One case of recurrent giant cell tumor of the larynx and literature review
-
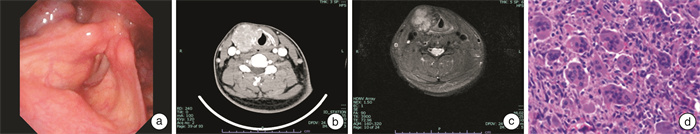
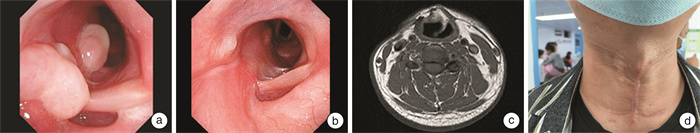
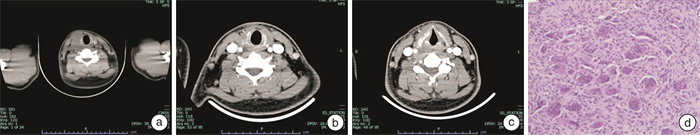
摘要: 原发于喉部的巨细胞肿瘤极为罕见,本文介绍了1例术后复发的喉巨细胞肿瘤(giant cell tumor of the larynx,GCTL)患者。男,28岁,2022年6月因甲状腺肿块接受了甲状腺全切手术,术后病理诊断为软组织巨细胞肿瘤。2023年6月因颈部肿物复发再次入院,行部分喉部分下咽切除术,完整切除肿瘤。依据术后病理、免疫组织化学(H3.3 G34W+)和基因检测等辅助检查结果,颈部肿物最终诊断为GCTL。患者未进行放化疗,术后12个月复诊,未见肿瘤复发表现。Abstract: Giant cell tumors originating in the larynx are extremely rare. This article presents a case of a recurrent postoperative giant cell tumor of the larynx(GCTL). The patient, a 28-year-old male, underwent a total thyroidectomy in June 2022 due to a thyroid mass. The postoperative pathological diagnosis was giant cell tumor of soft tissues. The patient was readmitted in June 2023 due to the recurrence of the neck mass and underwent partial laryngectomy and partial hypopharyngectomy to completely remove the tumor. Based on postoperative pathology, immunohistochemistry(H3.3 G34W+), and genetic testing, the neck mass was ultimately diagnosed as GCTL. The patient did not receive radiotherapy or chemotherapy, and at the 12-month postoperative follow-up, there was no evidence of tumor recurrence.
-
Key words:
- laryngeal carcinoma /
- giant cell tumor /
- recurrence
-

-
[1] 中华医学会骨科学分会骨肿瘤学组. 中国骨巨细胞瘤临床诊疗指南[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2018, 38(14): 833-840. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2352.2018.14.001
[2] Coyas A, Anastassiades OT, Kyriakos I. Malignant giant cell tumour of the larynx[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 1974, 88(8): 799-803. doi: 10.1017/S0022215100079378
[3] 来长荣, 李国璋. 甲状软骨巨细胞瘤一例[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 1992, 6(4): 219-219.
[4] 屈丽萍, 康战德, 张全忠, 等. 甲状软骨骨巨细胞瘤1例[J]. 陕西医学杂志, 1993, 22(11): 700-700.
[5] 何晓松. 甲状软骨骨巨细胞瘤1例[J]. 桂林医学院学报, 1994, 7(3): 38-38.
[6] 许元腾, 肖文惠, 杨劲松, 等. 喉巨细胞瘤1例[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2003, 17(3): 166-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1781.2003.03.035
[7] 王安群, 谢刚, 杨永红, 等. 喉巨细胞瘤的临床病理分析[J]. 华西医学, 2009, 24(2): 425-428.
[8] Arndt A, LeBlanc R, Spafford P. A large giant cell tumor of the larynx: case report and review of the literature[J]. Le J D'oto Rhino Laryngol De Chir Cervico Faciale, 2017, 46(1): 26.
[9] Acikalin RM, Özsan AV, Alimoglu Y, et al. Recurrence of giant cell tumor of the larynx[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2018, 29(3): e230-e232. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000004219
[10] 孟金丽, 何万林. 原发性甲状软骨骨巨细胞瘤恶变并累及甲状腺一例[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2018, 37(12): 2121-2122.
[11] Saud MRM, Salahuddin Z, Hassan A, et al. Laryngeal giant cell tumour presenting as a tongue base lesion causing severe dysphagia[J]. J Taibah Univ Med Sci, 2018, 13(2): 201-204.
[12] Zhang XR, Zhu XL, Li JN, et al. Fine needle aspiration of giant cell tumor involving thyroid gland: a case report of an unprecedented entity[J]. Diagn Cytopathol, 2018, 46(10): 879-882. doi: 10.1002/dc.24053
[13] Anandani GM, Yadav R, Verma H, et al. Giant cell tumor of thyroid cartilage: a diagnostic dilemma on aspiration cytology[J]. Diagn Cytopathol, 2021, 49(11): E423-E427.
[14] Kumar S, Sahni M, Bhatia K, et al. Management of giant cell tumor of the hyoid bone-a rare clinical entity with review of literature[J]. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2023, 75(4): 4232-4235. doi: 10.1007/s12070-023-04094-5
[15] Riaz UA, Wali H, Ansari SS, et al. A large, locally aggressive giant cell tumour arising from the laryngeal cartilage: a Rare Case Report[J]. J Pak Med Assoc, 2024, 74(6): 1167-1171. doi: 10.47391/JPMA.9173
[16] Creytens D. Expression of H3.3 G34W distinguishes giant cell tumor of bone from its major giant cell-containing bone and soft tissue mimics, in particular aneurysmal bone cyst and giant cell tumor of soft tissue[J]. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol, 2020, 28(5): e47-e48. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0000000000000636
[17] Gong LH, Bui MM, Zhang W, et al. H3F3A G34 mutation DNA sequencing and G34W immunohistochemistry analysis in 366 cases of giant cell tumors of bone and other bone tumors[J]. Histol Histopathol, 2021, 36(1): 61-68.
[18] Rekhi B, Dave V, Butle A, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of H3.3 G34W in 100 giant cell tumors of bone and its diagnostic mimics, including its value in resolving uncommon diagnostic scenarios: a single institutional study at a tertiary cancer referral center, India[J]. Indian J Pathol Microbiol, 2024, 67(3): 542-552. doi: 10.4103/ijpm.ijpm_886_23
[19] Sbaraglia M, Bellan E, Dei Tos AP. The 2020 WHO Classification of Soft Tissue Tumours: news and perspectives[J]. Pathologica, 2021, 113(2): 70-84.
[20] Tan XQ, Zhang Y, Wei DQ, et al. Denosumab for giant cell tumors of bone from 2010 to 2022: a bibliometric analysis[J]. Clin Exp Med, 2023, 23(7): 3053-3075. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01079-0
[21] Chen WH, Yan ZY, Tirumala V. Malignant giant cell tumor of bone or soft tissue treated by surgery with or without radiotherapy[J]. J Orthop Res, 2020, 38(10): 2139-2148. doi: 10.1002/jor.24698
[22] 黄志刚, 文卫平, 毛薇, 等. 头颈肿瘤的综合治疗策略[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(9): 673-690. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.09.001
-




 下载:
下载: