Analysis of complex cochlear implantation electrode repositioning strategies based on intraoperative CT
-
摘要: 目的 通过对复杂疑难人工耳蜗电极植入手术病例的分析,重点探讨术中CT辅助技术在复杂疑难人工耳蜗电极植入优化调整策略的应用价值。方法 回顾性分析术中CT辅助复杂疑难人工耳蜗植入病例的临床资料,总结术中并发症、电极调整次数,并对患者进行随访。结果 共51例(53耳)研究对象纳入本研究,内耳畸形患者46例,耳蜗骨化患者2例,其中7例患者行术中CT扫描后再调整电极位置后达到满意植入效果。结论 术中CT扫描是一种确定复杂人工耳蜗电极植入位置的可靠辅助手段,术中CT扫描提高了复杂疑难耳蜗植入手术的准确性。Abstract: Objective To investigate the application value of intraoperative sliding rail computed tomography (CT) in complicated and difficult cochlear implantation by analyzing the cases of complicated and difficult cochlear implantation.Methods The clinical data of patients with complicated and difficult cochlear implantation assisted by sliding rail CT were retrospectively analyzed, the intraoperative complications and the number of electrode adjustments were summarized, and the patients were followed up.Results A total of 51 subjects were included in this study, including 46 patients with inner ear malformation, 2 patients with cochlear ossification, there were 7 patients underwent secondary scanning to adjust the electrode and achieved satisfactory implantation position.Conclusion Intraoperative CT scanning is a reliable adjunctive tool for determining the placement of complex cochlear implantation, and it improves the accuracy of difficult cochlear implantation surgeries.
-
Key words:
- cochlear implantation /
- inner malformation /
- intraoperative CT
-

-
表 1 人工耳蜗电极植入后2次调整病例
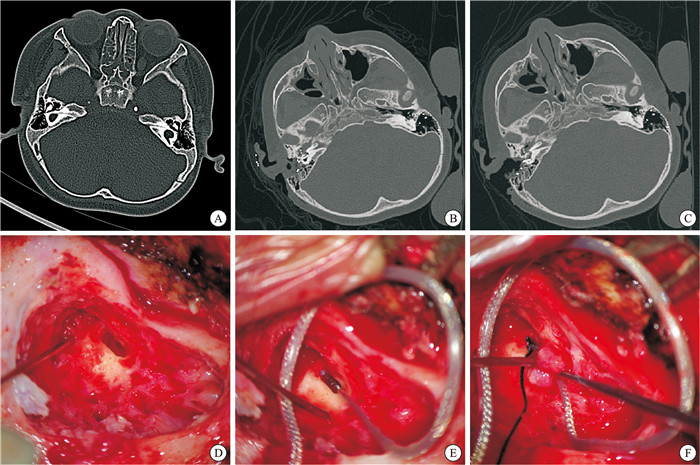
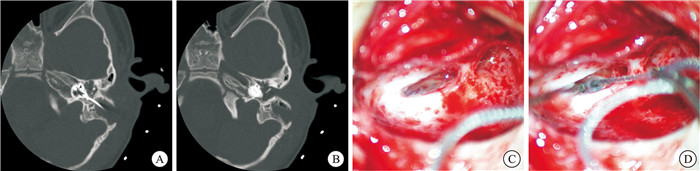
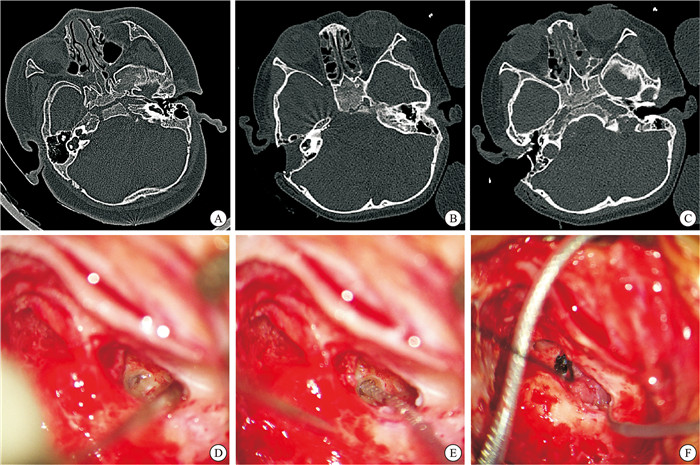
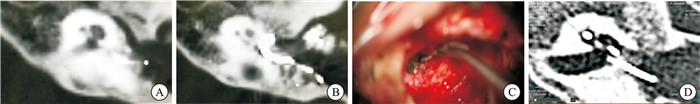
序号 诊断 年龄/岁 性别 侧别 位置 随访 1 IP-Ⅲ 12 男 左 电极位于底转、第二转,尖端弯折凸向内听道 CAP 6分,SIR 4分 2 CC 8 男 右 电极位于共同腔,但尖端误入内听道 CAP 4分,SIR 3分 3 IP-Ⅲ 6 男 右 电极在耳蜗内位置好,底部突出入内听道底 CAP 6分,SIR 4分 4 耳蜗骨化 71 女 左 磨开第二转后CT证实电极未进入残余耳蜗管腔 CAP 6分,SIR 4分 5 CC 2 女 左 电极位于融合的内耳共同腔内,局部悬空未贴紧骨壁 CAP 5分,SIR 3分 6 IP-Ⅰ 3 女 右 术中CT证实电极进入内听道和桥小脑角 CAP 4分,SIR 3分 7 CC 5 男 右 电极位于融合的共同腔内,后方电极贴壁欠佳 CAP 6分,SIR 4分 -
[1] Sennaro lu L, Bajin MD. Classification and current management of inner ear malformations[J]. Balkan Med J, 2017, 34(5): 397-411. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.2017.0367
[2] 戴朴, 蒋刈. 精准微创的人工耳蜗植入手术[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2018, 16(6): 737-741.
[3] Canzano F, Di Lella F, Guida M, et al. Revision cochlear implant surgery for clinical reasons[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2023, 43(1): 65-73. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-N2096
[4] Timar M, Saki N, Bayat A, et al. Cochlear implantation outcomes in pediatrics with inner ear malformations in a tertiary care hospital in Ahvaz[J]. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2023, 75(1): 197-203.
[5] 龚树生, 熊伟. 疑难病例人工耳蜗植入[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报, 2017, 31(5): 4-9.
[6] Ying YM, Lin JW, Oghalai JS, et al. Cochlear implant electrode misplacement: incidence, evaluation, and management[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123(3): 757-766. doi: 10.1002/lary.23665
[7] 刘智锋, 林晓德, 黄宏明, 等. HRCT对人工耳蜗植入术中脑脊液井喷的预测价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2024, 38(5): 421-425. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.05.014
[8] 张德军, 高搏, 戴朴. 术中CT在疑难人工耳蜗植入手术中的应用[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2018, 16(6): 812-815.
[9] Yuan YY, Song YS, Chai CM, et al. Intraoperative CT-guided cochlear implantation in congenital ear deformity[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2012, 132(9): 951-958. doi: 10.3109/00016489.2012.674214
[10] Daly MJ, Siewerdsen JH, Moseley DJ, et al. Intraoperative cone-beam CT for guidance of head and neck surgery: Assessment of dose and image quality using a C-arm prototype[J]. Med Phys, 2006, 33(10): 3767-3780. doi: 10.1118/1.2349687
[11] 黄宏明, 周正根, 葛润梅, 等. 内耳畸形CT分类在人工耳蜗植入手术中的应用[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2018, 16(5): 629-633.
[12] Demir B, Cesur S, Sahin A, et al. Outcomes of cochlear implantation in children with inner ear malformations[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 276(9): 2397-2403. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05475-9
[13] Dalgic A, Atsal G, Ceylan ME, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid gusher in cochlear implantation and its association with inner-ear malformations[J]. J Int Adv Otol, 2022, 18(6): 478-481. doi: 10.5152/iao.2022.21441
[14] Xu KF, Xiao Y, Luo JF, et al. Research progress on incomplete partition type 3 inner ear malformation[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2024, 281(8): 3943-3948. doi: 10.1007/s00405-024-08555-7
[15] Choi BY, An YH, Song JJ, et al. Clinical observations and molecular variables of patients with hearing loss and incomplete partition type Ⅲ[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126(3): E123-E128.
[16] 宋跃帅, 戴朴. 微创入路人工耳蜗植入术[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2013, 11(2): 212-215.
[17] Mitchell MB, Labadie RF. Cost-effectiveness of intraoperative CT scanning in cochlear implantation in fee-for-service and bundled payment models[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2022, 101(4): NP164-NP168. doi: 10.1177/0145561320952192
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 160
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: