Cochlear implantation through retro-facial approach with congenital microtia malformation with facial nerve deformity: a case report
-
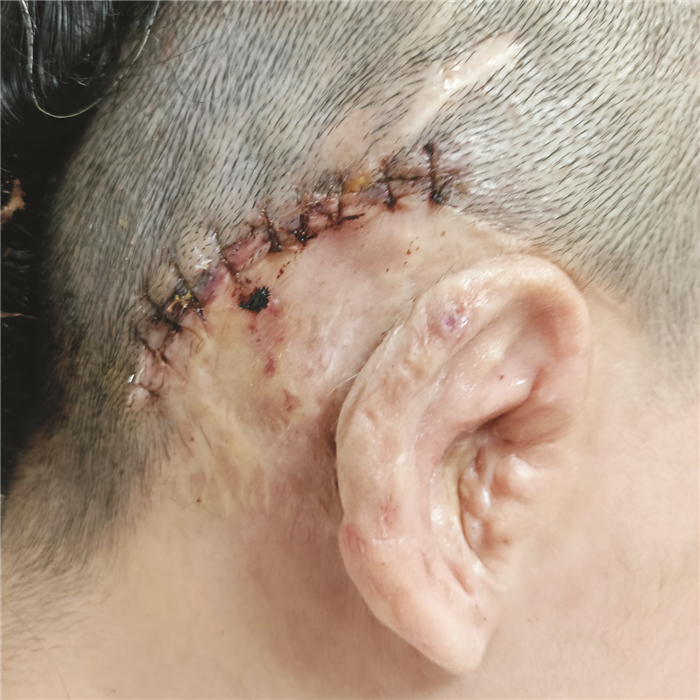
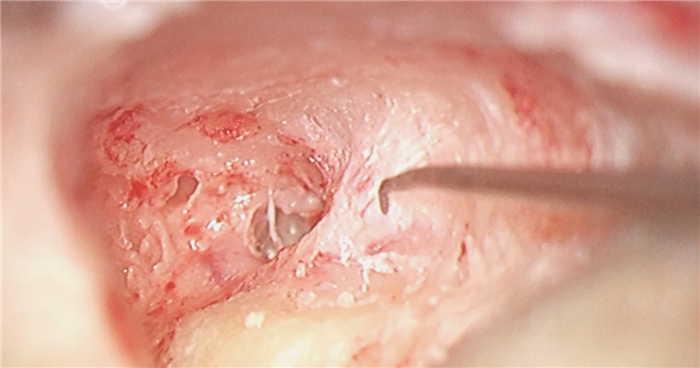
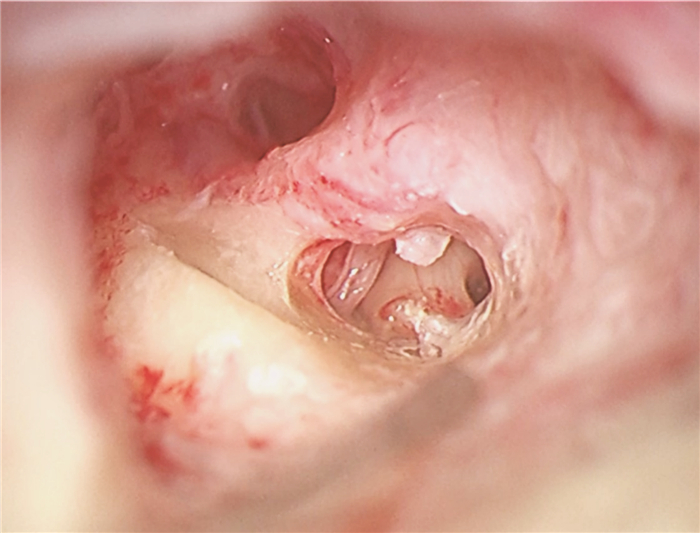
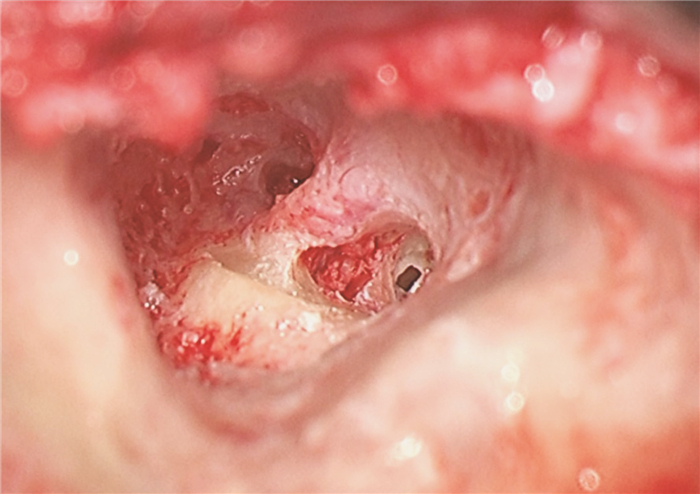
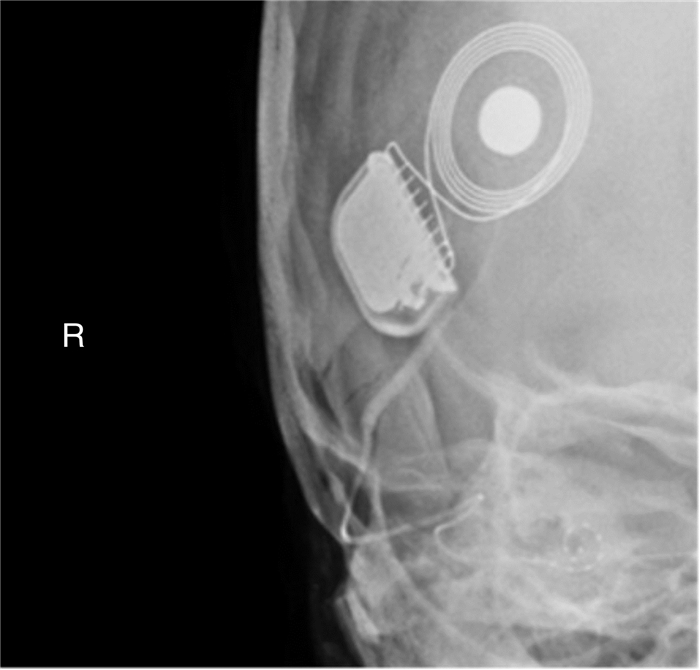
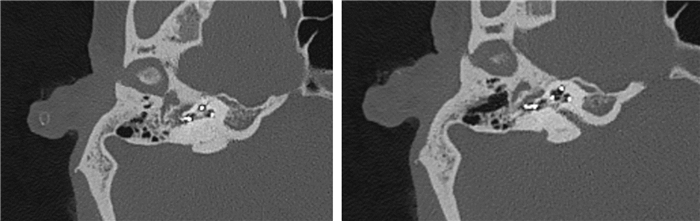
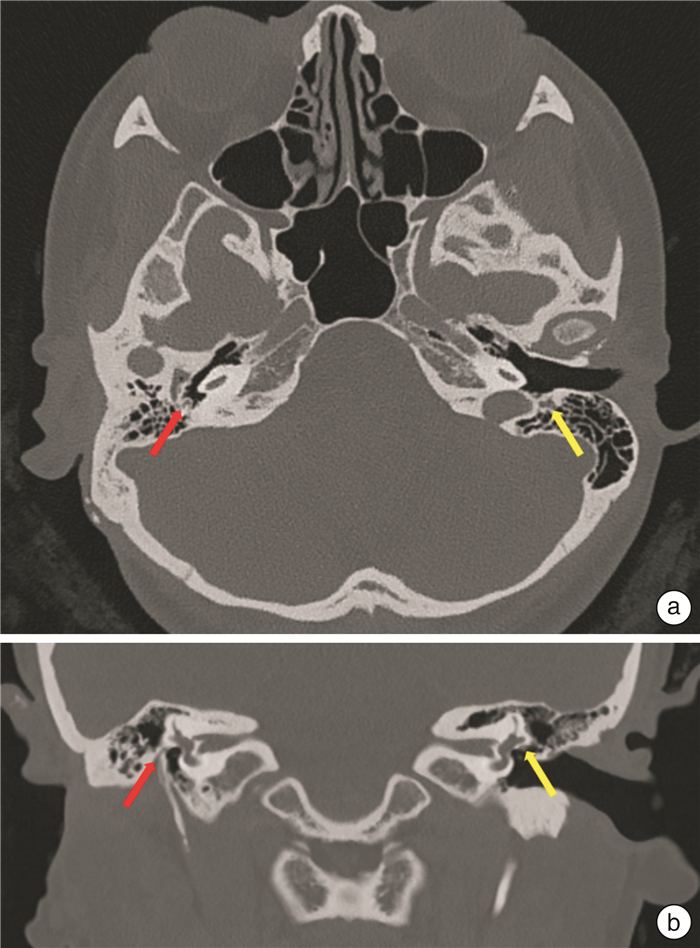
摘要: 先天性小耳畸形患者行人工耳蜗植入时通常因为解剖标识不清、面神经畸形使手术难度增加。面神经畸形的常见类型有面神经骨管缺失、面神经走行异常及面神经分叉畸形。面神经分叉畸形可能导致面神经遮蔽卵圆窗挤压镫骨、面神经于前庭窗分叉或遮蔽圆窗,正确识别面神经,选择合理的手术径路对于避免术后并发症有重要意义。本文介绍1例在我中心治疗的先天性外中耳畸形合并面神经畸形极重度感音神经性聋患者,行面后径路人工耳蜗植入手术,植入过程顺利,术后定期开机,按时调机。术后2年无面瘫、面肌痉挛等面神经损伤或功能异常症状,人工耳蜗正常使用。经听觉行为分级(CAP)问卷评分7分,言语可懂度分级(SIR)问卷评分4分。人工耳蜗植入术中无法经面隐窝入路暴露圆窗时,面后径路是可行手段,在为面神经畸形患者行中、内耳手术时,为避免出现面神经损伤可在术前完善颞骨薄层CT明确面神经走行,采用术中面神经监测仪明确神经形态,避免损伤面神经。Abstract: The difficulty of cochlear implantation in patients with congenital microtia is usually increased due to the vague anatomical marks and facial nerve malformation. The common types of facial nerve malformation include facial nerve bony cover loss, aberrant position, and bifurcation malformation. Bifurcation malformation may obscure the oval window, press against stapes, and bifurcate in the vestibular window while obscuring the round window. It is important to correctly identify the facial nerve and choose a reasonable surgical approach to avoid postoperative complications. This article describes a case of profound sensorineural hearing loss due to facial nerve malformation in our institution. The patient underwent cochlear implantation through the retro-facial approach. There was no facial nerve injury or dysfunction symptoms such as facial paralysis and hemifacial spasm 2 years after the operation, and the cochlear implant works well. The score of the categories of the auditory performance(CAP) questionnaire was 7, and the score of the speech intelligibility rating(SIR) questionnaire was 4. When the round window cannot be exposed through the facial recess approach during surgery, the retro-facial approach is a feasible method. To avoid facial nerve injury, a thin-section CT of the temporal bone should be performed before the middle and inner ear surgery for patients with facial nerve malformation, and the intraoperative facial nerve monitor should be used to clarify the course of the facial nerve to avoid injury.
-
Key words:
- microtia /
- facial nerve malformation /
- retro-facial approach /
- cochlear implant
-

-
[1] 张天宇, 陈鑫, 傅窈窈. 先天性外中耳畸形(4)——面神经畸形研究进展[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2019, 27(2): 230-232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2019.02.031
[2] Jahrsdoerfer RA. Embryology of the facial nerve[J]. Am J Otol, 1988, 9(5): 423-426.
[3] Stratigouleas ED, Perry BP, King SM, et al. Complication rate of minimally invasive cochlear implantation[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2006, 135(3): 383-386. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2006.03.023
[4] Ikeya J, Kawano A, Nishiyama N, et al. Long-term complications after cochlear implantation[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2013, 40(6): 525-529. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2013.04.012
[5] Song JJ, Park JH, Jang JH, et al. Facial nerve aberrations encountered during cochlear implantation[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2012, 132(7): 788-794. doi: 10.3109/00016489.2012.656765
[6] Kronenberg J, Migirov L, Dagan T. Suprameatal approach: new surgical approach for cochlear implantation[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2001, 115(4): 283-285.
[7] Li J, Zhao S, Yang L, et al. Preoperative evaluation and intraoperative protection of the facial nerve in congenital aural atresia[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2017, 96(12): E38-E43.
[8] 马晓波, 赵守琴, 李洁, 等. 正常耳颞骨内面神经形态分析[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2015, 22(6): 287-289. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201506010.htm
[9] 迟放鲁, 黄一波, 靳楷, 等. 面神经畸形的影像表现[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2011, 9(2): 124-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHER201102006.htm
[10] Verzijl HT, Valk J, de Vries R, et al. Radiologic evidence for absence of the facial nerve in Möbius syndrome[J]. Neurology, 2005, 64(5): 849-855. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000152980.92436.D9
[11] Sasaki M, Imamura Y, Sato N. Magnetic resonance imaging in congenital facial palsy[J]. Brain Dev, 2008, 30(3): 206-210. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2007.07.014
[12] 杨蓓蓓. 面神经监护在耳显微外科中的应用[C]//浙江省医学会耳鼻咽喉科学分会. 2014年浙江省医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学学术年会论文汇编. 2014: 1.
[13] Huang CC, Lin CY, Wu JL. Retrofacial approach of cochlear implantation in inner ear malformation with aberrant facial nerve: a case report[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2006, 33(2): 179-182.
[14] Allen KP, Bartels LJ, Isaacson B. Cochlear implantation requiring a retrofacial approach to the round window[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2015, 36(3): e84-e86. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000000687
[15] Yilmazer R, Gerring RC, Sidani C, et al. The Feasibility of Retrofacial Approach for Cochlear Implantation[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2018, 39(7): e550-e556. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001878
[16] Svrakic M, Friedmann DR, Berman PM, et al. Measurement of Cochlear Implant Electrode Position From Intraoperative Post-insertion Skull Radiographs: A Validation Study[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2015, 36(9): 1486-1491.
[17] Yuan YY, Song YS, Chai CM, et al. Intraoperative CT-guided cochlear implantation in congenital ear deformity[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2012, 132(9): 951-958. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/22668345
[18] Bloom JD, Rizzi MD, Germiller JA. Real-time intraoperative computed tomography to assist cochlear implant placement in the malformed inner ear[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2009, 30(1): 23-26.
[19] 张帆, 卢星, 张文静, 等. 术中CT辅助定位在疑难病例人工耳蜗植入术中的应用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(5): 329-333. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.05.002
[20] Guntinas-Lichius O, Arnold D, Volk GF, et al. Accessing the stapedius muscle via novel surgical retrofacial approach during cochlear implantation surgery: Intraoperative results on feasibility and safety[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(8): e0272943.
[21] Volk GF, Aschenbach R, Gadyuchko M, et al. Dyna-CT of the temporal bone for case-specific three-dimensional rendering of the stapedial muscle for planning of electrically evoked stapedius reflex threshold determination during cochlear implantation directly from the stapedius muscle via a retrofacial approach: a pilot study[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 277(4): 975-985.
-




 下载:
下载: