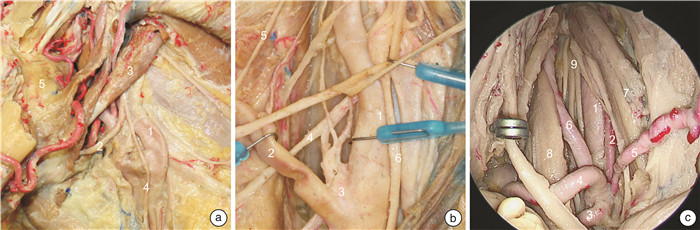
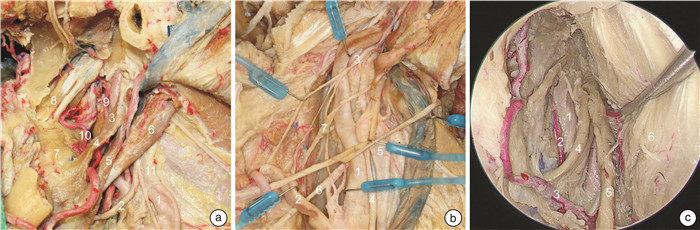
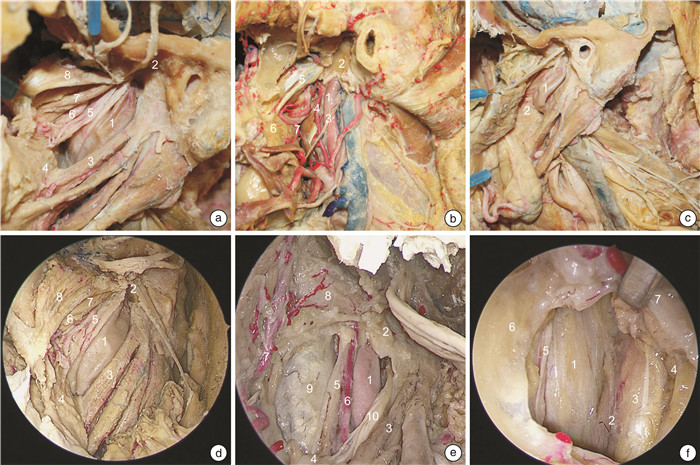
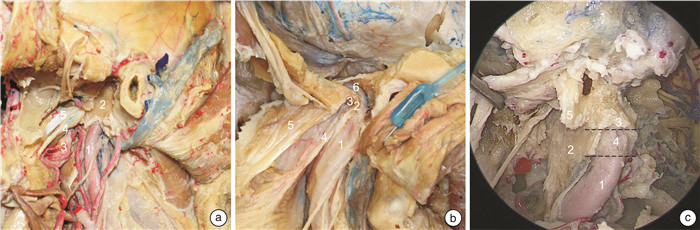
An anatomical road map of the parapharyngeal internal carotid artery in lateral and endoscopic ventral approaches
-
摘要: 目的 描述外侧入路和内镜腹侧入路咽旁段颈内动脉的解剖路图,提出亚分段方案,系统全面地理解该段动脉解剖以及其与周围结构的毗邻关系。方法 对5例(共10侧)新鲜尸头标本分别进行外侧入路和内镜腹侧入路解剖对照,评估咽旁段颈内动脉解剖及毗邻关系。结果 自颈总动脉分叉到颈内动脉管后垂直部,顺血流方向,咽旁段颈内动脉穿行通过4种截然不同的解剖组织,据此,该段颈内动脉可以划分为神经段、肌肉段、筋膜段、骨段4个亚分段。每个亚分段的边界和毗邻的重要解剖结构被详细描述。结论 咽旁段颈内动脉的解剖路图描述和亚分段方案,为降低颈内动脉损伤风险,模块化开展经外侧和内镜腹侧入路咽旁间隙等颅底手术,提供了应用解剖学依据。Abstract: Objective To describe the road map of the lateral and endoscopic ventral approaches for the pharyngeal segment of the internal carotid artery, propose a sub-segmentation scheme, systematically and comprehensively understand its anatomical details and relationships with the surrounding structures.Methods Five fresh cadaveric head specimens(10 sides in total) were dissected through lateral and endoscopic ventral approaches to evaluate the anatomical details of the parapharyngeal internal carotid artery and its relationship with the surrounding structures.Results From the bifurcation of the common carotid artery to the vertical part of the internal carotid artery, alongside the direction of blood flow, the parapharyngeal internal carotid artery passes through four distinct anatomical tissues. Based on this, the parapharyngeal internal carotid artery can be divided into four sub-segments: nerve, muscle, fascia and osseous sub-segments. The boundaries and important adjacent structures of each segment are described in detail.Conclusion The anatomical road map of the parapharyngeal internal carotid artery and the sub-segmentation scheme serving as a practical guide to navigate modular endoscopic skull base surgery of the parapharyngeal space while reduce the risk of internal carotid artery injury.
-

-
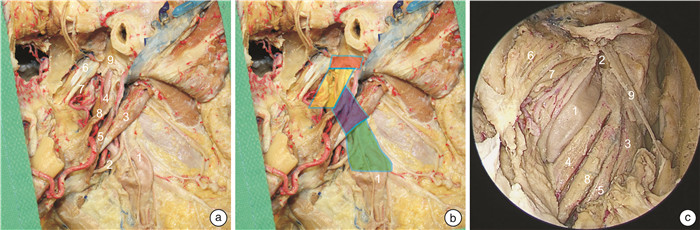
表 1 咽旁段颈内动脉亚分段边界、重要毗邻及内镜显露能力
ppICA亚分段 上界 紧贴颈鞘的重要毗邻解剖结构 内镜显露能力 神经段 二腹肌后腹下缘 舌下神经和颈襻上根;颈动脉窦颈动脉体的支配神经;喉上神经的内外支;颈外动脉及其分支 经口、经鼻均显露困难 肌肉段 茎突咽肌上缘 茎突诸肌和二腹肌;舌下神经和咽丛;舌咽、迷走神经、颈交感干及其交通支 经口显露全程经鼻显露困难 筋膜段 鼓骨鞘突下缘 “咽旁段颈内动脉窗”;咽升动脉及其分支;迷走、副神经和颈交感干 经口、经鼻均可显露全程 骨段 鼓骨前嵴下缘 颈动脉管入口的骨性解剖标记、腭帆提肌附着点、咽升动脉分支;颈交感神经 经口显露困难经鼻显露全程 -
[1] Locketz GD, Horowitz G, Abu-Ghanem S, et al. Histopathologic classification of parapharyngeal space tumors: a case series and review of the literature[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 273(3): 727-734. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3545-5
[2] Sun X, Yan B, Truong HQ, et al. A Comparative Analysis of Endoscopic-Assisted Transoral and Transnasal Approaches to Parapharyngeal Space: A Cadaveric Study[J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base, 2018, 79(3): 229-240. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1606551
[3] Kuet ML, Kasbekar AV, Masterson L, et al. Management of tumors arising from the parapharyngeal space: A systematic review of 1, 293 cases reported over 25 years[J]. Laryngoscope, 2015, 125(6): 1372-1381. doi: 10.1002/lary.25077
[4] Perry A, Graffeo CS, Meyer J, et al. Beyond the Learning Curve: Comparison of Microscopic and Endoscopic Incidences of Internal Carotid Injury in a Series of Highly Experienced Operators[J]. World Neurosurg, 2019, 131: e128-e135. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.07.074
[5] Labib MA, Prevedello DM, Carrau R, et al. A road map to the internal carotid artery in expanded endoscopic endonasal approaches to the ventral cranial base[J]. Neurosurgery, 2014, 10 Suppl 3: 448-471.
[6] Ozgur Z, Celik S, Govsa F, et al. A study of the course of the internal carotid artery in the parapharyngeal space and its clinical importance[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2007, 264(12): 1483-1489. doi: 10.1007/s00405-007-0398-6
[7] Bouthillier A, van Loveren HR, Keller JT. Segments of the internal carotid artery: a new classification[J]. Neurosurgery, 1996, 38(3): 425-432.
[8] DePowell JJ, Froelich SC, Zimmer LA, et al. Segments of the internal carotid artery during endoscopic transnasal and open cranial approaches: can a uniform nomenclature apply to both?[J]. World Neurosurg, 2014, 82(6 Suppl): S66-71.
[9] AlQahtani A, Castelnuovo P, Nicolai P, et al. Injury of the Internal Carotid Artery During Endoscopic Skull Base Surgery: Prevention and Management Protocol[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2016, 49(1): 237-252. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2015.09.009
[10] Li W, Chae R, Rubio RR, et al. Characterization of Anatomical Landmarks for Exposing the Internal Carotid Artery in the Infratemporal Fossa Through an Endoscopic Transmasticator Approach: A Morphometric Cadaveric Study[J]. World Neurosurg, 2019, 131: e415-e424. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.07.185
[11] Komune N, Matsuo S, Nakagawa T. The Fascial Layers Attached to the Skull Base: A Cadaveric Study[J]. World Neurosurg, 2019, 126: e500-e509. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.02.078
[12] Maheshwar AA, Kim EY, Pensak ML, et al. Roof of the parapharyngeal space: defining its boundaries and clinical implications[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2004, 113(4): 283-288. doi: 10.1177/000348940411300405
[13] Paulsen F, Tillmann B, Christofides C, et al. Curving and looping of the internal carotid artery in relation to the pharynx: frequency, embryology and clinical implications[J]. J Anat, 2000, 197 Pt 3(Pt 3): 373-381.
[14] Chengazi HU, Bhatt AA. Pathology of the carotid space[J]. Insights Imaging, 2019, 10(1): 21. doi: 10.1186/s13244-019-0704-z
[15] Tsang RK, Sorger JM, Azizian M, et al. Real-time navigation in transoral robotic nasopharyngectomy utilizing on table fluoroscopy and image overlay software: a cadaveric feasibility study[J]. J Robot Surg, 2015, 9(4): 311-314. doi: 10.1007/s11701-015-0532-1
[16] Amene C, Cosetti M, Ambekar S, et al. Johann Christian Rosenmüller(1771-1820): A Historical Perspective on the Man behind the Fossa[J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base, 2013, 74(4): 187-193. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1342927
[17] Fang X, Di G, Zhou W, et al. The anatomy of the parapharyngeal segment of the internal carotid artery for endoscopic endonasal approach[J]. Neurosurg Rev, 2020, 43(5): 1391-1401. doi: 10.1007/s10143-019-01176-3
[18] Wang C, Kundaria S, Fernandez-Miranda J, et al. A description of the anatomy of the glossopharyngeal nerve as encountered in transoral surgery[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126(9): 2010-2015. doi: 10.1002/lary.25706
[19] Sreenath SB, Rawal RB, Zanation AM. The combined endonasal and transoral approach for the management of skull base and nasopharyngeal pathology: a case series[J]. Neurosurg Focus, 2014, 37(4): E2. doi: 10.3171/2014.7.FOCUS14353
[20] 陈晓红. 经口内镜翼下颌韧带旁内进路咽旁间隙肿瘤切除的技巧和风险控制[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(9): 710-714. https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=1g3u0vt0tk4r02p07p5m0ax0rp667597&site=xueshu_se&hitarticle=1
[21] Davis L, Zeitouni A, Makhoul N, et al. Surgical Exposure to Control the Distal Internal Carotid Artery at the Base of the Skull during Carotid Aneurysm Repair[J]. Ann Vasc Surg, 2016, 34: 268. e5-8. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2015.11.016
[22] Froelich SC, Abdel Aziz KM, Levine NB, et al. Exposure of the distal cervical segment of the internal carotid artery using the trans-spinosum corridor: cadaveric study of surgical anatomy[J]. Neurosurgery, 2008, 62(5 Suppl 2): ONS354-361;discussion ONS361-362.
[23] Cairney J. Tortuosity of the Cervical Segment of the Internal Carotid Artery[J]. J Anat, 1924, 59(Pt 1): 87-96.
[24] Wang X, Gong S, Lu Y, et al. Endoscopy-assisted transoral resection of parapharyngeal space tumors: a retrospective analysis[J]. Cell Biochem Biophys, 2015, 71(2): 1157-1163. doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-0323-8
-




 下载:
下载: