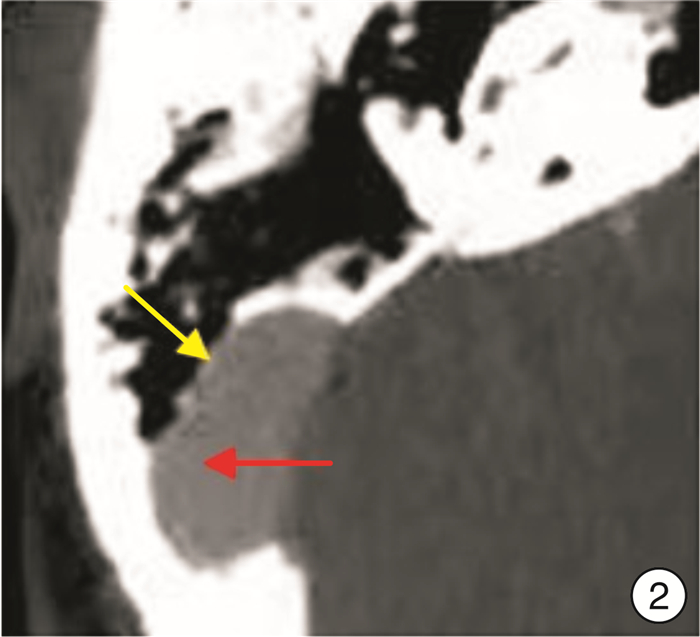
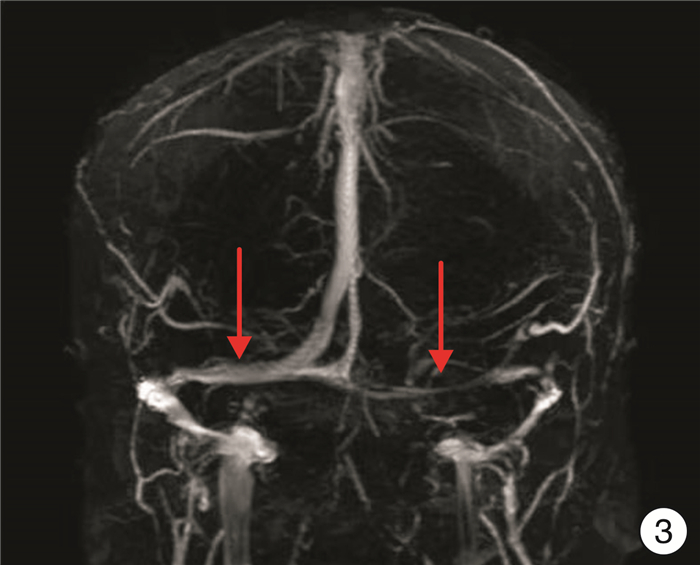
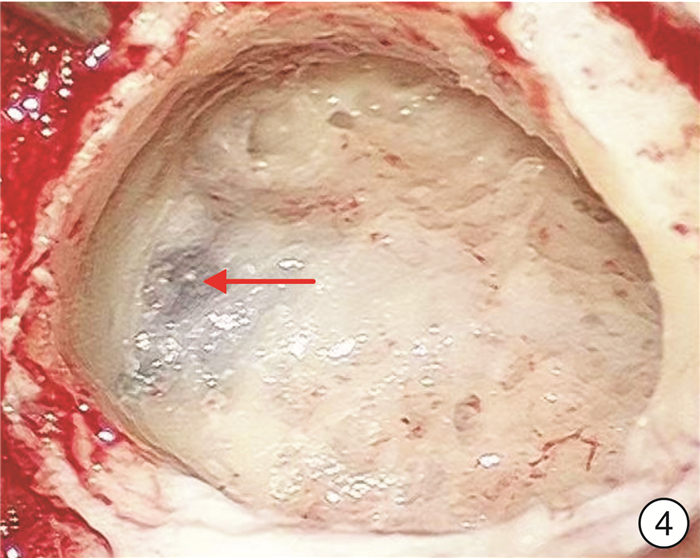
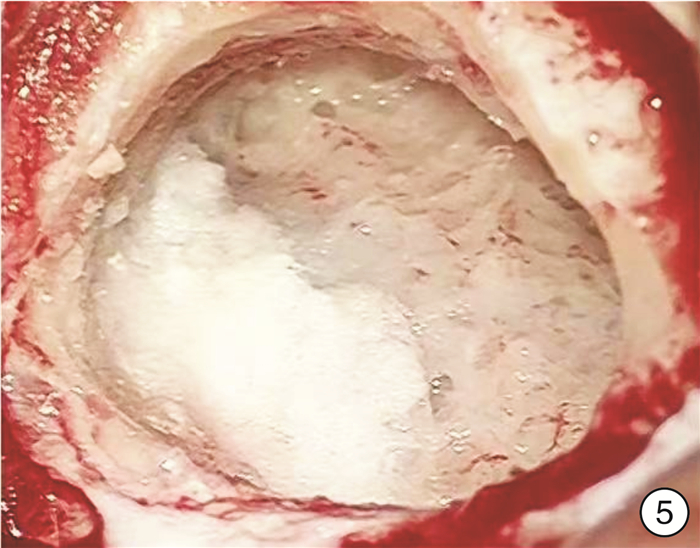
Surgical technique and effect of the pulsatile tinnitus associated with sigmoid sinus on the dominant side of reflux
-
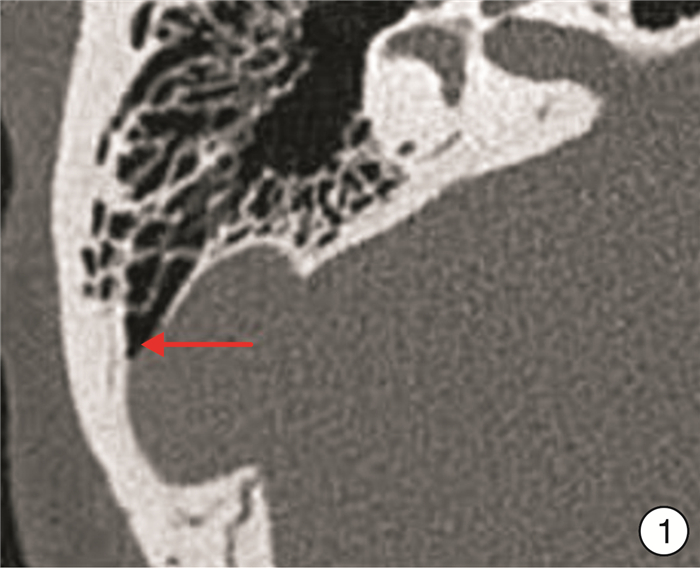
摘要: 目的 探讨回流优势侧乙状窦相关性搏动性耳鸣的临床外科技术及疗效。方法 回顾性研究2017年1月-2023年11月由同一位医生收治的43例回流优势侧搏动性耳鸣患者的临床资料,观察手术治疗的疗效。术式:应用“盖帽法”乙状窦骨壁缺损修复技术建立隔声屏障,不改变乙状窦血管壁和血流流变状态。结果 所有患者均未出现手术并发症。随访3个月~6.9年,43例患者痊愈14例(32.6%),显效18例(41.9%),有效4例(9.3%),无效7例(16.3%),手术前后耳鸣分级的差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 应用“盖帽法”乙状窦骨壁缺损修复技术建立隔声屏障,有效地规避了对血液流变学状态及血管壁的干扰,从而避免了优势回流侧静脉管壁狭窄及血栓形成的风险,手术方法容易掌握,疗效显著,值得临床推广。Abstract: Objective To explore the effect of surgical treatment of the pulsatile tinnitus associated with sigmoid sinus on the dominant side of reflux.Methods The clinical data of 43 patients with reflux dominant side pulsating tinnitus admitted by the same doctor from 2017 to 2023 were retrospectively studied to observe the curative effect of surgical treatment. Operation method: The sound insulation barrier was established by repair technique of bone wall defect of sigmoid sinus with "capping method", without changing the blood flow and blood vessel wall of sigmoid sinus.Results No surgical complications occurred in all patients. During the follow-up period of 3 months to 6.9 years, 14 patients(32.6%) were cured, 18 patients(41.9%) were significantly effective, 4 patients(9.3%) were effective, and 7 patients(16.3%) were ineffective. The difference of tinnitus grade before and after surgery was statistically significant.Conclusion In this group of cases, the sound insulation barrier was established by "capping method" technique of repairing bone wall defect of sigmoid sinus, which effectively avoided the disturbance of hemorheology status and vascular wall, thus avoiding the risk of venous wall stenosis and thrombosis on the dominant reflux side. The surgical method was easy to master, and the curative effect was significant, which was worthy of clinical promotion.
-
Key words:
- dominant side of reflux /
- sigmoid sinus /
- pulsatile tinnitus
-

-
[1] 余力生, 杨仕明, 王秋菊, 等. 耳鸣的诊断与治疗[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(5): 325-334. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.05.001
[2] 黄选兆, 汪吉宝, 孔维佳. 实用耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2008: 1039-1040.
[3] Wang GP, Zeng R, Ma XB, et al. Surgical treatment of pulsatile tinnitus caused by the sigmoid sinus diverticulum: a preliminary study[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2015, 94(21): e882.
[4] 彭佳丽, 赵蓉, 李格飞, 等. 乙状窦憩室致搏动性耳鸣的介入治疗成功案例报道[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2016, 36(12): 1820-1822. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHEY201612040.htm
[5] Schoeff S, Nicholas B, Mukherjee S, et al. Imaging prevalence of sigmoid sinus dehiscence among patients with and without pulsatile tinnitus[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2014, 150(5): 841-846. doi: 10.1177/0194599813520291
[6] 王振常, 罗德红, 沙炎, 等. 搏动性耳鸣影像学检查方法与路径指南[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2013, 93(33): 2611-2612.
[7] 刘蓬. 耳鸣程度分级与疗效评定标准的探讨[J]. 中国中西医结合耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2004, 12(4): 181-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYJH200404004.htm
[8] Wang AC, Nelson AN, Pino C, et al. Management of Sigmoid Sinus Associated Pulsatile Tinnitus: A Systematic Review of the Literature[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2017, 38(10): 1390-1396.
[9] 郭平, 王武庆. 乙状窦缩窄术治疗乙状窦相关静脉源性搏动性耳鸣的疗效分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2013, 48(4): 265-269.
[10] 周腊梅, 李轩毅, 李红权, 等. 乙状窦还纳术治疗搏动性耳鸣及特殊病例分析[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2021, 19(6): 890-893. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHER202106003.htm
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 350
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: