-
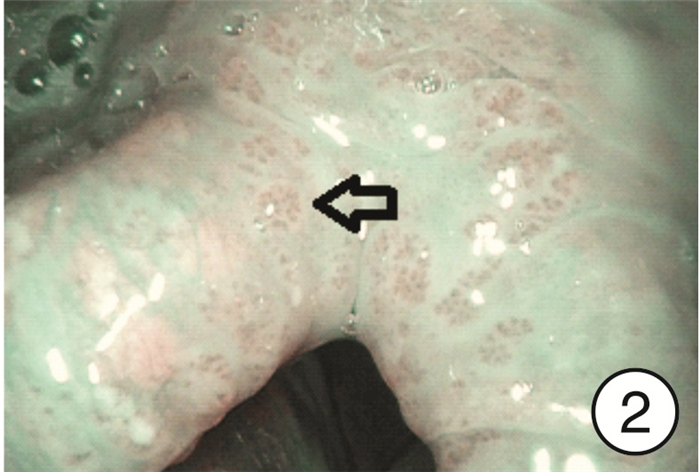
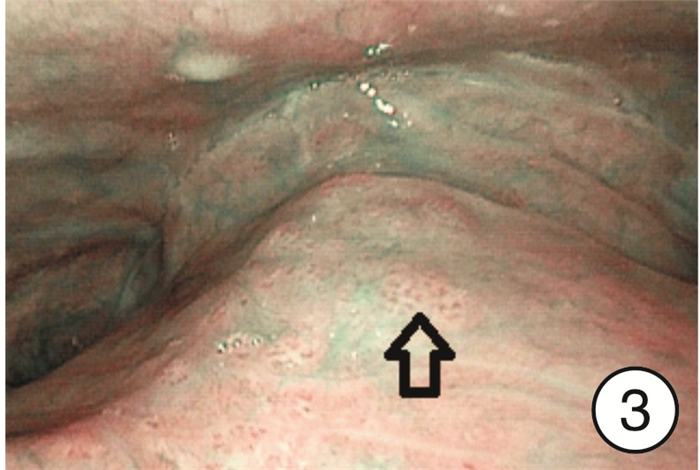
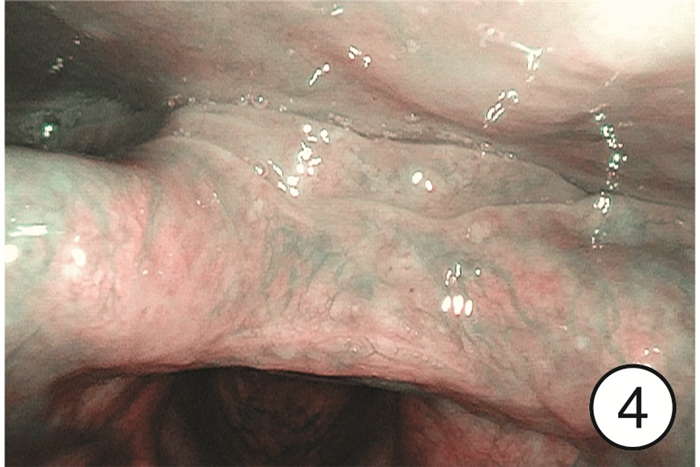
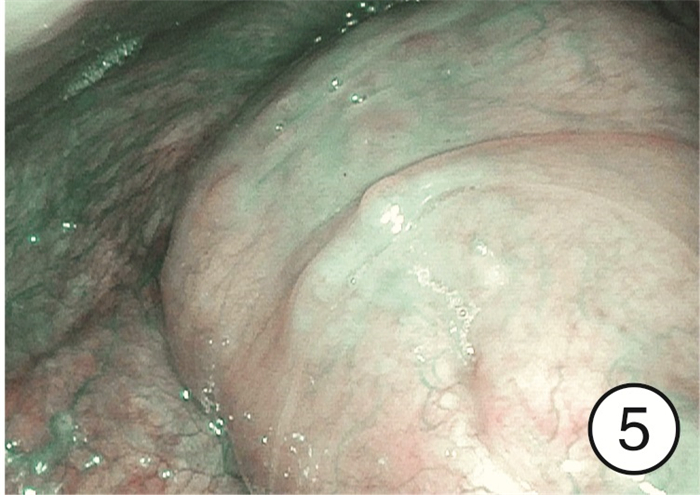
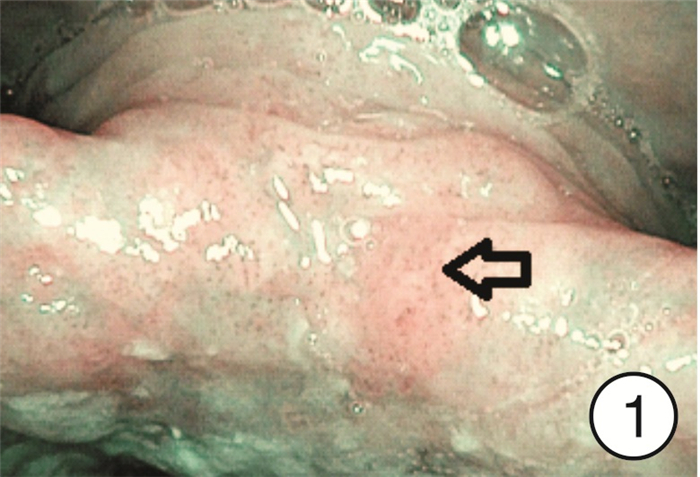
摘要: 目的 研究分析窄带成像(narrow band imaging,NBI)技术在咽喉反流(laryngopharyngeal reflux,LPR)诊断中的应用价值。方法 选取2022年9月-2023年4月因咽喉不适就诊于哈尔滨医科大学附属第一医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科住院部或喉镜室的患者共计275例作为研究对象,所有患者均完成RSI、RFS评分量表和电子喉镜检查(包括普通白光和NBI),根据2022年LPRD专家共识,以RSI和RFS评分量表为诊断标准分为LPR组和非LPR组,采用χ2检验分析不同组间NBI下特征性表现阳性率的差异,NBI与量表诊断方法的一致性采用Kappa分析,以RSI和RFS评分为诊断标准,分析NBI方法的诊断效能。结果 LPR组共有190例,其中157例在NBI模式下可见特征性表现,阳性率为82.6%(157/190),非LPR组共有85例,阳性16例,阳性率为18.8%(16/85),2组间阳性率差异有统计学意义(χ2=102.47,P < 0.05)。RSI、RFS量表诊断方法与NBI诊断方法的一致率为82.2%(226/275),采用Kappa一致性分析,Kappa=0.605(P < 0.05),提示两种诊断方法的一致性良好。以RSI、RFS量表为LPR诊断标准,NBI诊断方法的敏感度为82.6%(157/190),特异度为81.2%(69/85),阳性预测值为90.8%(157/173),阴性预测值为67.6%(69/102)。结论 NBI作为一项新型内镜成像技术,能够显示黏膜表面微血管的微小变化,可在LPR诊断中发挥重要作用。Abstract: Objective To study the application value of narrow-band imaging in the diagnosis of laryngopharyngeal reflux.Methods A total of 275 patients admitted to the inpatient department or laryngoscopy room of the Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Department of the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University from September 2022 to April 2023 due to throat discomfort were selected as the research subjects. All of them completed RSI, RFS scoring scales and electronic laryngoscopy(including ordinary white light and NBI). According to the expert consensus of LPRD in 2022, RSI and RFS scoring scale were used as diagnostic criteria to divide them into LPR group and non-LPR group. Chi-square test was used to analyze the differences of positive rates of characteristic manifestations under NBI among different groups. The consistency of NBI and scale diagnostic methods was analyzed by Kappa, and RSI and RFS scoring were used as diagnostic criteria, The diagnostic efficiency of NBI method was analyzed.Results There were 190 people in the LPR group, 157 of whom showed characteristic performance under the NBI mode, with a positive rate of 82.6%(157/190); there were 85 people in the non-LPR group, with a positive rate of 18.8%(16/85). There was a statistically significant difference in the positive rate between the two groups(χ2=102.47, P < 0.05). The consistency rate between RSI, RFS and NBI was 82.2%(226/275). Kappa consistency analysis was used, and Kappa=0.605(P < 0.05), indicating good consistency between the two diagnostic methods. Using RSI and RFS as diagnostic criteria for LPR, the sensitivity of NBI diagnostic method was 82.6%(157/190), specificity 81.2%(69/85), positive predictive value 90.8%(157/173) and negative predictive value 67.6%(69/102).Conclusion Narrow-band imaging, as a new endoscopic imaging technique, can show small changes in mucosal surface micro vessels and play an important role in the diagnosis of laryngopharyngeal reflux.
-
Key words:
- laryngopharyngeal reflux /
- narrow-band imaging /
- diagnosis /
- characteristic performance
-

-
表 1 RSI、RFS量表诊断方法与NBI诊断方法结果分析
例 NBI诊断 RSI、RFS诊断 合计 阳性 阴性 阳性 157 16 173 阴性 33 69 102 合计 190 85 275 -
[1] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会咽喉组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会咽喉学组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会嗓音学组. 咽喉反流性疾病诊断与治疗专家共识(2022年, 修订版)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 57(10): 1149-1172. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20220711-00428
[2] 徐志宇, 刘旭, 陈世彩, 等. 咽喉反流性疾病的发病机制及其与耳鼻咽喉疾病相关性研究进展[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2022, 30(6): 587-590. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2022.06.004
[3] Irjala H, Matar N, Remacle M, et al. Pharyngo-laryngeal examination with the narrow band imaging technology: early experience[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2011, 268(6): 801-806. doi: 10.1007/s00405-011-1516-z
[4] Boscolo Nata F, Tirelli G, Capriotti V, et al. NBI utility in oncologic surgery: An organ by organ review[J]. Surg Oncol, 2021, 36: 65-75. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2020.11.017
[5] Kasap E, Zeybel M, Asik, et al. Correlation among standard endoscopy, narrow band imaging, and histopathological findings in the diagnosis of nonerosive reflux disease[J]. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis, 2011, 20(2): 127-130.
[6] Guo L, Liu Y. Narrow-band imaging combined with salivary pepsin to diagnose patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2021, 141(8): 796-801. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2021.1950929
[7] Wu D, Cui X, Guo Y, et al. Narrow band imaging might contribute to the diagnosis of laryngopharyngeal reflux[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2020, 41(3): 102403. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102403
[8] Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA. Validity and reliability of the reflux symptom index(RSI)[J]. J Voice, 2002, 16(2): 274-277. doi: 10.1016/S0892-1997(02)00097-8
[9] Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA. The validity and reliability of the reflux finding score(RFS)[J]. Laryngoscope, 2001, 111(8): 1313-1317.
[10] Tan JJ, Wang L, Mo TT, et al. Pepsin promotes IL-8 signaling-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in laryngeal carcinoma[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2019, 19: 64. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0772-7
[11] Vageli DP, Doukas SG, Doukas PG, et al. Bile reflux and hypopharyngeal cancer (Review)[J]. Oncol Rep, 2021, 46(5): 244. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8195
[12] Restuti RD, Tamin S, Nugroho DA, et al. Factors affecting the occurrence of otitis media with effusion in preschool and elementary school children: a comparative cross-sectional study[J]. BMJ Open, 2022, 12(9): e065291. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-065291
[13] Huang YD, Tan JJ, Han XY, et al. [Study on the correlation between adenoid hypertrophy and laryngopharyngeal reflux in children][J]. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2018, 32(12): 899-904.
[14] 高竞逾, 罗仁婧, 阮标, 等. 胃蛋白酶免疫组织化学与胃蛋白酶检测试剂盒在咽喉反流诊断中的一致性分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(2): 97-102, 106. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.02.004
[15] Li Y, Xu G, Zhou B, et al. Effects of acids, pepsin, bile acids, and trypsin on laryngopharyngeal reflux diseases: physiopathology and therapeutic targets[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2022, 279(6): 2743-2752. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-07201-w
[16] Li J, Wang J, Wu M, et al. The role of nonacid reflux in laryngopharyngeal reflux diseases[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 277(10): 2813-2819. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-06015-6
[17] Hou C, Chen M, Chen T, et al. Study on laryngopharyngeal and esophageal reflux characteristics using 24-h multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH monitoring in healthy volunteers[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 277(10): 2801-2811. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05969-x
[18] Krause AJ, Walsh EH, Weissbrod PA, et al. An update on current treatment strategies for laryngopharyngeal reflux symptoms[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2022, 1510(1): 5-17. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14728
[19] Lechien JR, Akst LM, Hamdan AL, et al. Evaluation and Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease: State of the Art Review[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 160(5): 762-782. doi: 10.1177/0194599819827488
[20] Kim SI, Jeong SJ, Kwon OE, et al. Pharyngeal reflux episodes in patients with suspected laryngopharyngeal reflux versus healthy subjects: a prospective cohort study[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2021, 278(9): 3387-3392. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-06865-8
[21] 张青青, 谢萌, 郭瑞昕, 等. 质子泵抑制剂对咽喉反流患者唾液胃蛋白酶浓度的影响[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(11): 965-970. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.11.002
[22] Wang L, Wu W, Wang G. [Significance of pharyngeal biochemical indexes in the diagnosis of laryngopharyngeal reflux disease][J]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2018, 98(8): 596-600.
[23] Zhang J, Li J, Zhang Y, et al. Multitime point pepsin testing can double the rate of the diagnosis of laryngopharyngeal reflux[J]. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol, 2021, 6(6): 1389-1394. doi: 10.1002/lio2.700
[24] Wang J, Li J, Nie Q, et al. Are Multiple Tests Necessary for Salivary Pepsin Detection in the Diagnosis of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux?[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 166(3): 477-481. doi: 10.1177/01945998211026837
[25] Zhang M, Chia C, Stanley C, et al. Diagnostic Utility of Salivary Pepsin as Compared With 24-Hour Dual pH/Impedance Probe in Laryngopharyngeal Reflux[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2021, 164(2): 375-380. doi: 10.1177/0194599820951183
[26] Galli J, Meucci D, Salonna G, et al. Use OF NBI for the assessment of clinical signs of rhino-pharyngo-laryngeal reflux in pediatric age: Preliminary results[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 128: 109733. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.109733
[27] 朱增辉, 周鹏, 庞潇, 等. 窄带成像技术在诊断儿童咽喉反流中的应用[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2022, 28(4): 85-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZEBY202204016.htm
[28] He C, Yu J, Huang F, et al. The utility of narrow band imaging in endoscopic diagnosis of laryngopharyngeal reflux[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2019, 40(5): 715-719. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2019.06.009
[29] 何宁, 司勇锋, 杨涌, 等. 窄带成像高清电子鼻咽喉镜对咽喉反流病的诊疗价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2012, 26(18): 776-778. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2012.18.011
[30] Galli J, Settimi S, Salonna G, et al. Narrow Band Imaging for lingual tonsil hypertrophy and inflammation, in laryngo-pharyngeal reflux disease[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 277(3): 819-825. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05765-2
[31] Koufman JA, Aviv JE, Casiano RR, et al. Laryngopharyngeal reflux: position statement of the committee on speech, voice, and swallowing disorders of the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2002, 127(1): 32-35. doi: 10.1067/mhn.2002.125760
-

| 引用本文: | 郑念东, 刘江涛, 姜琳琳, 等. 咽喉反流在窄带成像下的特征性表现[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(10): 804-808. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.10.008 |
| Citation: | ZHENG Niandong, LIU Jiangtao, JIANG Linlin, et al. Characteristics performance of laryngopharyngeal reflux in narrow band imaging[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2023, 37(10): 804-808. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.10.008 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.
- Figure 5.



 下载:
下载: