-
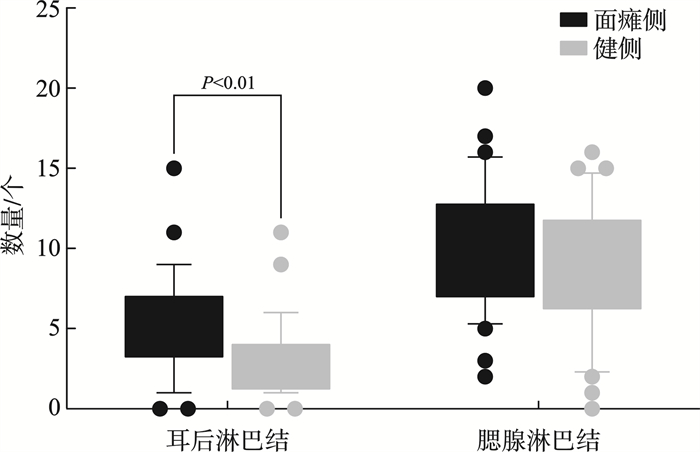
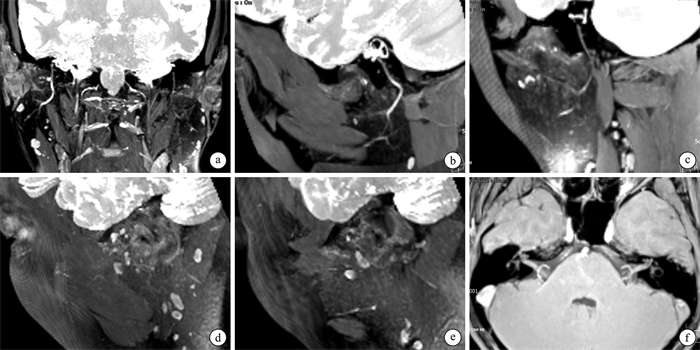
摘要: 目的 探讨MR神经成像定量评估急性周围性面瘫患者面神经及周围淋巴结的价值。方法 采用前瞻性实验设计,纳入32例急性周围性面瘫患者,基于MR神经成像技术采集双侧面神经MR高分辨薄层图像,测量双侧面神经不同节段(包括迷路段、膝状神经节、水平段、垂直段、茎乳孔段、腮腺段主干、颞面干、颈面干)直径以及耳周、腮腺淋巴结的定量指标(数量、最大淋巴结的长短径)。采用配对t检验及Wilcoxon符号秩检验,比较双侧面神经直径、周围淋巴结定量指标差异。结果 面瘫侧膝状神经节、茎乳孔段、腮腺段主干、颞面干、颈面干直径明显大于健侧(均P < 0.05),但迷路段、水平段、垂直段直径与健侧比较差异无统计学意义;面瘫侧耳周淋巴结的数量明显多于健侧(P=0.001)。结论 MR神经成像可定量评估急性周围性面瘫患者面神经结构变化:膝状神经节、茎乳孔段、腮腺段主干、颞面干及颈面干增粗;同时发现患侧耳周淋巴结数量增多。上述发现可辅助评估疗效、判断预后。Abstract: Objective To exploring the value of MR neuroimaging for quantitative assessment of the facial nerve and peripheral lymph nodes in patients with acute peripheral facial paralysis.Methods Based on a prospective experimental design, 32 patients with idiopathic peripheral facial palsy were enrolled in the experiment. Based on MR neuroimaging technology, MR high-resolution thin-layer images of bilateral facial nerves were acquired. The diameters of different segments of the bilateral facial nerve were measured, including the labyrinthine segment, the geniculate ganglion, the horizontal segment, the vertical segment, the stem-mammary foramen segment, the trunk of the parotid segment, the temporal trunk, and the cervical trunk, as well as the quantitative indicators of peri-auricular and parotid lymph nodes(number, length and diameter of the largest lymph nodes). Differences in quantitative indices of nerve diameter and peripheral lymph nodes between the paraplegic and healthy sides were compared using the paired t-test and Wilcoxon signed rank test.Results The diameter of geniculate ganglion, mastoid foramen stem, parotid main trunk, temporal facial trunk, and cervical facial trunk were notably increased on the facial paralysis side compared to the contralateral side(P < 0.05). However, no significant differences were observed in the diameter of labyrinthine segment, horizontal segment, or vertical segment compared to the contralateral side. There were significantly more periauricular lymph nodes on the facial paralysis side than the contralateral side(P=0.001).Conclusion MR neuroimaging enables the quantitative assessment of structural changes in the facial nerve of patients with acute peripheral facial paralysis, demonstrating nerve enlargement in the geniculate ganglion, stylomastoid foramen segment, main trunk of the parotid segment, temporal facial trunk, and cervical facial trunk. Additionally, an increased number of periauricular lymph nodes is observed on the affected side. These findings may aid clinicians in assessing the efficacy of treatments and predict the prognosis of these patients.
-
Key words:
- acute peripheral facial palsy /
- Bell facial palsy /
- hunt syndrome /
- MR neurography /
- facial nerve
-

-
表 1 面瘫侧与健侧面神经不同节段直径和淋巴结的比较
组别 阳性 阴性 统计值 P 迷路段 0.98±0.24 1.00±0.23 0.440 0.662 膝状神经节长径 2.56±0.53 2.29±0.39 3.340 0.002 膝状神经节短径 2.02±0.48 1.81±0.35 2.290 0.029 水平段 1.19±0.29 1.13±0.23 0.880 0.387 垂直段 1.65±0.34 1.59±0.20 0.830 0.413 茎乳孔 1.83±0.31 1.5±0.22 6.996 < 0.001 腮腺段主干 1.63±0.31 1.35±0.31 3.640 0.001 颞面干 1.36(1.24,1.56) 1.05(0.70,1.25) 3.820 < 0.001 颈面干 1.26±0.38 0.86±0.28 5.760 < 0.001 最大淋巴结长径 10.58±4.07 10.63±3.95 0.070 0.943 最大淋巴结短径 5.95±1.98 5.83±1.89 0.340 0.736 耳周淋巴结 5.00(3.25,7.00) 3.00(1.25,4.00) 3.480 0.001 腮腺淋巴结 10.00(7.00,12.75) 9.00(6.25,11.75) 1.903 0.053 -
[1] Kline LB, Kates MM, Tavakoli M. Bell Palsy[J]. Jama, 2021, 326(19): 1983. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.18504
[2] 王璞, 张文阳, 王咏峰, 等. 面神经减压术治疗贝尔面瘫和亨特综合征效果分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2024, 38(5): 391-394. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.05.008
[3] 韩宇, 刘红生, 杨润琴, 等. 面神经鞘膜瘤临床表现及影像学特征分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2024, 38(5): 380-385. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.05.006
[4] Abramov DM, de Silva DS, Salles TRS, et al. The reality of multiple sclerosis assessment in middle-income countries[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2022, 21(3): 215. http://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35182501/
[5] Kandemirli SG, Altundag A, Yildirim D, et al. Olfactory bulb MRI and paranasal sinus CT findings in persistent COVID-19 anosmia[J]. Acad Radiol, 2021, 28(1): 28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2020.10.006
[6] Kwee RM, Borghans RAP, Bruls RJM, et al. Diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted MR neurography as an adjunct to conventional MRI for the assessment of brachial plexus pathology[J]. Eur Radiol, 2022, 32(4): 2791-2797. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08324-8
[7] Pedrick EG, Sneag DB, Colucci PG, et al. Three-dimensional MR neurography of the brachial plexus: vascular suppression with low-dose ferumoxytol[J]. Radiology, 2023, 307(1): e221087. doi: 10.1148/radiol.221087
[8] Sneag DB, Kiprovski K. MR neurography of bilateral parsonage-Turner syndrome[J]. Radiology, 2021, 300(3): 515. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021204688
[9] Preisner F, Behnisch R, Foesleitner O, et al. Reliability and reproducibility of sciatic nerve magnetization transfer imaging and T2 relaxometry[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(12): 9120-9130. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08072-9
[10] Jende JME, Groener JB, Kender Z, et al. Structural nerve remodeling at 3-T MR neurography differs between painful and painless diabetic polyneuropathy in type 1 or 2 diabetes[J]. Radiology, 2020, 294(2): 405-414. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019191347
[11] Daniels DL, Czervionke LF, Millen SJ, et al. MR imaging of facial nerve enhancement in Bell palsy or after temporal bone surgery[J]. Radiology, 1989, 171(3): 807-809. doi: 10.1148/radiology.171.3.2717756
[12] Woolen SA, Shankar PR, Gagnier JJ, et al. Risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in patients with stage 4 or 5 chronic kidney disease receiving a group Ⅱ gadolinium-based contrast agent: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. JAMA Intern Med, 2020, 180(2): 223-230. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.5284
[13] Galley J, Sutter R, Germann C, et al. High-resolution in vivo MR imaging of intraspinal cervical nerve rootlets at 3 and 7 Tesla[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(7): 4625-4633. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07557-3
[14] Lin Y, Tan ET, Campbell G, et al. Improved 3D DESS MR neurography of the lumbosacral plexus with deep learning and geometric image combination reconstruction[J]. Skeletal Radiol, 2024, 53(8): 1529-1539. doi: 10.1007/s00256-024-04613-7
[15] 洪桂洵, 汪倩倩, 初建平, 等. 采用小线圈和三维双回波稳态水激励序列显示下颌神经的价值[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2018, 52(6): 421-425.
[16] Qin Y, Zhang J, Li P, et al. 3D double-echo steady-state with water excitation MR imaging of the intraparotid facial nerve at 1.5T: a pilot study[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2011, 32(7): 1167-1172. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2480
[17] Bogner W, Pinker-Domenig K, Bickel H, et al. Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging improves the diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted MR breast examinations at 3.0 T[J]. Radiology, 2012, 263(1): 64-76. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12111494
[18] Chen XY, Yang SS, Lin MG, et al. Multi-b-values-fitting readout-segmentation of long variable echo-trains diffusion-weighted imaging(RESOLVE DWI)in evaluation of disease activity and curative effect of axial spondyloarthritis(axSpA)[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1136925. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1136925
[19] Li CT, Li Y, Zhang DS, et al. 3D-FIESTA MRI at 3 T demonstrating branches of the intraparotid facial nerve, parotid ducts and relation with benign parotid tumours[J]. Clin Radiol, 2012, 67(11): 1078-1082. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2012.03.014
[20] Kress B, Griesbeck F, Stippich C, et al. Bell palsy: quantitative analysis of MR imaging data as a method of predicting outcome[J]. Radiology, 2004, 230(2): 504-509. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2302021353
[21] Saatçi I, Sahintürk F, Sennaroǧlu L, et al. MRI of the facial nerve in idiopathic facial palsy[J]. Eur Radiol, 1996, 6(5): 631-636. doi: 10.1007/BF00187662
[22] Kinoshita T, IshⅡ K, Okitsu T, et al. Facial nerve palsy: evaluation by contrast-enhanced MR imaging[J]. Clin Radiol, 2001, 56(11): 926-932. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035536639310_c67b.html
[23] Singh A, Deshmukh P. Bell's palsy: a review[J]. Cureus, 2022, 14(10): e30186.
[24] Koji H, Atsunobu T, Reiko T, et al. Measurement of the facial nerve caliber in facial palsy: implications for facial nerve decompression[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2011, 32(4): 686-689.
[25] Krishnamurty AT, Turley SJ. Lymph node stromal cells: cartographers of the immune system[J]. Nat Immunol, 2020, 21(4): 369-380. http://www.xueshufan.com/publication/3012821758
[26] Strawbridge J, Fu KA, Chan J, et al. Facial diplegia with paresthesia associated with anti-GD1a antibodies[J]. Proc, 2022, 35(3): 387-388.
-

| 引用本文: | 刘丽华, 黄慧敏, 冀晓东, 等. 基于MR神经成像定量评估周围性面瘫患者面神经及周围淋巴结[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2025, 39(1): 29-33. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2025.01.007 |
| Citation: | LIU Lihua, HUANG Huimin, JI Xiaodong, et al. The value of MR neuroimaging in image evaluation of facial neuritis[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2025, 39(1): 29-33. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2025.01.007 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.




 下载:
下载: