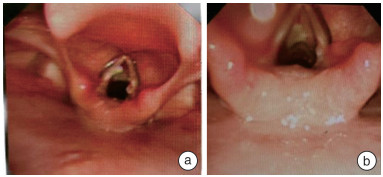
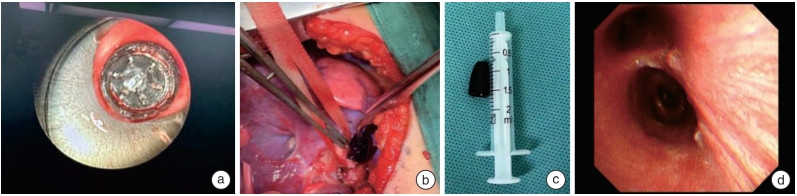
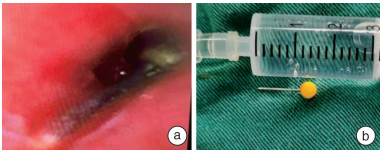
Analysis of the diagnosis and treatment of 10 cases of complex respiratory foreign bodies in children
-
摘要: 目的 探讨儿童复杂呼吸道异物的诊治经验。 方法 回顾性分析1 243例儿童呼吸道异物的临床资料,其中10例(0.8%)复杂呼吸道异物。 结果 10例复杂呼吸道异物患儿中,2例通过开胸手术取出; 1例气管切开取出; 1例予以肺叶切除取出; 1例因伴有先天性肺动脉吊带导致困难气道,予纤维支气管镜下取出后同步进行肺动脉吊带矫治术; 3例通过纤维支气管镜下钬激光和(或)冷冻方法使异物变形、碎裂后通过声门取出; 2例因异物特殊,硬支气管镜联合纤维支气管镜下取出。术后2例患儿因声门水肿明显,脱氧困难予插管送至ICU,2例因心脏或胸外科手术后,转至ICU病房,其余均在术后回普通病房。术后患儿均恢复良好。 结论 呼吸道异物合并气道狭窄,异物种类、形状、嵌顿位置特殊,异物过大时,需合理选择异物取出的方法,必要时可采取多种方法联合使用,确保以最佳方案快速解除呼吸道梗阻。Abstract: Objective To explore the diagnosis and treatment experience of complex respiratory foreign bodies in children. Methods The clinical data of 1 243 cases of respiratory foreign bodies in children were retrospectively analyzed, among which 10 cases(0.8%) were complicated respiratory foreign bodies. Results Among the 10 cases of complex respiratory foreign bodies, 2 cases were removed by open thoracotomy, 1 case was removed by tracheotomy, 1 case was removed by lobectomy, 1 case was removed by fiberoptic bronchoscopy because of difficult airway caused by the accompanying congenital pulmonary artery sling, and the pulmonary artery sling correction was synchronized with the fiberoptic bronchoscopic removal, 3 cases were removed by fiberoptic bronchoscopic holmium laser and/or freezing method to make the foreign body deformed and fragmented and then taken out by the sound gate, and 2 cases were removed because of the In 3 cases, the foreign bodies were deformed and fragmented by fiberoptic bronchoscopy, and in 2 cases, the foreign bodies were removed through the vocal folds because of their special characteristics. Two cases were intubated and sent to ICU after surgery because of obvious vocal edema and difficulty in deoxygenation, two cases were transferred to ICU after cardiac or thoracic surgery, and the rest of them returned to ordinary wards after surgery, and all 10 cases recovered well after surgery. Conclusion Respiratory foreign body combined with airway stenosis, when the foreign body type, shape, embedded location of special foreign body, foreign body is too large, need to rationally choose the method of foreign body removal. If necessary, a combination of methods can be used to ensure that the airway obstruction is quickly relieved with the best program.
-
Key words:
- children /
- respiratory foreign body /
- bronchoscopy /
- thoracotomy
-

-
表 1 10例呼吸道异物患儿临床资料
序号 性别 年龄 入院情况 异物存在时间 术前检查 异物位置 合并基础疾病 1 男 9岁2个月 呼吸平稳 10 h 胸部CT 右主支气管 无 2 男 12岁8个月 呼吸平稳 3 d 胸部CT及纤维支气管镜 右肺下叶 无 3 女 3岁3个月 呼吸平稳 2 d 胸部平扫及增强 左主支气管 肺动脉吊带 4 男 1岁 呼吸平稳 1 d 胸部CT 左主及下叶支气管 无 5 男 8个月16天 呼吸平稳 1 d 胸部CT 左主支气管 无 6 男 8岁10个月 呼吸平稳 10 d 胸部CT 右主支气管 无 7 女 1岁8个月 呼吸平稳 10 d 胸部CT 左肺内 无 8 男 9岁2个月 呼吸平稳 1个月 胸部增强CT及纤维支气管镜 左肺下叶 无 9 女 1岁6个月 呼吸平稳 1个月 胸部CT 右肺中间叶 无 10 男 8岁10个月 呼吸平稳 1 d 胸部CT 右主支气管 无 序号 肺部并发症 异物类型 手术次数 术后并发症 异物取出方法 转归 1 肺气肿 笔帽 2 肺不张 开胸 治愈 2 右下肺炎 坚果 2 肺炎 右肺下叶基底段切除 治愈 3 肺气肿 花生 2 肺不张 纤维支气管镜取出异物同步行肺动脉吊带矫正术 治愈 4 肺气肿 瓜子 3 肺炎 钬激光烧灼合并纤维支气管镜 治愈 5 肺气肿 大头针 2 喉水肿 支气管镜联合纤维支气管镜 治愈 6 肺气肿 笔帽 1 喉水肿、声带损伤 钬激光、冷冻联合硬支气管镜 治愈 7 无 5 cm长钢钉 1 无 开胸c型壁可移动X线机定位下取出 治愈 8 左肺下叶炎症 坚果 2 肺炎 纤维支气管镜 治愈 9 右肺中间叶实变 松子壳 3 肺炎 硬支气管镜 治愈 10 肺气肿 笔帽 1 喉水肿 气管切开联合硬支气管镜 治愈 -
[1] Powers KF, Reese AD, Carr MM. Pediatric Bronchoscopy for Airway Foreign in the ACS NSQIP-P: Morbidity and Mortality 2014-2019[J]. Laryngoscope, 2022, 11.
[2] 孙虹, 张罗. 耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2018: 389-389.
[3] Razafimanjato NNM, Ralaivao RA, Ravelomihary TDN, et al. Pneumonectomy in a child due to belated diagnosis of foreign body aspiration: a case report[J]. J Med Case Rep, 2021, 15(1): 533. doi: 10.1186/s13256-021-03015-w
[4] Ngamsanga S, Vathanophas V, Ungkanont K, et al. Pediatric respiratory tract foreign bodies in children: A systematic review[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2023, 50: 607-613. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2022.10.003
[5] 倪鑫. 中国儿童气管支气管异物诊断与治疗专家共识[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 5(53): 325-338.
[6] 王亚芳, 宋英鸾, 赫莉, 等. 42例儿童笔帽类气管支气管异物的诊治体会[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 9(35): 836-838. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.09.015
[7] 刘玺诚, 孟晨, 焦安夏, 等. 中国儿童中心气道狭窄呼吸介入与多学科协作诊疗专家共识[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志, 2021, 36(15): 1121-1137.
[8] Yan S, Jiang P, Chen G, et al. Characteristics and Treatment of Pediatric Tracheobronchial Foreign Bodies: A Retrospective Analysis of 715 Cases[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2022, 28: e937928.
[9] Harada A, Shimojima N, Shimotakahara A, et al. Surgical in-dication for congenital tracheal stenosis complicated by pul-monary artery sling[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2019, 11(12): 5474-5479. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.11.31
[10] Harumatsu T, Shimojima N, Tomita H, et al. Successful surgical treatment of congenital tracheal stenosis combined with tracheal bronchus and left pulmonary artery sling: a 10-year single-institution experience[J]. Pediatric Surgery International, 2022, 38(10): 1363-1370. doi: 10.1007/s00383-022-05161-8
[11] 孟繁峥, 孟晨. 中国儿童气道异物呼吸介入诊疗专家共识[J]. 中华实用儿科临床志, 2018, 33(18): 1392-1402.
[12] Bai C, Li Q. Bronchoscopy Training Course[M]. Shanghai: World Book Publishing Company, 2015: 198-206.
[13] 王亚芳, 宋英鸾, 崔莉, 等. 儿童气管支气管异物误诊致气管切开2例[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 20(32): 1588-1589. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2018.20.013
[14] 成钊, 孙敬武. 高危疑难呼吸道异物的处理[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 13(31): 981-983, 987. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2017.13.002
-




 下载:
下载: