Evolution of auditory brainstem response in 0-6 years old normal hearing children and characteristics of children with abnormal acoustic conduction
-
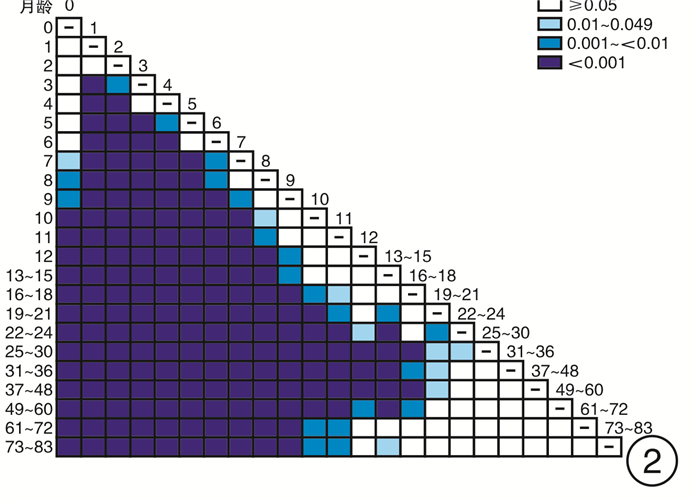
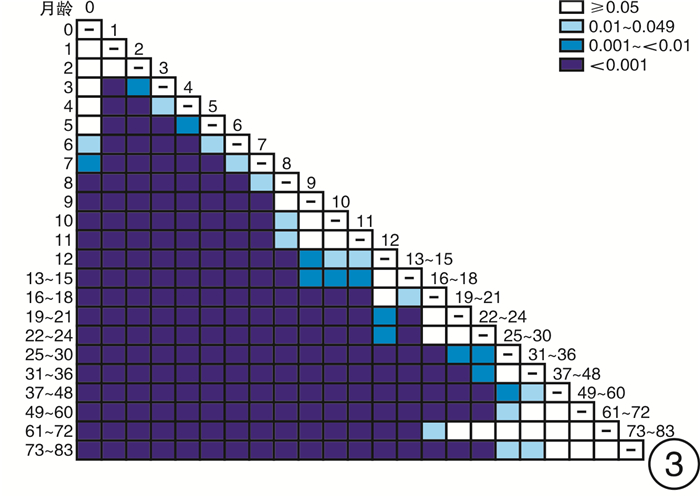
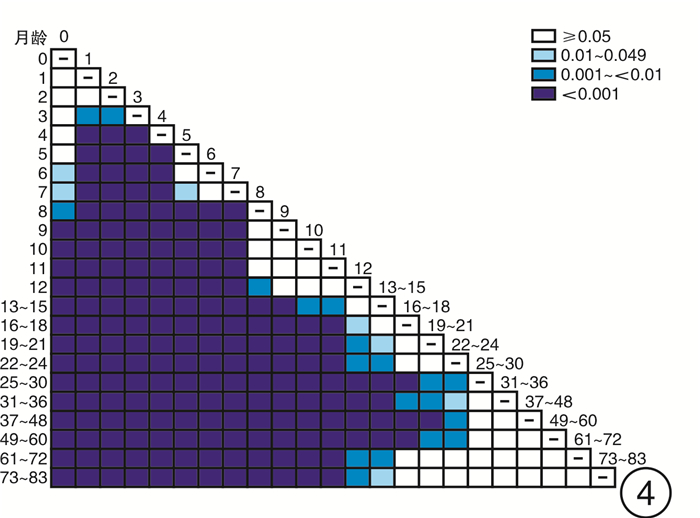
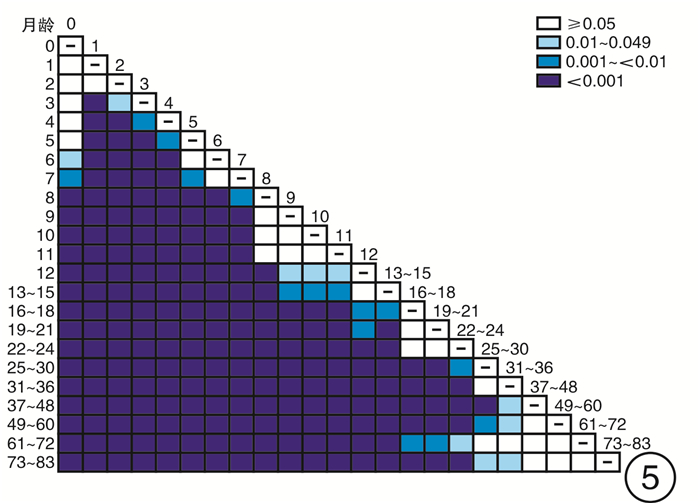
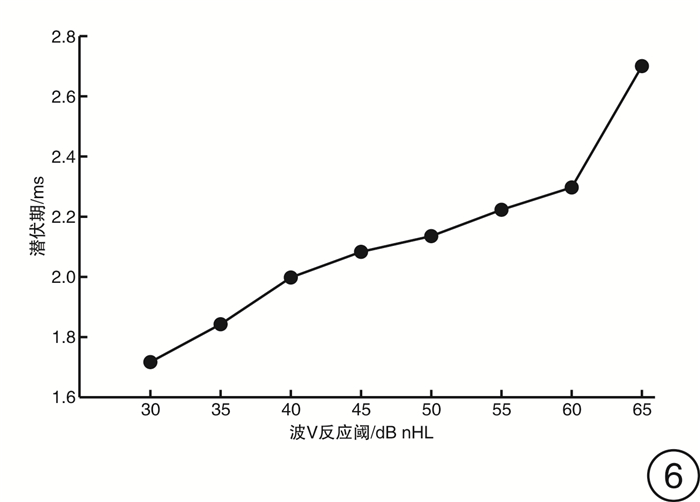
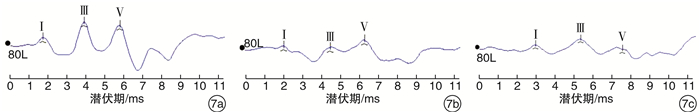
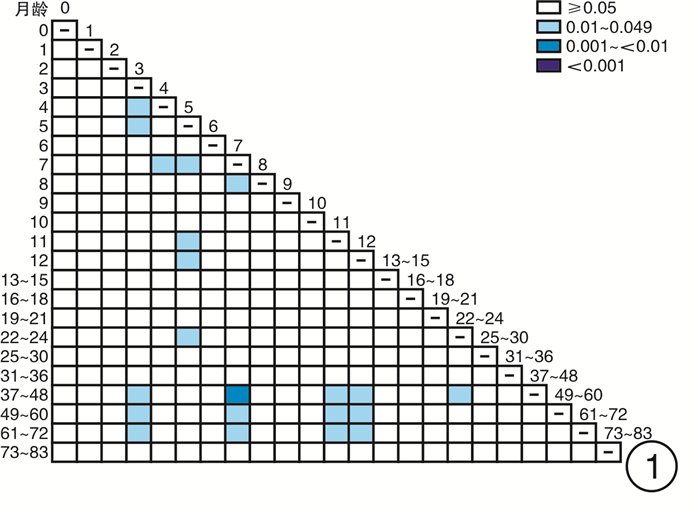
摘要: 目的 探索0~6岁儿童短声诱发听性脑干反应(Click-ABR)潜伏期及波间期的正常参考范围,分析声传导功能异常儿童Click-ABR的临床特征。方法 分别对1791例(3582耳)0~6岁听力正常儿童及176例(258耳)声传导功能异常儿童进行Click-ABR。分析不同月龄听力正常儿童Click-ABR各项参数的差异,同时比较声传导功能异常儿童Click-ABR波Ⅴ反应阈与潜伏期及波间期的相关性。结果 波Ⅰ潜伏期与月龄不相关,波Ⅲ潜伏期、波Ⅴ潜伏期、波Ⅰ-Ⅲ间期和波Ⅰ-Ⅴ间期均与月龄呈明显负相关; 波Ⅲ潜伏期自25个月起不随年龄增长而缩短,波Ⅴ潜伏期自37个月起不随年龄增长而缩短。声传导功能异常儿童在80 dB nHL刺激声下波Ⅰ潜伏期与听阈呈正相关,波Ⅰ-Ⅲ、Ⅰ-Ⅴ间期与听力正常儿童标准值无差异。结论 0~6岁儿童Click-ABR波Ⅲ、Ⅴ潜伏期及波Ⅰ-Ⅲ、Ⅰ-Ⅴ间期随年龄增长而缩短,本研究建立了本实验室0~6岁不同年龄段儿童Click-ABR潜伏期及波间期的正常参考范围; 结合Click-ABR听阈以及80 dB nHL刺激声下波Ⅰ潜伏期,可初步筛选出声传导功能异常儿童,同时应进一步补充其他听力诊断组合。Abstract: Objective To explore the normal reference range of Click-ABR latency and interwave period in 0-6 years old children, and to analyze the clinical characteristics of Click-ABR in children with sound transmission function is abnormal.Methods A total of 1791(3582 ears) normal hearing children aged 0-6 years and 176(258 ears) conductive hearing loss children were selected for Click-ABR. The differences of Click-ABR parameters in children of different months were analyzed, and the correlation between the degree of conductive hearing loss and Click-ABR parameters was explored.Results The incubation period of wave Ⅰ was not correlated with the age of month, while the incubation period of wave Ⅲ, wave Ⅴ, waveⅠ-Ⅲ and wave Ⅰ-Ⅴ were highly correlated with the age of month. There was a positive correlation between the latency of wave Ⅰ and hearing threshold in the children with sound transmission function is abnormal under 80 dB nHL stimulation, and there was no difference between the standard values of wave Ⅰ-Ⅲ and Ⅰ-Ⅴ in the children with sound transmission function is abnormal and normal children.Conclusion The latency of ABR wave Ⅲ and Ⅴ, and the interval between wave Ⅰ-Ⅲ and Ⅰ-Ⅴ shorten with the increase of age in children aged 0-6 years. The normal ABR values of children of different ages should be established in each hearing clinic for children as a reference. Combined with Click-ABR threshold and 80 dB nHL acoustic subwave Ⅰlatency, the abnormal conduction function can be preliminatively screened out, which should be further supplemented with other combinations of hearing diagnosis.
-
Key words:
- child /
- auditory brainstem response /
- conductive hearing loss
-

-
表 1 听力正常组和声传导功能异常组儿童年龄分布
例 月龄 听力正常组 声传导功能异常组 0 3 0 1 24 0 2 47 1 3 263 16 4 157 12 5 70 7 6 75 13 7 71 9 8 41 5 9 45 7 10 41 6 11 42 9 12 40 9 13~15 103 15 16~18 64 11 19~21 76 8 22~24 94 7 25~30 193 10 31~36 132 12 37~48 140 14 49~60 37 3 61~72 20 2 73~83 13 0 表 2 0~6岁听力正常儿童ABR波Ⅰ、Ⅲ、Ⅴ潜伏期及波Ⅰ-Ⅲ间期和波Ⅰ-Ⅴ间期的正常参考范围
测试月龄 耳数 波Ⅰ潜伏期 波Ⅲ潜伏期 波Ⅴ潜伏期 波Ⅰ-Ⅲ间期 波Ⅰ-Ⅴ间期 0 6 1.34±0.05 4.02±0.09 6.24±0.07 2.68±0.06 4.90±0.08 1 48 1.36±0.10 4.10±0.24 6.35±0.39 2.75±0.25 4.99±0.40 2 94 1.35±0.11 4.07±0.22 6.25±0.29 2.73±0.20 4.90±0.29 3 526 1.33±0.13 4.00±0.21 6.17±0.26 2.67±0.18 4.84±0.25 4 314 1.34±0.13 3.97±0.20 6.13±0.27 2.63±0.17 4.78±0.26 5 140 1.35±0.14 3.91±0.21 6.05±0.26 2.56±0.18 4.70±0.27 6 150 1.34±0.13 3.87±0.21 5.99±0.27 2.53±0.18 4.65±0.25 7 142 1.32±0.10 3.82±0.24 5.91±0.32 2.51±0.23 4.60±0.32 8 82 1.35±0.14 3.78±0.21 5.83±0.28 2.43±0.16 4.48±0.28 9 90 1.35±0.16 3.74±0.18 5.76±0.25 2.40±0.19 4.41±0.27 10 82 1.32±0.13 3.71±0.18 5.74±0.24 2.39±0.18 4.42±0.26 11 84 1.32±0.12 3.69±0.19 5.73±0.23 2.38±0.15 4.42±0.22 12 80 1.31±0.11 3.66±0.19 5.64±0.25 2.34±0.17 4.32±0.24 13~15 206 1.34±0.16 3.66±0.24 5.65±0.32 2.32±0.21 4.30±0.29 16~18 128 1.35±0.15 3.63±0.20 5.57±0.23 2.29±0.16 4.23±0.21 19~21 152 1.33±0.12 3.60±0.16 5.54±0.21 2.28±0.14 4.21±0.19 22~24 188 1.33±0.12 3.59±0.19 5.52±0.30 2.26±0.19 4.20±0.30 25~30 386 1.33±0.11 3.55±0.16 5.45±0.22 2.22±0.15 4.12±0.21 31~36 264 1.34±0.13 3.56±0.17 5.44±0.23 2.22±0.15 4.09±0.24 37~48 280 1.35±0.13 3.56±0.18 5.39±0.28 2.21±0.15 4.04±0.26 49~60 74 1.36±0.11 3.55±0.15 5.37±0.21 2.20±0.15 4.02±0.21 61~72 40 1.37±0.12 3.60±0.24 5.45±0.44 2.23±0.24 4.08±0.43 73~83 26 1.34±0.13 3.57±0.16 5.33±0.18 2.24±0.14 3.99±0.18 表 3 声传导功能异常组儿童波Ⅰ-Ⅲ间期与听力正常组标准值间的差异
月龄 听力正常组 声传导功能异常组 P值 2 2.73 2.53 0.51 3 2.67 2.57 0.06 4 2.63 2.66 0.98 5 2.56 2.46 0.58 6 2.53 2.43 0.10 7 2.51 2.43 0.31 8 2.43 2.35 0.63 9 2.40 2.30 0.21 10 2.39 2.26 0.20 11 2.38 2.36 0.80 12 2.34 2.51 0.15 13~15 2.32 2.23 0.14 16~18 2.29 2.17 0.07 19~21 2.28 2.29 0.90 22~24 2.26 2.31 0.68 25~30 2.22 2.24 0.74 31~36 2.22 2.28 0.22 37~48 2.21 2.17 0.31 49~60 2.20 2.06 0.13 61~72 2.23 2.04 0.11 表 4 声传导功能异常组儿童波Ⅰ-Ⅴ间期与听力正常组标准值间的差异
月龄 听力正常组 声传导功能异常组 P值 2 4.90 4.70 0.11 3 4.84 4.66 0.07 4 4.78 4.78 0.98 5 4.70 4.47 0.54 6 4.65 4.58 0.43 7 4.60 4.48 0.12 8 4.48 4.17 0.16 9 4.41 4.27 0.17 10 4.42 4.23 0.13 11 4.42 4.32 0.39 12 4.32 4.50 0.30 13~15 4.30 4.20 0.21 16~18 4.23 4.07 0.05 19~21 4.21 4.13 0.35 22~24 4.20 4.12 0.43 25~30 4.12 4.08 0.63 31~36 4.09 4.10 0.91 37~48 4.04 3.96 0.10 49~60 4.02 3.89 0.28 61~72 4.08 4.25 0.63 -
[1] 李兴启, 王秋菊. 听觉诱发反应及应用[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2015: 154-162.
[2] 丁伟, 侯小娟, 张伦, 等. 不同年龄段听力正常学龄前儿童短声及短纯音ABR正常参考值研究[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2021, 29(1): 39-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2021.01.009
[3] 刘娅, 孙建军. 儿童分泌性中耳炎多国指南研读与解析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(12): 1065-1069. http://lceh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=8018dbcd-50f8-4b55-9a55-f8f2ac2a3b24
[4] 吴文瑾, 黄琦. 儿童化脓性中耳炎并发症的临床分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(7): 587-591. http://lceh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=3218f3de-e853-4d29-bb17-cb60189327fa
[5] 孙敬涛, 刘海红, 王雪瑶, 等. 听性脑干反应对于婴幼儿不同性质听力损失的应用分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(2): 120-125. http://lceh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=8a35e497-c57c-483f-9325-7872c60125c9
[6] Stuermer KJ, Foerst A, Sandmann P, et al. Maturation of auditory brainstem responses in young children with congenital monaural atresia[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2017, 95: 39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2017.01.029
[7] Seethapathy J, Boominathan P, Uppunda AK, et al. Changes in Auditory Brainstem Response in very preterm and late preterm infants[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 121: 88-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.03.008
[8] Johnson KL, Nicol T, Zecker SG, et al. Developmental plasticity in the human auditory brainstem[J]. J Neurosci, 2008, 28(15): 4000-4007. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0012-08.2008
[9] Sharma M, Bist SS, Kumar S. Age-Related Maturation of Wave V Latency of Auditory Brainstem Response in Children[J]. J Audiol Otol, 2016, 20(2): 97-101. doi: 10.7874/jao.2016.20.2.97
[10] 陈平, 王智楠. 3~5岁儿童短声听性脑干反应正常值及演化[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2016, 24(5): 455-457. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2016.05.008
[11] 曾祥丽, 王树芳, 陈玉莲, 等. 正常新生儿ABR的表现形式及建立正常参考值的可行性探讨[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2008, 16(1): 36-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TLXJ200801010.htm
[12] Olsén P, Yliherva A, Pääkkö E, et al. Brainstem auditory-evoked potentials of 8-year-old preterm children in relation to their psycholinguistic abilities and MRI findings[J]. Early Hum Dev, 2002, 70(1/2): 25-34.
[13] 徐亚雄, 龙孝斌, 谭淑娟, 等. 分泌性中耳炎儿童Chirp声与短声诱发听性脑干反应的对比研究[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2020, 28(3): 328-330. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TLXJ202003020.htm
[14] 王秋菊, 史伟, 兰兰, 等. 婴幼儿中耳炎的听力学特征分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2008, 43(12): 891-895.
[15] 沈翎, 王旭萌, 齐秀琴. 听性脑干反应(ABR)测试在儿童分泌性中耳炎诊疗中的作用[J]. 中国听力语言康复科学杂志, 2009, 7(1): 26-30.
-




 下载:
下载: