Clinical study of ear keloids with surgical excision and intraoperative low-energy X-ray irradiation therapy
-
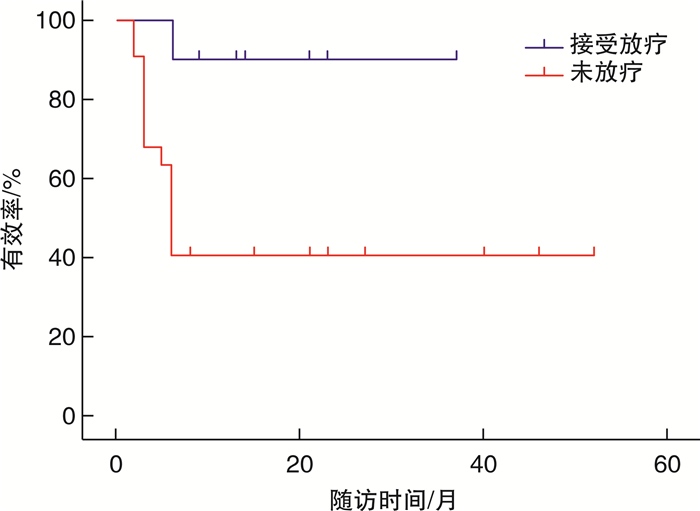
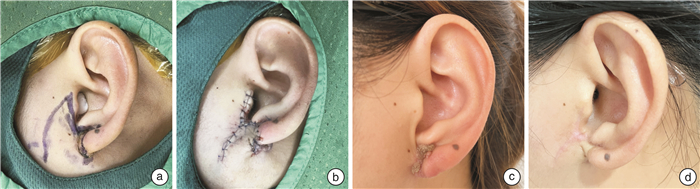
摘要: 目的 探讨手术切除联合术中低能X射线照射治疗耳部瘢痕疙瘩的临床疗效。方法 回顾性分析2019年3月—2022年11月在天津市第一中心医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科接受单纯手术治疗或手术联合放射治疗的32例耳部瘢痕疙瘩病灶的临床资料。其中接受放疗10例,未接受放疗22例。放疗组接受大分割剂量50 kV低能X射线进行照射。分割方式为:第1次于术中放疗10 Gy,第2次于术后第3天放疗8 Gy,总量18 Gy。随访8~52个月,观察其局部疗效及皮肤放射反应。结果 中位随访26个月,截止最后一次随访日期,放疗组9例治愈,1例无效,有效率90%;未放疗组9例治愈,13例无效,有效率40.9%。耳部瘢痕疙瘩的复发与患者发病的侧别、部位、病因均无关(P>0.05)。复发与是否接受放疗有关(χ2=4.885,P<0.05),放疗组的复发率(10.0%)明显低于未放疗组(59.1%)。结论 手术切除联合低能X射线照射是治疗耳部瘢痕疙瘩的一种有效方法,尤其是采用术中放疗可取得较为满意的疗效。Abstract: Objective To explore the clinical efficacy of surgical excision combined with low-energy X-ray irradiation in the treatment of ear keloids.Methods Clinical data of 32 cases of ear keloid lesions that received surgical treatment alone or surgery combined with radiotherapy from March 2019 to November 2022 in the Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery of the Tianjin First Central Hospital were retrospectively analyzed. Among them, 10 cases received radiotherapy and 22 cases did not receive radiotherapy. The radiotherapy group received irradiation with a large divided dose of 50 kV low-energy X-rays. The mode of fractionation radiotherapy was as follows: the first was 10 Gy of intraoperative radiation therapy and the second was 8 Gy on the 3rd postoperative day for a total of 18 Gy. The local efficacy and skin radiation reaction were observed at a follow-up of 8-52 months.Results The median follow-up was 26 months, and as of the date of the last follow-up, 9 cases were cured and 1 case was ineffective in the radiotherapy group, with an effective rate of 90.0%, while 9 cases were cured and 13 cases were ineffective in the no-radiotherapy group, with an effective rate of 40.9%. The recurrence of ear keloids was not related to the side, site, or etiology of the patient's onset(P>0.05). Recurrence was related to whether or not the patients received radiotherapy(χ2=4.885, P < 0.05), and the recurrence rate in the radiotherapy group(10.0%) was significantly lower than that in the non-radiotherapy group(59.1%).Conclusion Surgical excision combined with low-energy X-ray irradiation therapy is an effective method of treating keloids in the ear, especially with intraoperative radiation therapy can achieve more satisfactory results.
-
Key words:
- ear keloid /
- radiotherapy /
- intraoperative radiation therapy
-

-
表 1 耳部瘢痕疙瘩患者治疗后复发情况
项目 例数 复发/例(%) χ2 P 性别 2.930 0.087 男 6 5(83.3) 女 26 9(34.6) 侧别 0.000 1.000 左 18 8(44.4) 右 14 6(42.9) 部位 5.206 0.157 耳垂 10 4(40.0) 耳轮 15 6(40.0) 耳后 5 4(80.0) 舟状窝 2 0(0) 病因 2.397 0.494 打耳洞 20 8(40.0) 外伤 4 2(50.0) 手术 4 3(75.0) 原因不详 4 1(25.0) 是否放疗 4.885 <0.05 是 10 1(10.0) 否 22 13(59.1) -
[1] Ghazawi FM, Zargham R, Gilardino MS, et al. Insights into the Pathophysiology of Hypertrophic Scars and Keloids: How Do They Differ?[J]. Adv Skin Wound Care, 2018, 31(1): 582-595. doi: 10.1097/01.ASW.0000527576.27489.0f
[2] Al-Attar A, Mess S, Thomassen JM, et al. Keloid pathogenesis and treatment[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2006, 117(1): 286-300. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000195073.73580.46
[3] 朱莲花, 李美玲, 李周娜, 等. 瘢痕疙瘩发病机制的研究[J]. 中国皮肤性病学杂志, 2017, 31(5): 560-562. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZBFX201705035.htm
[4] 中国整形美容协会瘢痕医学分会常务委员会专家组. 中国瘢痕疙瘩临床治疗推荐指南[J]. 中国美容整形外科杂志, 2018, 29(5): 245-256. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SMZW201805002.htm
[5] Kim K, Son D, Kim J. Radiation Therapy Following Total Keloidectomy: A Retrospective Study over 11 Years[J]. Arch Plast Surg, 2015, 42(5): 588-595. doi: 10.5999/aps.2015.42.5.588
[6] Shin JY, Lee JW, Roh SG, et al. A Comparison of the Effectiveness of Triamcinolone and Radiation Therapy for Ear Keloids after Surgical Excision: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2016, 137(6): 1718-1725. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000002165
[7] Calvo FA. Intraoperative irradiation: precision medicine for quality cancer control promotion[J]. Radiat Oncol, 2017, 12(1): 36. doi: 10.1186/s13014-017-0764-5
[8] 蔡景龙. 瘢痕整形美容外科学[M]. 浙江: 浙江科学技术出版社, 2015: 20-24, 646-647.
[9] Yamawaki S, Naitoh M, Ishiko T, et al. Keloids can be forced into remission with surgical excision and radiation, followed by adjuvant therapy[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 2011, 67(4): 402-406. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e31820d684d
[10] 李晶晶, 刘暾. 耳垂瘢痕疙瘩的机制探讨及治疗进展[J]. 中国美容整形外科杂志, 2020, 31(11): 658-661. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SMZW202011010.htm
[11] 毛学飞, 刘坤, 潘晓峰, 等. 瘢痕疙瘩综合疗法的治疗效果[J]. 中华医学美学美容杂志, 2017, 23(5): 328-331.
[12] 张芳, 杨博, 杜莉, 等. 应用手术联合术后放疗治疗耳廓瘢痕疙瘩的疗效分析[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2018, 25(8): 435-438. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201808011.htm
[13] 曲春安, 刘悦, 王晓雨, 等. 病理性瘢痕治疗研究新进展[J]. 中国美容整形外科杂志, 2017, 28(10): 639-640. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SMZW201710023.htm
[14] Bautista Hernandez Y, Villavicencio Queijero MA, Quezada Bautista AA, et al. Surface brachytherapy in the treatment of keloid scars in Mexico[J]. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother, 2020, 25(1): 133-138. doi: 10.1016/j.rpor.2019.11.002
[15] Rei Ogawa, Mamiko Tosa, Teruyuki Dohi, et al. Surgical excision and postoperative radiotherapy for keloids[J]. Scars Burn Heal, 2019, 5: 2059513119891113.
[16] 王宇婷, 王嘉玺. 手术联合局部放疗治疗耳部瘢痕疙瘩的临床观察[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2020, 26(1): 84-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZEBY202001024.htm
[17] Debenham BJ, Hu KS, Harrison LB. Present status and future directions of intraoperative radiotherapy[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2013, 14(11): E457-E464. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70270-5
[18] van Leeuwen MCE, Stokmans SC, Bulstra AJ, et al. High-dose-rate brachytherapy for the treatment of recalcitrant keloids: a unique, effective treatment protocol[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2014, 134(3): 527-534. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000000415
[19] van Leeuwen MC, Stokmans SC, Bulstra AE, et al. Surgical Excision with Adjuvant Irradiation for Treatment of Keloid Scars: A Systematic Review[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open, 2015, 3(7): E440. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000000357
[20] Jiang P, Geenen M, Siebert FA, et al. Efficacy and the toxicity of the interstitial high-dose-rate brachytherapy in the management of recurrent keloids: 5-year outcomes[J]. Brachytherapy, 2018, 17(3): 597-600. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2017.12.002
[21] Liu CL, Yuan ZY. Retrospective study of immediate postoperative electron radiotherapy for therapy-resistant earlobe keloids[J]. Arch Dermatol Res, 2019, 311(6): 469-475. doi: 10.1007/s00403-019-01922-z
[22] 杨爱琴. 76例瘢痕疙瘩术后放射治疗临床疗效分析[J]. 中国实用医药, 2009, 4(7): 61-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSSA200907040.htm
[23] Sedlmayer F, Reitsamer R, Wenz F, et al. Intraoperative radiotherapy (IORT) as boost in breast cancer[J]. Radiat Oncol, 2017, 12(1): 23. doi: 10.1186/s13014-016-0749-9
[24] Tuschy B, Berlit S, Romero S, et al. Clinical aspects of intraoperative radiotherapy in early breast cancer: short-term complications after IORT in women treated with low energy X-rays[J]. Radiat Oncol, 2013, 8: 95. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-8-95
[25] Kyrgias G, Hajiioannou J, Tolia M, et al. Intraoperative radiation therapy (IORT) in head and neck cancer: A systematic review[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2016, 95(50): E5035.
[26] 陈志深, 范娇娇, 于雷, 等. 肿瘤术中放疗的研究进展[J]. 中华放射肿瘤学杂志, 2018, 27(5): 517-521. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYYA202402040.htm
[27] 景莉, 刘天星. 常规分割与大分割放射治疗骨转移癌疼痛疗效对比研究[J]. 人民军医, 2011, 54(6): 500-501. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RMJZ201106047.htm
[28] Shen J, Lian X, Sun Y, et al. Hypofractionated electron-beam radiation therapy for keloids: retrospective study of 568 cases with 834 lesions[J]. J Radiat Res, 2015, 56(5): 811-817. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrv031
[29] Bijlard E, Verduijn GM, Harmeling JX, et al. Optimal High-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy Fractionation Scheme After Keloid Excision: A Retrospective Multicenter Comparison of Recurrence Rates and Complications[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2018, 100(3): 679-686. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.10.044
[30] 王庆国, 李晓梅, 张敏, 等. 107例瘢痕疙瘩术后两种分割剂量放疗疗效分析[J]. 北京大学学报: 医学版, 2014, 46(1): 169-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BYDB201401037.htm
-




 下载:
下载: