Application of vestibular function examination in the analysis of damaged site in patients with acute vestibular neuritis
-
摘要: 目的 通过对前庭神经炎急性期患者进行前庭功能检查,分析前庭神经受损的部位。方法 收集57例前庭神经炎急性期患者,每位患者进行双温试验、视频头脉冲试验(video head impulse test,vHIT)、前庭诱发肌源性电位(vestibular evoked myogenic potentials,VEMPs)检查,对所有患者的检查结果进行统计学分析。结果 双温试验异常率为92.98%,水平半规管vHIT异常率为92.98%,前半规管vHIT异常率为92.98%,后半规管vHIT异常率为52.63%,眼肌VEMPs(ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials,oVEMP)异常率为89.47%,颈肌VEMPs(cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potentials,cVEMP)异常率为52.63%;双温试验、水平与前半规管vHIT及oVEMP的异常率明显高于后半规管vHIT及cVEMP的异常率(P < 0.01)。双温试验、水平、前及后半规管vHIT、oVEMP及cVEMP均异常即全前庭神经受损者26例(45.61%),双温试验、水平及前半规管vHIT、oVEMP均异常即前庭上神经受损者25例(43.86%),后半规管vHIT及cVEMP受损即前庭下神经受损者4例(7.02%),双温试验、水平及前半规管vHIT异常即末梢前庭神经受损者2例(3.51%);全前庭神经及前庭上神经受损率明显高于前庭下神经及末梢前庭神经受损率(P < 0.01)。结论 前庭神经炎急性期亚型可分为四类:全前庭神经炎,前庭上神经炎,前庭下神经炎及末梢前庭神经炎。在对前庭神经炎急性期的患者进行亚型诊断时,vHIT能精确地评估前庭神经受损的部位,并且vHIT联合VEMPs能为末梢前庭神经炎的诊断提供客观依据。Abstract: Objective To analyze the site of vestibular nerve damaged in patients with acute vestibular neuritis.Methods Fifty-seven patients with acute vestibular neuritis were recruited, and each patient underwent caloric irrigation test, video head impulse test(vHIT) and vestibular evoked myogenic potentials(VEMPs). The results were further analyzed.Results Analysis of abnormal rates of different vestibular function tests: the abnormal rate of caloric irrigation test, horizontal semicircular canal vHIT, anterior semicircular canal vHIT, and posterior semicircular canal vHIT were 92.98%, 92.98%, 92.98%, and 52.63%, respectively. The abnormal rate of cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potentials(cVEMP) and ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials(oVEMP) were 52.63% and 89.47%. The abnormal rate of caloric irrigation test, horizontal semicircular canal vHIT, anterior semicircular canal vHIT, and oVEMP were significantly higher than posterior semicircular canal vHIT and cVEMP(P < 0.01). Combination analysis of different vestibular function tests: there are twenty-six patients(45.61%, superior and inferior vestibular nerve) with abnormal caloric irrigation test, video head impulse test, and VEMPs. There are twenty-five patients(43.86%, superior vestibular nerve) with abnormal caloric irrigation test, horizontal semicircular canal vHIT, anterior semicircular canal vHIT, and oVEMP. There are 4 patients(7.02%, inferior vestibular nerve) with abnormal posterior semicircular canal vHIT and cVEMP. There are two patients(3.51%, ampullary vestibular nerve) with abnormal caloric irrigation test, horizontal semicircular canal vHIT, and anterior semicircular canal vHIT. The rate of superior and inferior vestibular neuritis and superior vestibular neuritis were significantly higher than inferior vestibular neuritis and ampullary vestibular neuritis(P < 0.01).Conclusion Acute vestibular neuritis subtypes can be divided into four categories: superior and inferior vestibular neuritis, superior vestibular neuritis, inferior vestibular neuritis, and ampullary vestibular neuritis. Video head impulse test can accurately assess the site of vestibular nerve damage in patients with acute vestibular neuritis. In addition, vHIT combined with VEMPs can provide objective evidence for the diagnosis of ampullary vestibular neuritis.
-

-
表 1 前庭神经炎急性期患者神经损伤分布特征(n=57)
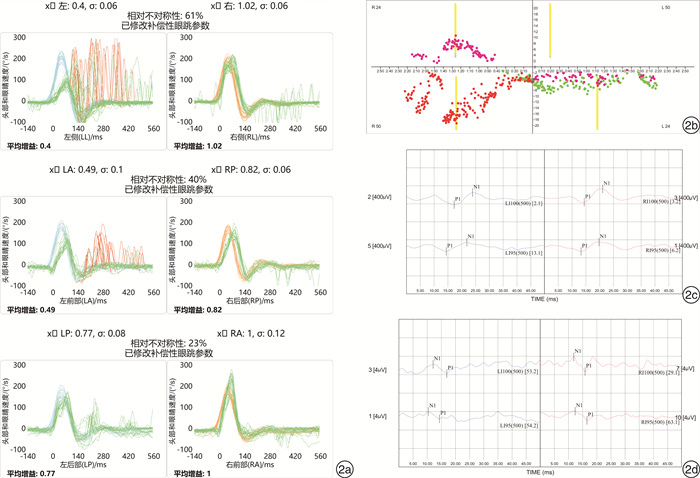
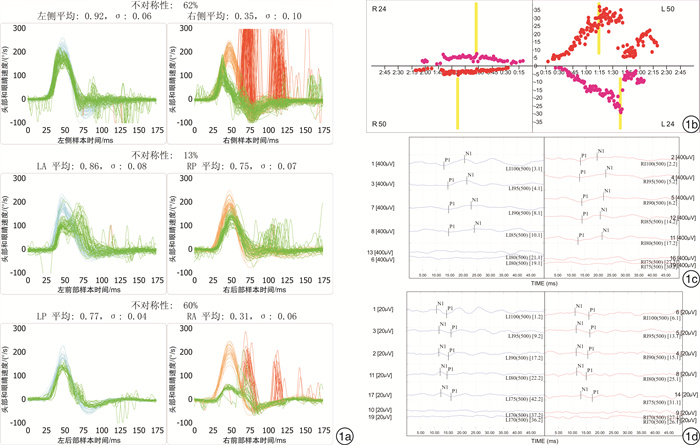
受损部位 例数(%) 双温试验 vHIT-H vHIT-A vHIT-P oVEMP cVEMP 全前庭神经 26(45.61) + + + + + + 前庭上神经 25(43.86) + + + - + - 前庭下神经 4(7.02) - - - + - + 壶腹神经 2(3.51) + + + - - - +:结果异常;-:结果无异常。 -
[1] 中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华神经科杂志编辑委员会. 眩晕诊治多学科专家共识[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2017, 50(11): 805-812. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2017.11.002
[2] 中国医师协会神经内科分会眩晕专业委员会, 中国卒中学会卒中与眩晕分会, 李斐, 等. 前庭神经炎诊治多学科专家共识[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2020, 39(9): 985-994. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-9026.2020.09.001
[3] Starkov D, Strupp M, Pleshkov M, et al. Diagnosing vestibular hypofunction: an update[J]. J Neurol, 2021, 268(1): 377-385. doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-10139-4
[4] 郝维明, 黄若男, 赵卫东, 等. 听神经瘤患者前庭功能评估及临床价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(12): 910-915. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.12.004
[5] 孙晓梅, 区永康, 许耀东. 前庭功能检查组合在梅尼埃病前庭功能分期中的应用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 35(9): 825-828. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.09.012
[6] Shepard NT, Jacobson GP. The caloric irrigation test[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2016, 137: 119-1131.
[7] Fu W, He F, Zhao R, et al. Effects of Hand Positions During Video Head-Impulse Test(vHIT)in Patients With Unilateral Vestibular Neuritis[J]. Front Neurol, 2018, 9: 531. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00531
[8] Fu W, Wang Y, He F, et al. Vestibular and oculomotor function in patients with vestibular migraine[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2021, 42(6): 103152. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2021.103152
[9] Navari E, Casani AP. Lesion Patterns and Possible Implications for Recovery in Acute Unilateral Vestibulopathy[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2020, 41(2): e250-e255. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002476
[10] Yan T, Zong F, Han X, et al. Vestibular Neuritis in Patients Among Different Age Groups: Clinical Features and Outcomes[J]. J Am Acad Audiol, 2020, 31(9): 629-635. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1717067
[11] Taylor RL, McGarvie LA, Reid N, et al. Vestibular neuritis affects both superior and inferior vestibular nerves[J]. Neurology, 2016, 87(16): 1704-1712. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003223
[12] Hwang K, Kim BG, Lee JD, et al. The extent of vestibular impairment is important in recovery of canal paresis of patients with vestibular neuritis[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2019, 46(1): 24-26. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2018.05.009
[13] Fu W, He F, Wei D, et al. Recovery Pattern of High-Frequency Acceleration Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex in Unilateral Vestibular Neuritis: A Preliminary Study[J]. Front Neurol, 2019, 10: 85. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00085
[14] Tighilet B, Bordiga P, Cassel R, et al. Peripheral vestibular plasticity vs central compensation: evidence and questions[J]. J Neurol, 2019, 266(Suppl 1): 27-32.
[15] Shin BS, Oh SY, Kim JS, et al. Cervical and ocular vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials in acute vestibular neuritis[J]. Clin Neurophysiol, 2012, 123(2): 369-375. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2011.05.029
[16] Govender S, Dennis DL, Colebatch JG. Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials(VEMPs)evoked by air-and bone-conducted stimuli in vestibular neuritis[J]. Clin Neurophysiol, 2015, 126(10): 2004-2013. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.12.029
[17] Kim HA, Hong JH, Lee H, et al. Otolith dysfunction in vestibular neuritis: recovery pattern and a predictor of symptom recovery[J]. Neurology, 2008, 70(6): 449-453. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000297554.21221.a0
[18] Magliulo G, Gagliardi S, Ciniglio Appiani M, et al. Selective vestibular neurolabyrinthitis of the lateral and superior semicircular canal ampulla and ampullary nerves[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2012, 121(10): 640-644.
-




 下载:
下载: