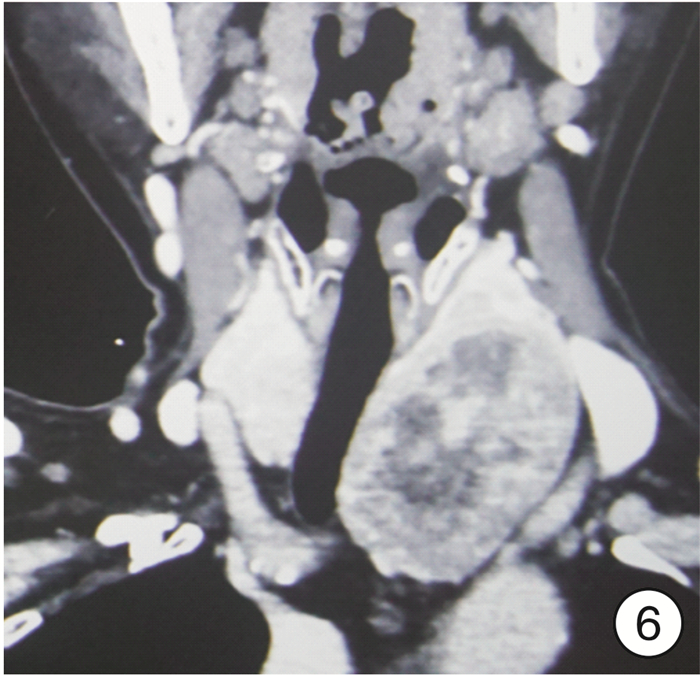
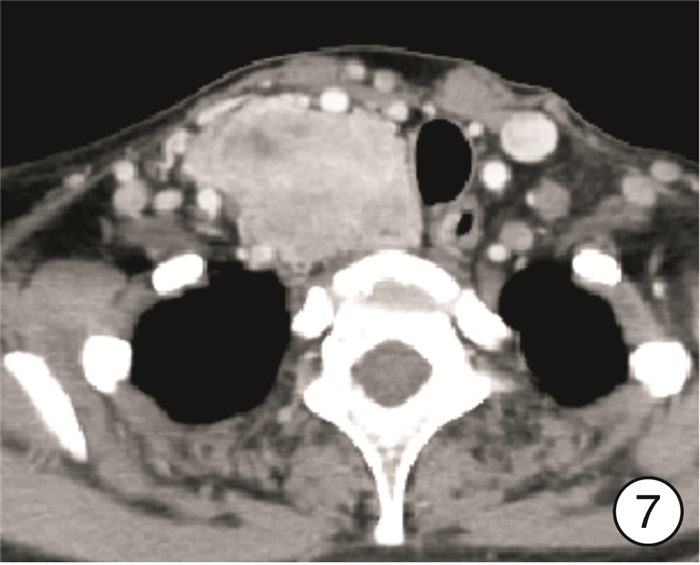
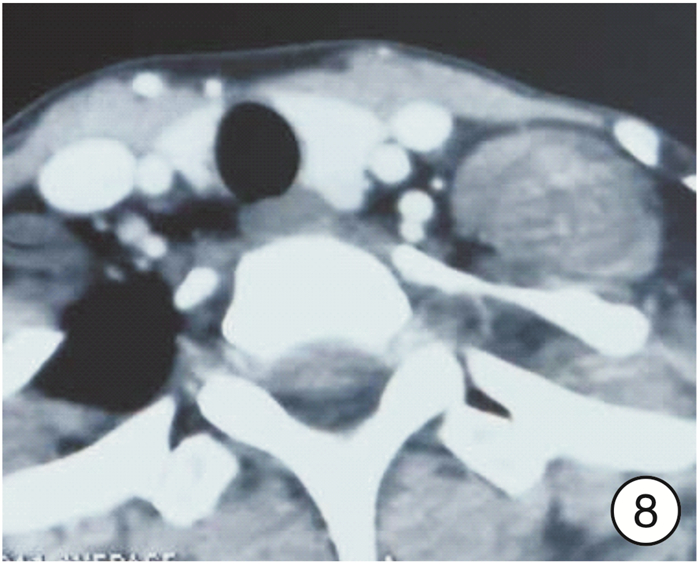
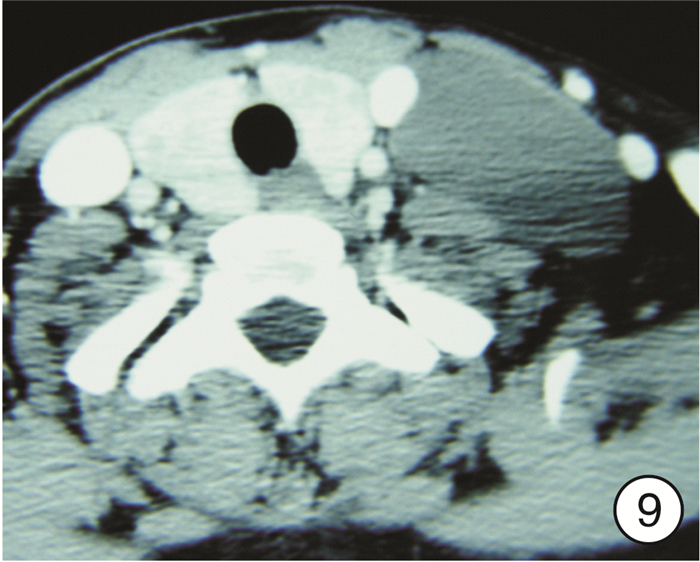
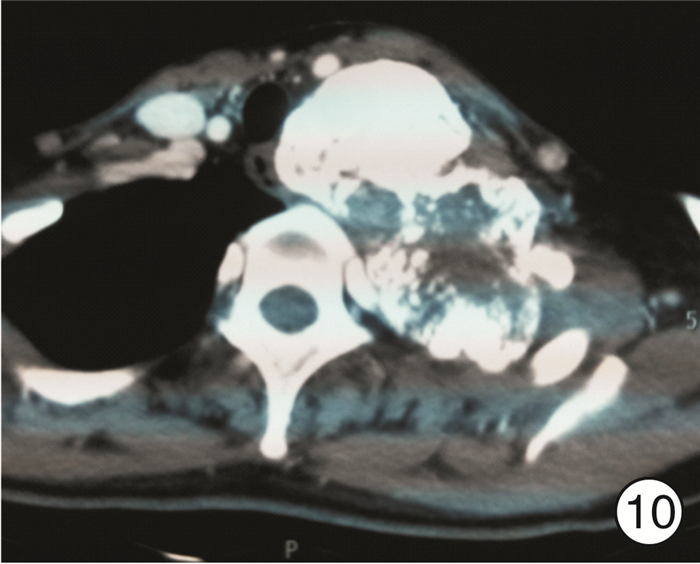
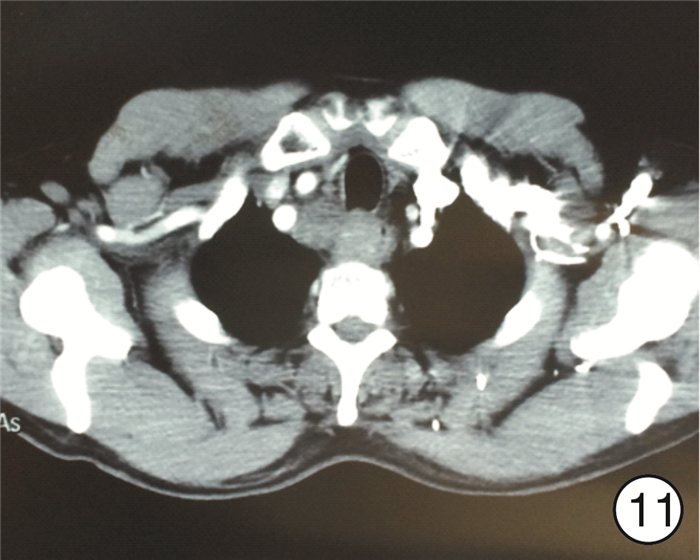
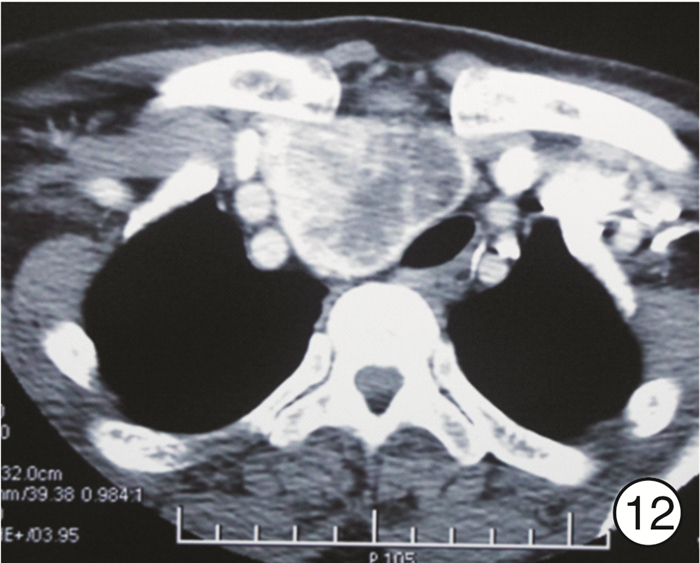
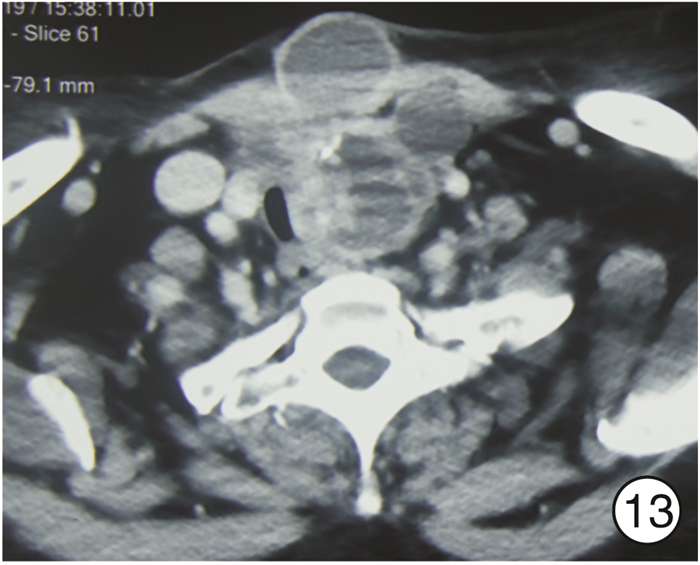
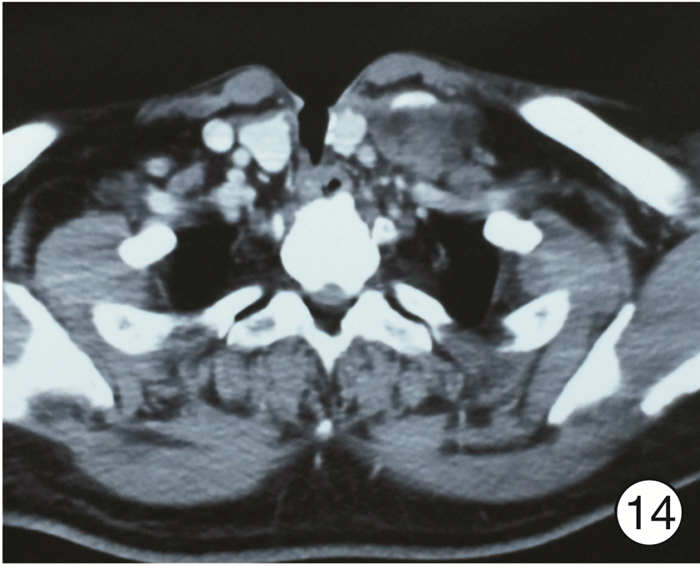
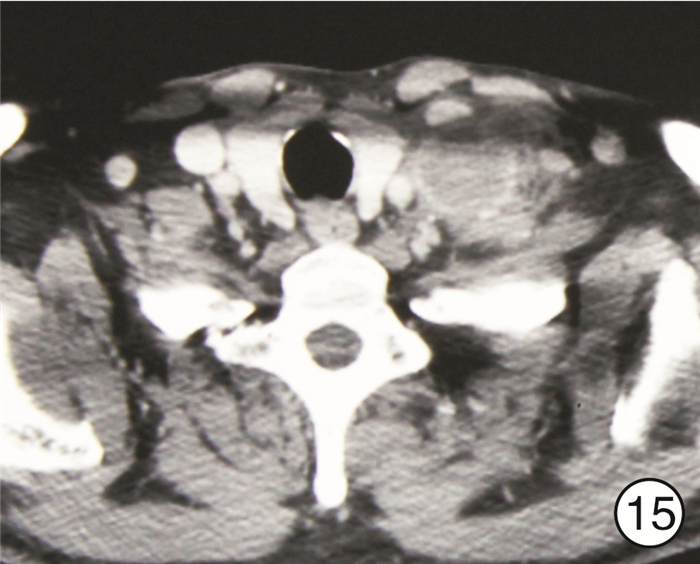
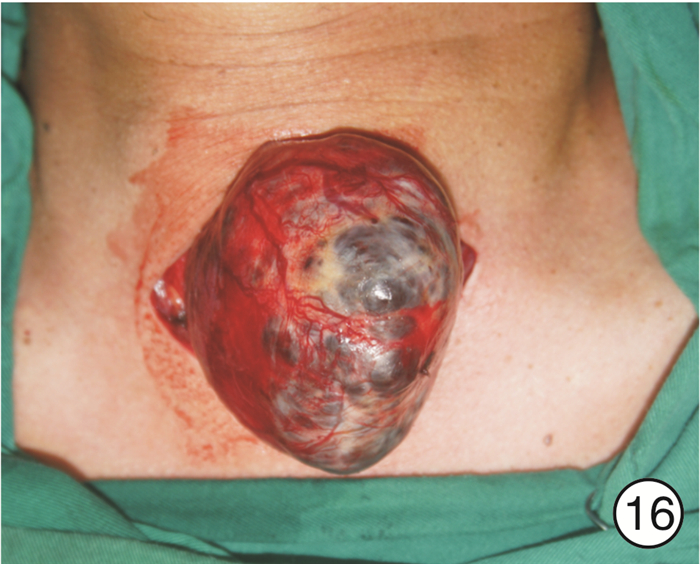
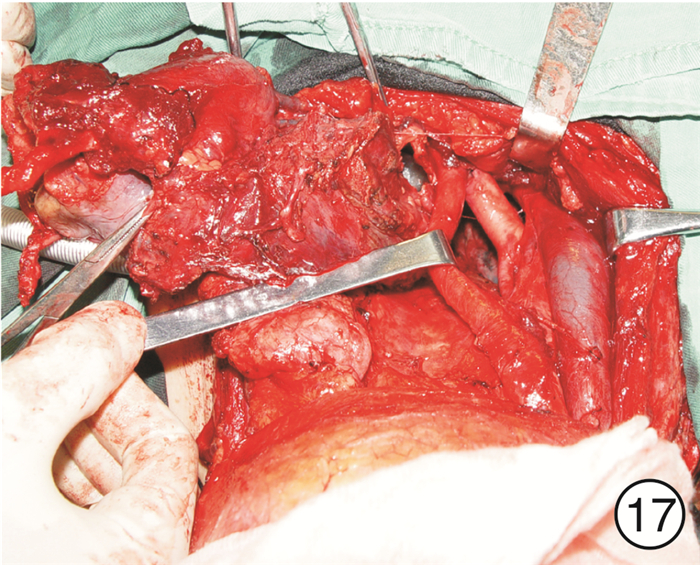
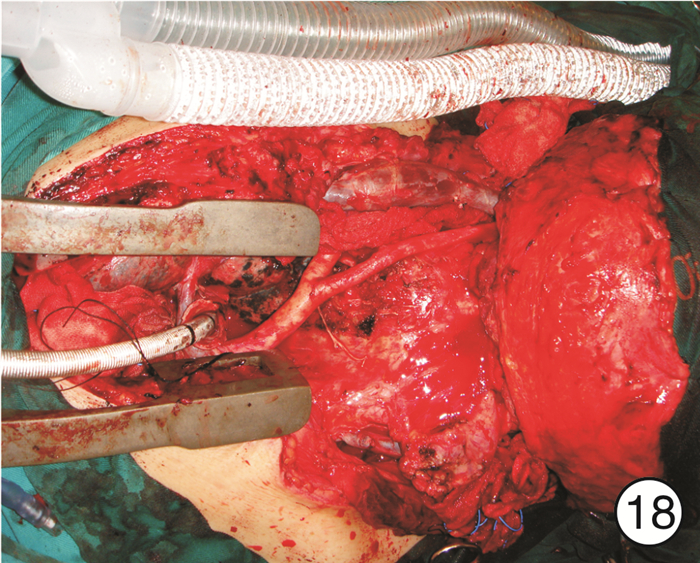
图 17 颈段食管癌(图 11患者)颈部入路
表 1 良性肿瘤和恶性肿瘤的病理类型
病理类型 例数 病理类型 例数 良性肿瘤 37 恶性肿瘤 36 胸骨后甲状腺肿 17 颈段食管癌 15 结节性甲状腺肿 14 甲状腺癌 10 滤泡性腺瘤 3 乳头状癌伴淋巴结转移 6 脂肪瘤 5 结节性甲状腺肿合并乳头状癌 1 淋巴管瘤 5 乳头状癌复发 1 神经源性肿瘤 5 滤泡状癌复发 1 神经鞘膜瘤 3 未分化癌 1 副神经节瘤 1 造瘘口复发癌 3 节细胞神经瘤 1 原发灶不明的淋巴结转移性鳞癌 2 Castleman病 1 淋巴瘤 2 非坏死性肉芽肿 1 下咽癌术后淋巴结转移 1 钙化腱膜纤维瘤 1 食管癌术后淋巴结转移 1 胸腺增生 1 喉癌术后淋巴结转移 1 异位甲状腺 1 恶性外周神经纤维瘤 1 -
[1] 廖海星, 张石川, 任光国. 颈根部手术15例分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2000, 35(3): 165-167. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:1673-0860.2000.03.001
[2] Kraus DH, Huo J, Burt M. Surgical access to tumors of the cervicothoracic junction[J]. Head Neck, 1995, 17(2): 131-136. doi: 10.1002/hed.2880170210
[3] 王涛, 刘业海, 牛开元, 等. 颈根部涉及甲状腺占位疾病诊治体会[J]. 中国中西医结合耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2014, 22(4): 279-282. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4856.2014.04.011
[4] Dartevelle PG, Chapelier AR, Macchiarini P, et al. Anterior transcervical-thoracic approach for radical resection of lung tumors invading the thoracic inlet[J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 1993, 105(6): 1025-1034. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5223(19)33774-2
[5] Korst RJ, Burt ME. Cervicothoracic tumors: results of resection by the "hemi-clamshell" approach[J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 1998, 115(2): 286-295. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5223(98)70271-5
[6] Prezerakos GK, Sayal P, Kourliouros A, et al. Paravertebral tumours of the cervicothoracic junction extending into the mediastinum: surgical strategies in a no man's land[J]. Eur Spine J, 2018, 27(4): 902-912. doi: 10.1007/s00586-018-5512-5
[7] 姜震, 雷大鹏, 刘大昱, 等. 颈根部占位性病变的诊断与治疗[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报, 2018, 32(1): 53-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYU201801019.htm
[8] 张少强, 王林古, 李随勤. 颈根部肿块的外科治疗(附26例报告)[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2011, 25(12): 529-530. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201112003.htm
[9] 魏伯俊, 祝小莉, 陈艳丽, 等. 颈部和胸腔以及腋窝交汇区域肿瘤的手术治疗[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2007, 42(9): 679-682. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:1673-0860.2007.09.010
-




 下载:
下载: