Surgical approach analysis of endoscopic resection of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
-
摘要: 目的 探讨经鼻内镜手术入路切除鼻咽纤维血管瘤(juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma,JNA)的手术经验及效果。方法 回顾性分析87例行鼻内镜下切除JNA的患者的临床资料。根据肿瘤的部位、大小、侵犯的范围及肿瘤与瞳孔中线的解剖位置关系对JNA进行分类,根据分类选择了3种内镜手术入路方式,并对术后症状、并发症和复发情况进行调查分析。结果 87例经鼻内镜手术肿瘤切除率100%,经中鼻道入路35例(肿瘤较小,位于鼻腔鼻窦及翼腭窝),经鼻腔外侧壁入路45例(肿瘤侵犯翼腭窝但未超过瞳孔中线),经鼻腔外侧壁+同侧上颌窦前壁入路7例(肿瘤超过瞳孔中线侵及颞下窝或侵犯海绵窦、中颅窝硬脑膜外)。术后患者鼻塞、鼻腔间断流鼻血、头痛头晕、视力下降等症状得到不同程度改善。无手术死亡、颅内感染病例。术后随访6~78个月,复发率3.44%。结论 经鼻内镜切除JNA手术是治疗JNA的主要手段,术前是否选择行肿瘤营养血管栓塞术可根据肿瘤的位置和分期以及术者的临床操作水平综合考虑;选择合适的鼻内镜入路切除JNA,能够根据人体鼻腔固有解剖空间最大限度的利用鼻内镜设备的优势,以达到切除JNA、减少术中术后并发症、减小复发率、提高预后的目的。Abstract: Objective To investigate the surgical approach for the resection of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma(JNA) under nasal endoscopy.Methods The clinical data of 87 patients undergoing endoscopic resection of nasopharyngeal fibroangioma were retrospectively analyzed. We classified JNA according to tumor site, size, invasion scope and anatomic position relationship between tumor and midline of pupil. Three endoscopic surgical approaches were selected according to the classification, and the postoperative symptoms, complications and recurrence were investigated and analyzed.Results The tumor resection rate of 87 cases by nasal endoscopic surgery was 100%. Thirty-five cases were approached through the middle nasal passage(small tumors located in the nasal sinuses and pterygopalatine fossa), forty-five cases were approached through the lateral wall of the nasal cavity(tumor invaded the pterygopalatine fossa but did not exceed the midline of the pupil), and seven cases were approached via the lateral wall of nasal cavity + ipsilateral anterior wall of maxillary sinus(tumor invaded the infratemporal fossa beyond the midline of pupil or invaded the cavernous sinus and the middle cranial fossa epidural), Postoperative patients with nasal congestion, nasal bleeding, headache, dizziness, vision loss and other symptoms showed varying degrees of improvement. No surgical death or intracranial infection occurred. The postoperative follow-up was 6-78 months, and the recurrence rate was 3.44%.Conclusion Endoscopic resection of nasopharyngeal fibroangioma is the main treatment method for JNA. Selecting suitable endoscopic approach to resect JNA, To maximize the advantage of nasal endoscopic equipment according to the inherent anatomical space of the human nasal cavity, In order to achieve the purpose of JNA resection, reduce intraoperative and postoperative complications, reduce the recurrence rate and improve the prognosis.
-
Key words:
- nasal endoscopy /
- juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma /
- surgical approach
-

-
表 1 87例患者的Fisch分型
临床分期 例数 肿瘤侵犯范围 Ⅰ期 21 肿瘤局限于鼻腔或鼻咽部无骨质破坏 Ⅱ期 47 肿瘤侵犯翼腭窝或鼻窦伴骨质破坏 Ⅲ期 17 肿瘤侵犯颞下窝、眶区、海绵窦侧壁的蝶鞍旁区 Ⅳ期 2 侵犯海绵窦、视交叉或垂体窝、颅内 表 2 JNA手术入路选择
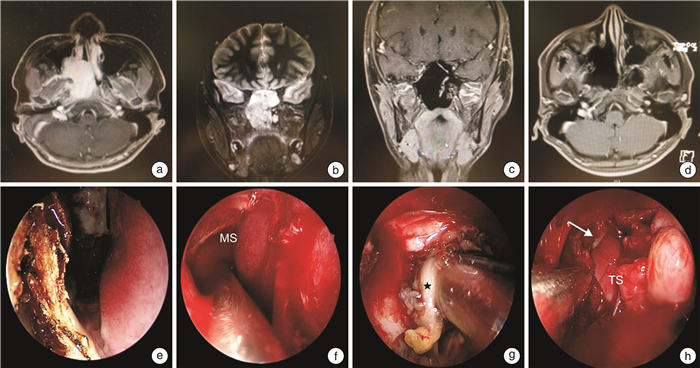
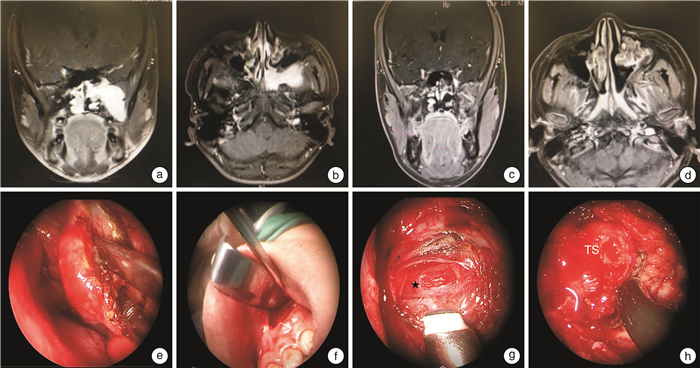
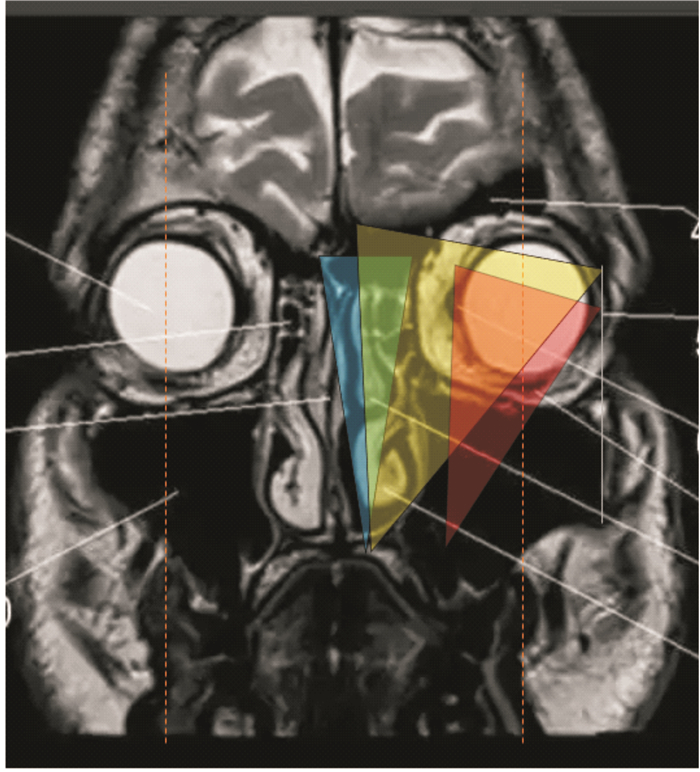
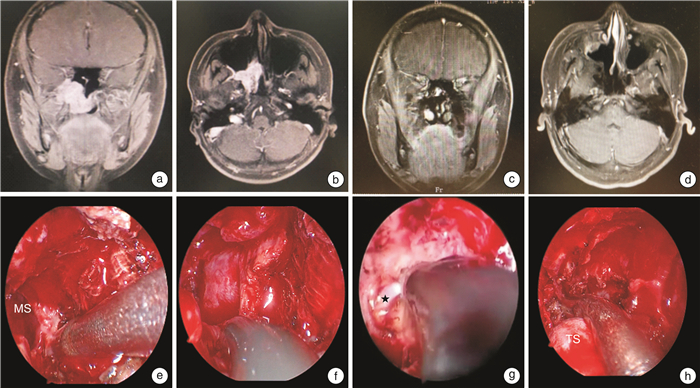
手术入路 适用肿瘤范围 例数 中鼻道入路 肿瘤局限于翼板之内 35(Ⅰ期21,Ⅱ期14) 鼻腔外侧壁入路 肿瘤位于翼腭窝或鼻窦但未超过瞳孔中线 45(Ⅱ期33,Ⅲ期12) 鼻内镜双入路方式 肿瘤超过瞳孔中线侵及颞下窝或侵犯海绵窦、中颅窝硬脑膜外 7(Ⅲ期5,Ⅳ期2) 表 3 不同手术入路术中出血情况
手术入路 术前栓塞/例 出血量/mL 是 否 栓塞 未栓塞 中鼻道入路 0 35 — 10~150 鼻腔外侧壁入路 1(Ⅲ期) 44 500~600 300~850 鼻内镜双入路方式 2(Ⅲ期1例、Ⅳ期1例) 5 1 500~2 000 1 800~2 500 表 4 JNA患者术前症状及术后改善情况
症状 术前/例 术后/例(%) 改善 未改善 鼻塞 79 79(100.0) 0 间断流鼻血 87 87(100.0) 0 头痛头晕 13 10(76.9) 3(23.1) 视力下降 1 1(100.0) 0 失明 1 0 1(100.0) 耳鸣 2 2(100.0) 0 听力减退 2 2(100.0) 0 -
[1] Fyrmpas G, Konstantinidis I, Constantinidis J. Endoscopic treatment of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibromas: our experience and review of the literature[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2012, 269(2): 523-529. doi: 10.1007/s00405-011-1708-6
[2] López F, Triantafyllou A, Snyderman CH, et al. Nasal juvenile angiofibroma: Current perspectives with emphasis on management[J]. Head Neck, 2017, 39(5): 1033-1045. doi: 10.1002/hed.24696
[3] 王德辉. 鼻咽纤维血管瘤的诊断和治疗进展[J]. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志, 2009, 9(3): 140-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YRBH200903005.htm
[4] Boghani Z, Husain Q, Kanumuri VV, et al. Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: a systematic review and comparison of endoscopic, endoscopic-assisted, and open resection in 1047 cases[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123(4): 859-869. doi: 10.1002/lary.23843
[5] Giorgianni A, Molinaro S, Agosti E, et al. Twenty Years of Experience in Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma(JNA)Preoperative Endovascular Embolization: An Effective Procedure with a Low Complications Rate[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(17): 3926. doi: 10.3390/jcm10173926
[6] Shah SR, Keshri A, Patadia S, et al. Stage Ⅲ nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: Improving results with endoscopic-assisted midfacial degloving and modification to the Fisch staging system[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2015, 43(8): 1678-1683. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2015.07.025
[7] Hofmann T, Bernal-Sprekelsen M, Koele W, et al. Endoscopic resection of juvenile angiofibromas--long term results[J]. Rhinology, 2005, 43(4): 282-289.
[8] Khoueir N, Nicolas N, Rohayem Z, et al. Exclusive endoscopic resection of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: a systematic review of the literature[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2014, 150(3): 350-358. doi: 10.1177/0194599813516605
[9] 孙正良, 刘阳云, 冯秀荣, 等. 鼻咽纤维血管瘤手术方式与疗效分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2009, 23(3): 135-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH200903013.htm
[10] Carle TR, Wung V, Heaney AP, et al. Sinonasal Symptom Outcomes following Endoscopic Anterior Cranial Base Surgery in the Pediatric Population[J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base, 2021, 83(Suppl 2): e312-e317.
[11] Andrade NA, Pinto JA, Nóbrega Mde O, et al. Exclusively endoscopic surgery for juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2007, 137(3): 492-496. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2007.03.003
[12] Eloy P, Watelet JB, Hatert AS, et al. Endonasal endoscopic resection of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma[J]. Rhinology, 2007, 45(1): 24-30.
[13] 周兵, 韩德民, 崔顺九, 等. 鼻内镜下鼻腔外侧壁切开上颌窦手术[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2007, 42(10): 743-748. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHEB200710011.htm
[14] 张秋航, 杨大章, 韩军. 内镜经鼻翼腭窝肿瘤切除术[J]. 中国微侵袭神经外科杂志, 2006, 11(10): 441-442. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWQX200610003.htm
[15] 杜伟嘉, 陈福权. 颞下窝肿瘤内镜手术径路的研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(1): 68-72. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.01.016
[16] 王剑, 杜伟嘉, 朱正茹, 等. 内镜下经鼻和经口颞下窝良性肿瘤手术36例报告[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(8): 597-603. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.08.006
[17] Zalzal HG, Turner MT. Robotic-assisted transmaxillary approach for removal of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma of the pterygopalatine and infratemporal fossa[J]. Head Neck, 2020, 42(9): 2745-2749.
[18] Lao WP, Lagabon KJ, Arom GA, et al. Combined endoscopic and transoral resection of a high-staged juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: A pictorial essay[J]. Head Neck, 2021, 43(2): 719-724.
[19] Liu JK, Husain Q, Kanumuri V, et al. Endoscopic graduated multiangle, multicorridor resection of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: an individualized, tailored, multicorridor skull base approach[J]. J Neurosurg, 2016, 124(5): 1328-1338.
[20] 柏瑞, 孔建新, 钱海鹏, 等. 内镜下经唇下上颌窦入路切除侧颅底肿瘤[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2019, 26(5): 330-335. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QLZL201905012.htm
[21] 李海艳, 翟翔, 何京川, 等. 经鼻内镜切除旁中线颅底良性病变的手术入路选择[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(5): 352-356. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.05.006
[22] Cohen-Cohen S, Carlstrom LP, Janus JR, et al. Combined Anterior Transmaxillary(Caldwell-Luc)With an Endoscopic Endonasal Transpterygoid Approach for Resection of a Large Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma: 2-Dimensional Operative Video[J]. Oper Neurosurg(Hagerstown), 2021, 20(3): E227-E228.
[23] Fang R, Sun W, Shi J, et al. Risk Factors and Characteristics of the Recurrence of Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma: A 22-Year Experience With 123 Cases at a Tertiary Center[J]. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol, 2022, 15(4): 364-371.
-




 下载:
下载: