Application of internal carotid artery stent in glomus jugular paraganglioma surgery
-
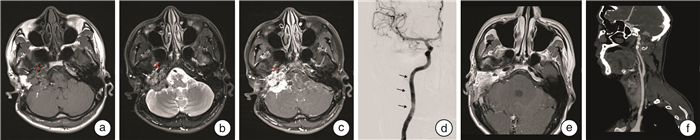
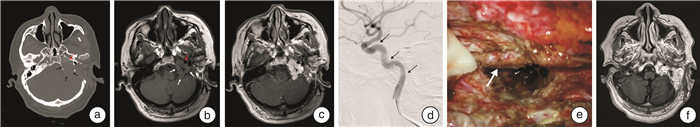
摘要: 目的 本文旨在总结颈内动脉支架在颈静脉球副神经节瘤手术中的应用,为降低颈内动脉损伤风险提供了有效的策略。方法 本文回顾了2018年6月至2022年12月采用颈内动脉支架的手术案例,并探讨了支架置入方法、治疗方案及围手术期的管理策略。结果 本研究共5例患者,术前根据MRI、颈动脉CT血管造影(CTA)及数字减影血管造影(DSA)等影像学技术,对颈内动脉受侵犯程度进行全面评估,显示所有患者颈内动脉均受到不同程度的累及。术前对所有患者行颈内动脉支架置入术,置入过程顺利,未发生颈内动脉损伤。支架置入后3个月行肿瘤全切或次全切除手术,术中避免了颈内动脉损伤,手术过程顺利完成。术后随访4个月~2年,支架置入后颈内动脉通畅,内皮化进程良好,未出现支架相关并发症。结论 对于颈静脉球副神经节瘤患者,若术前影像学显示颈内动脉受累,术前支架置入是一种安全有效的治疗策略,可加固动脉壁结构,保护并维持动脉完整性,降低手术过程中血管损伤的风险。本文总结了颈内动脉支架在颈静脉球副神经节瘤手术中的应用经验,为临床实践提供了重要参考。Abstract: Objective To summarize the application of internal carotid artery stent in glomus jugular paraganglioma surgery, and to provide an effective strategy for reducing the risk of internal carotid artery injury.Methods This article reviewed the surgical cases of internal carotid artery stent implanting from 2018.06 to 2022.12, and discussed the stent placement method, treatment protocols, and perioperative management strategies.Results A total of 5 patients underwent a comprehensive evaluation of the degree of internal carotid artery invasion using imaging techniques such as MRI, carotid CT angiography (CTA), and digital silhouette angiography (DSA). All patients were found to have varying degrees of internal carotid artery involvement. Stenting of the internal carotid artery was performed in all patients before surgery, and the stenting process went smoothly without any internal carotid artery injury. Three months after stenting, tumor resection or subtotal resection surgery was performed to avoid internal carotid artery injury during the surgery, and the surgical process was successfully completed. Postoperative follow-up from 4 months to 2 years showed that the internal carotid artery was patent after stent placement, with great endothelialization process and no stent-related complications.Conclusion In patients with glomus jugular paraganglioma, when preoperative imaging shows internal carotid artery involvement, preoperative stenting is a safe and effective therapeutic strategy to reinforce the arterial wall structure, protect and maintain the integrity of the artery, and reduce the risk of vascular injury during the surgery. This article summarizes the experience of internal carotid artery stent in glomus jugular paraganglioma surgery, which provides an important reference for clinical practice.
-

-
表 1 颈静脉球副神经节瘤患者的临床资料
例数 年龄/岁 性别 侧别 主要症状及体征 肿瘤分期 手术入路 颈内动脉受累节段 支架放置原因 放置支架 1 49 男 左 混合性聋、搏动性耳鸣、左侧周围性面瘫(面神经功能Ⅴ级)、饮水呛咳 改良Fisch C3Di1型 颞下窝A型+迷路 C1 颈内动脉局限节段血管壁狭窄、病变包绕颈内动脉周长超过180° Willis覆膜支架 2 62 男 左 感音神经性聋、搏动性耳鸣、左侧周围性面瘫(面神经功能Ⅲ级) 改良Fisch C4Di1型 颞下窝A型+迷路 C2~C4 颈内动脉局限节段血管壁狭窄、病变包绕颈内动脉周长超过180°、既往曾行手术治疗 Neuroform支架 3 28 男 右 感音神经性聋、搏动性耳鸣、右侧周围性面瘫(面神经功能Ⅴ级) 改良Fisch C4Di2型 颞下窝A型+迷路 C1~C2 颈内动脉局限节段血管壁狭窄、病变包绕颈内动脉周长超过180°、既往曾行手术治疗 LEO支架 4 63 女 右 传导性聋、声音嘶哑(右声带麻痹)、饮水呛咳 改良Fisch C3Di1型 颞下窝A型 C1~C2 颈内动脉局限节段血管壁狭窄、病变包绕颈内动脉周长超过180° LEO支架 5 56 女 左 感音神经性聋、搏动性耳鸣 改良Fisch C3Di2型 颞下窝A型+迷路 C1 颈内动脉局限节段血管壁欠规则、既往曾行手术治疗且肿瘤侵及部分脑组织 LEO支架 -
[1] Sanna M, Shin SH, de Donato G, et al. Management of complex tympanojugular paragangliomas including endovascular intervention[J]. Laryngoscope, 2011, 121(7): 1372-1382. doi: 10.1002/lary.21826
[2] Al-Mefty O, Teixeira A. Complex tumors of the Glomus jugulare: criteria, treatment, and outcome[J]. J Neurosurg, 2002, 97(6): 1356-1366. doi: 10.3171/jns.2002.97.6.1356
[3] Dharnipragada R, Butterfield JT, Dhawan S, et al. Modern management of complex tympanojugular paragangliomas: systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. World Neurosurg, 2023, 170: 149-156. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2022.11.037
[4] Fayad JN, Keles B, Brackmann DE. Jugular foramen tumors: clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2010, 31(2): 299-305. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e3181be6495
[5] Genç AL, Bicer A, Abacioglu U, et al. Gamma knife radiosurgery for the treatment of Glomus jugulare tumors[J]. J Neurooncol, 2010, 97(1): 101-108. doi: 10.1007/s11060-009-0002-6
[6] 李瑞, 杨润琴, 张昌明, 等. 以外耳道肉芽为临床体征的耳科疾病特点及诊疗分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(7): 501-505. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.07.004
[7] Fatima N, Pollom E, Soltys S, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for head and neck paragangliomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Neurosurg Rev, 2021, 44(2): 741-752. doi: 10.1007/s10143-020-01292-5
[8] Prasad SC, Mimoune HA, Khardaly M, et al. Strategies and long-term outcomes in the surgical management of tympanojugular paragangliomas[J]. Head Neck, 2016, 38(6): 871-885. doi: 10.1002/hed.24177
[9] Sanna M, Piazza P, de Donato G, et al. Combined endovascular-surgical management of the internal carotid artery in complex tympanojugular paragangliomas[J]. Skull Base, 2009, 19(1): 26-42. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1103126
[10] Sanna M, Khrais T, Menozi R, et al. Surgical removal of jugular paragangliomas after stenting of the intratemporal internal carotid artery: a preliminary report[J]. 2006, 116(5): 742-746.
[11] Chen G, Wu Q, Dai C. Management of complex jugular paragangliomas: surgical resection and outcomes[J]. J Int Adv Otol, 2022, 18(6): 488-494. doi: 10.5152/iao.2022.22675
[12] Jackson CG, McGrew BM, Forest JA, et al. Lateral skull base surgery forGlomustumors: long-term control[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2001, 22(3): 377-382. doi: 10.1097/00129492-200105000-00018
[13] Sanna M, Flanagan S. Surgical management of lesions of the internal carotid artery using a modified Fisch Type A infratemporal approach[J]. Otol Neurotol Off Publ Am Otol Soc Am Neurotol Soc Eur Acad Otol Neurotol, 2007, 28(7): 994.
[14] Andrews JC, Valavanis A, Fisch U. Management of the internal carotid artery in surgery of the skull base[J]. Laryngoscope, 1989, 99(12): 1224-1229. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198912000-00003
[15] Miyazaki S, Fukushima T, Fujimaki T. Resection of high-cervical paraganglioma with cervical-to-petrous internal carotid artery saphenous vein bypass. Report of two cases[J]. J Neurosurg, 1990, 73(1): 141-146. doi: 10.3171/jns.1990.73.1.0141
[16] Shin SH, Piazza P, de Donato G, et al. Management of vagal paragangliomas including application of internal carotid artery stenting[J]. Audiol Neurootol, 2012, 17(1): 39-53. doi: 10.1159/000329213
[17] Galego O, Nunes C, Morais R, et al. Monitoring balloon test occlusion of the internal carotid artery with transcranial Doppler. A case report and literature review[J]. Neuroradiol J, 2014, 27(1): 115-119. doi: 10.15274/NRJ-2014-10014
[18] Bacciu A, Prasad SC, Sist N, et al. Management of the cervico-petrous internal carotid artery in class C tympanojugular paragangliomas[J]. Head Neck, 2016, 38(6): 899-905. doi: 10.1002/hed.24284
[19] Piazza P, di Lella F, Bacciu A, et al. Preoperative protective stenting of the internal carotid artery in the management of complex head and neck paragangliomas: long-term results[J]. Audiol Neurootol, 2013, 18(6): 345-352. doi: 10.1159/000354158
[20] Nussbaum ES, Levine SC, Hamlar D, et al. Carotid stenting and"extarterectomy"in the management of head and neck cancer involving the internal carotid artery: technical case report[J]. Neurosurgery, 2000, 47(4): 981-984. doi: 10.1097/00006123-200010000-00041
[21] Briggs R. Atlas of microsurgery of the lateral skull base, 2nd edition[J]. ANZ J Surg, 2009, 79(9): 657.
[22] Markiewicz MR, Pirgousis P, Bryant C, et al. Preoperative protective endovascular covered stent placement followed by surgery for management of the cervical common and internal carotid arteries with tumor encasement[J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base, 2017, 78(1): 52-58.
[23] Shobayashi Y, Tanoue T, Tateshima S, et al. Mechanical design of an intracranial stent for treating cerebral aneurysms[J]. Med Eng Phys, 2010, 32(9): 1015-1024. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2010.07.002
[24] Toyota N, Pavcnik D, VanAlstine W, et al. Comparison of small intestinal submucosa-covered and noncovered nitinol stents in sheep iliac arteries: a pilot study[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2002, 13(5): 489-498. doi: 10.1016/S1051-0443(07)61529-2
[25] Cejna M, Virmani R, Jones R, et al. Biocompatibility and performance of the Wallstent and the Wallgraft, Jostent, and Hemobahn stent-grafts in a sheep model[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2002, 13(8): 823-830. doi: 10.1016/S1051-0443(07)61992-7
[26] Ozaki S, Tagawa M, Matsumoto S, et al. Pathogenesis of in-stent thrombosis after carotid artery stenting[J]. No Shinkei Geka, 2014, 42(11): 1009-1017.
-




 下载:
下载: