Diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma with convolutional neural network on narrowband imaging
-
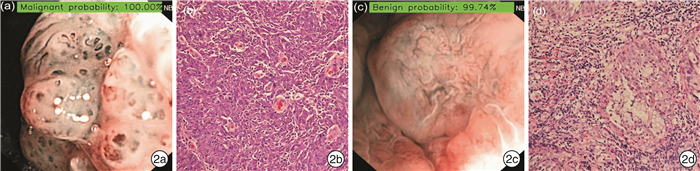
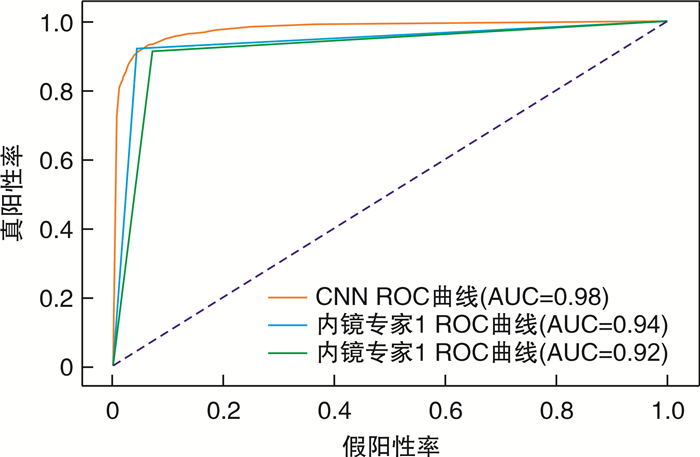
摘要: 目的 探讨卷积神经网络(convolutional neural network,CNN)技术对鼻咽癌窄带成像内镜图像的诊断效能。方法 收集2014-2016年广西壮族自治区人民医院834例鼻咽病变的窄带成像内镜图像和临床病理资料。使用DenseNet 201模型训练分类任务,利用测试数据集对模型进行检测和性能评价,并和内镜医生的判别效果进行比较。结果 CNN诊断鼻咽癌的受试者工作特征曲线下面积为0.98。CNN的敏感度为91.90%,特异度为94.69%,而2名内镜专家的敏感度分别为92.08%和91.06%,特异度分别为95.58%和92.79%,CNN与2名内镜专家的诊断结果比较差异均无统计学意义(P=0.282,P=0.085)。此外,CNN对早期鼻咽癌的识别准确率与晚期鼻咽癌比较,差异无统计学意义(P=0.382)。测试集图像识别时间为0.1 s/张。结论 CNN模型能快速区别鼻咽癌和鼻咽良性病变,有助于内镜医生判断鼻咽病变,减少鼻咽部活检率。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of the convolutional neural network(CNN) in diagnosing nasopharyngeal carcinoma using endoscopic narrowband imaging.Methods A total of 834 cases with nasopharyngeal lesions were collected from the People's Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region between 2014 and 2016. We trained the DenseNet201 model to classify the endoscopic images, evaluated its performance using the test dataset, and compared the results with those of two independent endoscopic experts.Results The area under the ROC curve of the CNN in diagnosing nasopharyngeal carcinoma was 0.98. The sensitivity and specificity of the CNN were 91.90% and 94.69%, respectively. The sensitivity of the two expert-based assessment was 92.08% and 91.06%, respectively, and the specificity was 95.58% and 92.79%, respectively. There was no significant difference between the diagnostic accuracy of CNN and the expert-based assessment (P=0.282, P=0.085). Moreover, there was no significant difference in the accuracy in discriminating early-stage and late-stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma(P=0.382). The CNN model could rapidly distinguish nasopharyngeal carcinoma from benign lesions, with an image recognition time of 0.1 s/piece.Conclusion The CNN model can quickly distinguish nasopharyngeal carcinoma from benign nasopharyngeal lesions, which can aid endoscopists in diagnosing nasopharyngeal lesions and reduce the rate of nasopharyngeal biopsy.
-

-
表 1 内镜专家和CNN对鼻咽NBI图像判读效能的比较
% 项目 CNN 内镜专家1 内镜专家2 敏感度 91.90 92.08 91.06 特异度 94.69 95.58 92.79 PPV 94.54 95.41 92.66 NPV 92.12 92.35 91.21 表 2 不同诊断模型对不同T分期鼻咽癌的判别准确率比较
诊断模型 T1+2/% T3+4/% χ2 P CNN 91.29 92.31 0.764 0.382 内镜专家1 90.96 92.83 2.608 0.106 内镜专家2 89.75 91.94 3.221 0.073 -
[1] Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Lancet, 2019, 394(10192): 64-80. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30956-0
[2] Weng JJ, Wei JZ, Li M, et al. Effects of Surgery Combined with Chemoradiotherapy on Short-and Long-Term Outcomes of Early-Stage Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2020, 12: 7813-7826. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S262567
[3] Lee A, Ngan R, Ng WT, et al. NPC-0501 trial on the value of changing chemoradiotherapy sequence, replacing 5-fluorouracil with capecitabine, and altering fractionation for patients with advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Cancer, 2020, 126(16): 3674-3688. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32972
[4] Yu X, Ji M, Cheng W, et al. A Retrospective Cohort Study of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Screening and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Screening in Zhongshang City[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10(8): 1909-1914. doi: 10.7150/jca.27676
[5] Si YF, Deng ZX, Weng JJ, et al. A study on the value of narrow-band imaging(NBI)for the general investigation of a high-risk population of nasopharyngeal carcinoma(NPC)[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2018, 16(1): 126. doi: 10.1186/s12957-018-1423-5
[6] 倪晓光, 张宝根. 窄带成像内镜在鼻咽癌早期诊断中的作用[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 53(1): 44-44.
[7] Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa RA, et al. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks[J]. Nature, 2017, 542(7639): 115-118. doi: 10.1038/nature21056
[8] Song B, Li S, Sunny S, et al. Exploring uncertainty measures in convolutional neural network for semantic segmentation of oral cancer images[J]. J Biomed Opt, 2022, 27(11): 115001.
[9] Li C, Jing B, Ke L, et al. Development and validation of an endoscopic images-based deep learning model for detection with nasopharyngeal malignancies[J]. Cancer Commun(Lond), 2018, 38(1): 59. http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/efed/036b7bc03915d3d2ae7b6e568ab7ffc58e3e.pdf
[10] Huang G, Liu Z, Laurens V, et al. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks[J]. IEEE Computer Society, 2016: 4700-4708.
[11] Chen YP, Liu X, Zhou Q, et al. Metronomic capecitabine as adjuvant therapy in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a multicentre, open-label, parallel-group, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet, 2021, 398(10297): 303-313. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01123-5
[12] Zhang B, Li Y, Weng J, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Endoscopic Nasopharyngectomy Combined With Low-Dose Radiotherapy for Primary T1-2 Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2021, 20: 15330338211011975. http://doc.paperpass.com/foreign/rgArti2021279014930.html
[13] Suwondo S, Surarso B, Kristyono I. Biopsy Examination Validity Based on Narrow Band Imaging Guidance of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Suspected Patients[J]. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 71(Suppl 1): 395-399. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040407360310_2c8e.html
[14] Ni XG, Zhang QQ, Wang GQ. Classification of nasopharyngeal microvessels detected by narrow band imaging endoscopy and its role in the diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2017, 137(5): 546-553. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2016.1253869
[15] Hirasawa T, Aoyama K, Tanimoto T, et al. Application of artificial intelligence using a convolutional neural network for detecting gastric cancer in endoscopic images[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2018, 21(4): 653-660 doi: 10.1007/s10120-018-0793-2
[16] Mascharak S, Baird BJ, Holsinger FC. Detecting oropharyngeal carcinoma using multispectral, narrow-band imaging and machine learning[J]. Laryngoscope, 2018, 128(11): 2514-2520. doi: 10.1002/lary.27159
[17] Wu L, He X, Liu M, et al. Evaluation of the effects of an artificial intelligence system on endoscopy quality and preliminary testing of its performance in detecting early gastric cancer: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Endoscopy, 2021, 53(12): 1199-1207. doi: 10.1055/a-1350-5583
[18] Park J, Jang BG, Kim YW, et al. A Prospective Validation and Observer Performance Study of a Deep Learning Algorithm for Pathologic Diagnosis of Gastric Tumors in Endoscopic Biopsies[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2021, 27(3): 719-728. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3159
[19] Nagao S, Tsuji Y, Sakaguchi Y, et al. Highly accurate artificial intelligence systems to predict the invasion depth of gastric cancer: efficacy of conventional white-light imaging, nonmagnifying narrow-band imaging, and indigo-carmine dye contrast imaging[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2020, 92(4): 866-873. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2020.06.047
[20] 胡蓉, 钟琦, 徐文等. 基于深度卷积神经网络的人工智能在喉鳞状细胞癌窄带成像辅助诊断中的应用[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 56(5): 454-458.
-




 下载:
下载: