Hyoid body morphology of thyroglossal duct cyst: a comparative study based on imaging
-
摘要: 目的 研究舌骨体形态的改变,为甲状舌管囊肿的术前诊断及治疗提供参考。方法 采集2016年1月—2021年10月期间经病理确诊的先天性甲状舌管囊肿(甲舌组)以及对照组的CT(正中矢状位)资料,比较两组间舌骨体高度、舌骨体宽度、舌骨体厚度、舌骨体宽度/舌骨体高度、舌骨体厚度/舌骨体高度的差异性。舌骨体高度、舌骨体宽度、舌骨体厚度数据采用t检验;舌骨体宽度/舌骨体高度、舌骨体厚度/舌骨体高度采用Mann-Whitney U检验。结果 甲舌组29例,对照组58例。甲舌组和对照组舌骨体高度分别为(8.93±0.22) mm和(8.94±0.12) mm,两组比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);甲舌组和对照组舌骨体宽度分别为(5.09±0.21)mm和(4.48±0.11) mm,舌骨体厚度分别为(3.84±0.12) mm和(3.13±0.08) mm,两组比较均差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);甲舌组和对照组舌骨体宽度/舌骨体高度秩和平均值分别为53.95和39.03,舌骨体厚度/舌骨体高度秩和平均值分别为59.90和36.05,两组比较均差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 甲状舌管囊肿舌骨体形态的改变有助于术前诊断,舌骨体切除有助于减少术后复发。Abstract: Objective To provide reference for preoperative diagnosis and treatment of thyroglossal duct cyst by studying the morphological changes of hyoid body.Methods The CT data(midsagittal image) of congenital thyroglossal duct cyst(TGDC group) diagnosed by pathology and the control group(C group) were collected from January 2016 to October 2021. The differences of hyoid body height(HBH), hyoid body width(HBW), hyoid bone thickness(HBT), HBW/HBH, HBT/HBH between the two groups were compared. HBH, HBW and HBT were analyzed by t-test; The HBW/HBH and HBT/HBH were analyzed by Mann-Whitney U test.Results Twenty-nine cases were included in the TGDC group and 58 in the C group. The HBH in the TGDC group was(8.93 ±0.22) mm and that in the C group was(8.94±0.12) mm, there was no significant difference between the two groups(P > 0.05). The HBW in the TGDC group and the C group were(5.09±0.21) mm and(4.48±0.11) mm, and the HBT were(3.84±0.12) mm and(3.13±0.08) mm, respectively, the difference between the two groups was statistically significant(P < 0.05). The average rank sum of HBW/HBH in the TGDC group and the C group was 53.95 and 39.03, respectively, and the average rank sum of HBT/HBH was 59.90 and 36.05, respectively, the difference between the two groups was statistically significant(P < 0.05).Conclusion The morphological changes of hyoid body of thyroglossal duct cyst may be helpful for preoperative diagnosis, and it also suggests that hyoid body resection may reduce the possibility of postoperative recurrence.
-
Key words:
- thyroglossal duct cyst /
- hyoid body /
- CT
-
甲状舌管囊肿由甲状舌管不完全闭塞所致,可发生在从舌盲孔至颈部中线的任何地方。虽然影像学检查可以显示这些病变的囊性特征[1],但是对疾病的鉴别诊断帮助有限[2]。本研究通过对我科2016年1月—2021年10月期间经病理确诊的先天性甲状舌管囊肿患者的CT资料进行回顾性分析,研究甲状舌管囊肿的舌骨体形态改变,为术前诊断及手术治疗提供参考。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象及纳入标准
我院2016年1月—2021年10月期间经病理确诊的先天性甲状舌管囊肿298例,按照研究对象的纳入标准设立甲舌组和对照组。
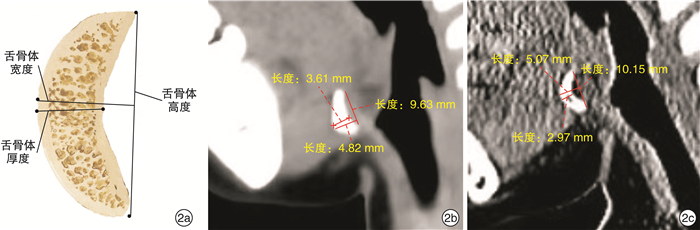
甲舌组纳入标准:①年龄3~4岁;②病理检查发现囊肿壁内衬鳞状上皮,确诊为甲状舌管囊肿(图 1a);③囊肿位于舌骨下或舌骨水平(图 1b);④术前含有颈部CT检查;⑤颈部CT检查含有矢状位成像;⑥矢状位成像位置标准,成像和舌骨体的长轴垂直(图 1c、1d);⑦矢状位成像在舌骨体位置至少有3张图片,或者图片数目≥5;⑧骨体矢状位成像如有3张、5张、7张图片,选取中间图片;如有6张、8张、10张图片,选取更靠近中线图片;⑨CT扫描电压100~120 kV。
对照组纳入标准:①年龄同实验组;②门诊怀疑气管异物或者食管异物行颈部CT检查;③CT检查未发现颈部低密度灶,排除甲状舌管囊肿;④图像选取标准同甲舌组。
符合甲舌组纳入标准者29例,其中男19例,女10例;3岁12例,4岁17例。对照组和甲舌组以2∶1的比例设计,为减少发育中的舌骨受年龄、性别的影响,对照组对年龄、性别予以同比例限制。对照组纳入58例,其中男38例,女20例;3岁24例,4岁34例。
1.2 图像分析及数据统计
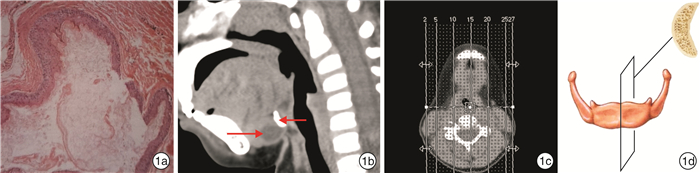
将符合纳入标准的矢状位成像统一调整窗宽、窗位(窗宽300~350,窗位35~60),采集舌骨体高度(舌骨体上下缘之间连线的距离)、舌骨体宽度(舌骨体前缘至后缘的距离)、舌骨体厚度(舌骨体中段前后缘之间的距离)以及舌骨体宽度/舌骨体高度和舌骨体厚度/舌骨体高度的比值(图 2)。同一图片的数据采集由3名医师共同完成,以降低医师个体主观性的影响。
1.3 统计学方法
数据采用SPSS 26.0统计软件进行分析。舌骨体高度、舌骨体宽度、舌骨体厚度为连续变量数据,采用t检验比较两组间的差异有无统计学意义;舌骨体宽度/舌骨体高度和舌骨体厚度/舌骨体高度的比值为定比变量,采用Mann-Whitney U检验比较两组间的差异有无统计学意义。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
甲舌组的舌骨体高度与对照组比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);甲舌组的舌骨体宽度、舌骨体厚度以及舌骨体宽度/舌骨体高度、舌骨体厚度/舌骨体高度与对照组比较,均差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表 1。
表 1 甲舌组和对照组相关数据比较组别 例数 舌骨体高度/mm 舌骨体宽度/mm 舌骨体厚度/mm 舌骨体宽度/舌骨体高度秩和平均值 舌骨体厚度/舌骨体高度秩和平均值 甲舌组 29 8.93±0.22 5.09±0.21 3.84±0.12 53.95 59.90 对照组 58 8.94±0.12 4.48±0.11 3.13±0.08 39.03 36.05 t值 -0.040 2.845 4.816 Z值 -2.598 -4.154 P值 0.968 0.006 0.001 0.009 0.001 3. 讨论
甲状腺原基起源于第一、二咽囊之间的内胚层组织。大约胚胎发育的第4周,这些组织开始增厚,分化形成甲状腺原基。接下来的3周,这些甲状腺组织穿透下方的间充质,走行于舌骨和甲状软骨的前方,到达下颈部。甲状腺下行的这一通道,收缩退化形成甲状舌管[1],如果甲状舌管不能完全闭塞,则会形成甲状舌管囊肿。
甲状舌管囊肿可发生于舌盲孔至颈下部中线的任何地方,如舌体内(3%)、舌骨上(15%~50%)、舌骨水平(20%~25%)、舌骨下方(25%~65%)[3]。临床中,怀疑甲状舌管囊肿时所做的术前检查评估也各不相同,这些评估包括体格检查、颈部CT、颈部超声检查、甲状腺扫描和细针吸取细胞学检查等[4]。甲状舌管囊肿的主要临床表现是无症状的颈部肿块,约占颈部囊肿的70%。肿块随吞咽或者伸舌而活动是甲状舌管囊肿的特征性表现[5]。
颈部CT可以很好地评估颈部肿块,提供囊肿位置、大小、与周围结构的关系等相关重要信息[6]。甲状舌管囊肿的典型CT表现为低密度、单腔(但偶尔有分隔)、边界清楚、囊壁清晰的肿块[1-2, 4, 7]。虽然影像学检查可以显示这些病变的囊性特征,同时对实质性的肿块如异位甲状腺的鉴别诊断提供帮助,然而对其他囊性肿块的鉴别诊断,如喉囊肿、皮样囊肿、舌下腺囊肿、炎症性病灶等,帮助并不大[2]。比如当甲状舌管囊肿逐渐增大、长时间压迫喉部结构使喉部结构薄弱时,囊肿可向喉内生长,侵犯喉部和梨状窝,给鉴别喉囊肿以及肿瘤带来挑战[8]。炎症性病灶可以有典型的CT表现,如病灶中心的低密度和病灶边缘的完全强化[9],但当甲状舌管囊肿合并感染时,鉴别诊断就很困难。再者,虽然多项研究表明,CT对感染性和炎性病变的诊断具有高度敏感性,却不具有特异性。细针吸取细胞学检查对于儿童甲状舌管囊肿的常规诊断是不必要的,因其敏感性低,阳性预测值低[2]。迄今甲状舌管囊肿的术前诊断仍然具有挑战性,术前诊断为甲状舌管囊肿者最终得到病理证实的比例只有55%[2]。因此,寻找一个甲状舌管囊肿的特异性影像学诊断指标,对于术前诊断有着重要意义。
胚胎学研究认为甲状舌管囊肿是因为起源于第二、三咽囊间的甲状腺原基下行后残留的通道未完全闭合所致,舌骨体起源于鳃下隆起,也有人认为其起源于第二、第三鳃弓[10]。临床研究发现,甲状舌管囊肿可发生于舌体内、舌骨上、舌骨水平、舌骨下方。在舌骨水平,甲状舌管分支最远距中线0.96 cm[1, 4, 11-14]。基于此,我们假设,如果甲状舌管囊肿位于舌骨水平或者舌骨下方,其瘘管走行可能通过舌骨影响舌骨发育,导致舌骨体形态的改变,而这些改变可以成为甲状舌管囊肿的特异性影像学变化,提高术前诊断的精确性。为此我们设立甲舌组和对照组,并设立相应的纳入标准,比较两组在舌骨体高度、舌骨体宽度、舌骨体厚度,以及舌骨体宽度/舌骨体高度和舌骨体厚度/舌骨体高度的比值间的差异。结果显示虽然甲舌组和对照组间的舌骨体高度差异无统计学意义,但是舌骨体宽度、舌骨体厚度、舌骨体宽度/舌骨体高度、舌骨体厚度/舌骨体高度方面的差异均有统计学意义。这些研究结果支持了我们的假设,即甲状舌管囊肿如果位于舌骨水平或者舌骨下方,其瘘管走行可能通过舌骨进而影响舌骨体发育,并在影像学上表现出来,为甲状舌管囊肿的术前诊断及鉴别诊断提供参考指标。
对于甲状舌管囊肿的治疗,如果仅仅切除囊肿,则有着较高的复发率,而采用Sistrunk手术,复发率在5%左右[15-16]。Sistrunk(1920)术式的切除范围包括囊肿、舌骨体中间的1/3,并分离瘘管至舌盲孔周围,然后缝合舌盲孔。手术中对于舌骨体中间1/3的定位有实际困难,因此有学者建议切除舌骨中段至少1.0 cm以上及其附着组织,可以降低复发率[14]。徐夏等[17]通过对术后复发病例的研究发现,手术中未切除舌骨中段,或者切除舌骨范围不够,可能是导致甲状舌管囊肿复发的主要原因,因此,切除舌骨中段1.0 cm可能不够,导致瘘管残留复发。结合我们的影像学研究结果,可以推测,术中切除整个舌骨体,而不仅仅是舌骨中段的1/3,或许可以进一步减少瘘管残留可能,降低复发率。然而刘平凡等[18]认为,甲状舌管囊肿术后复发并非取决于是否切除舌骨,而是取决于其分支的残留。我们目前的结论与这一研究结果存在矛盾,需要进一步研究,比如扩大样本量,纳入舌内型甲状舌管囊肿,设立前瞻性对照研究等,结论或许更有意义。
综上所述,甲状舌管囊肿舌骨体形态的改变可能有助于术前诊断,舌骨体切除可能有助于减少术后复发。
利益冲突 所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
-
表 1 甲舌组和对照组相关数据比较
组别 例数 舌骨体高度/mm 舌骨体宽度/mm 舌骨体厚度/mm 舌骨体宽度/舌骨体高度秩和平均值 舌骨体厚度/舌骨体高度秩和平均值 甲舌组 29 8.93±0.22 5.09±0.21 3.84±0.12 53.95 59.90 对照组 58 8.94±0.12 4.48±0.11 3.13±0.08 39.03 36.05 t值 -0.040 2.845 4.816 Z值 -2.598 -4.154 P值 0.968 0.006 0.001 0.009 0.001 -
[1] Policeni BA, Smoker WR, Reede DL. Anatomy and embryology of the thyroid and parathyroid glands[J]. Semin Ultrasound CT MR, 2012, 33(2): 104-114. doi: 10.1053/j.sult.2011.12.005
[2] Lee DH, Jung SH, Yoon TM, et al. Preoperative computed tomography of suspected thyroglossal duct cysts in children under 10-years-of-age[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2013, 77(1): 45-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2012.09.027
[3] Patel S, Bhatt AA. Thyroglossal duct pathology and mimics[J]. Insights Imaging, 2019, 10(1): 12. doi: 10.1186/s13244-019-0694-x
[4] Mondin V, Ferlito A, Muzzi E, et al. Thyroglossal duct cyst: personal experience and literature review[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2008, 35(1): 11-25. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2007.06.001
[5] Deaver MJ, Silman EF, Lotfipour S. Infected thyroglossal duct cyst[J]. West J Emerg Med, 2009, 10(3): 205.
[6] Davenport M. ABC of general surgery in children. Acute problems of the scrotum[J]. BMJ, 1996, 312(7028): 435-437. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7028.435
[7] Friedman ER, John SD. Imaging of pediatric neck masses[J]. Radiol Clin North Am, 2011, 49(4): 617-632, v. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2011.05.005
[8] Ng A, Yuen HW, Huang XY. Atypical thyroglossal duct cyst with intra-laryngeal and para-glottic extension[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2019, 40(4): 601-604. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2019.04.007
[9] Malloy KM, Christenson T, Meyer JS, et al. Lack of association of CT findings and surgical drainage in pediatric neck abscesses[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2008, 72(2): 235-239. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2007.10.016
[10] Rodríguez-Vázquez JF, Kim JH, Verdugo-López S, et al. Human fetal hyoid body origin revisited[J]. J Anat, 2011, 219(2): 143-149. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2011.01387.x
[11] Bezerra Júnior GL, Silva LF, Pimentel GG, et al. Treatment of Large Thyroglossal Duct Cyst[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2017, 28(8): e794-e795. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000002915
[12] Hsiao JH, Chao WC, Lee YC. Infected Lingual Thyroglossal Duct Cyst Mimicking Supraglottitis[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2019, 30(4): e380-e382. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000005427
[13] Mukul S, Kumar A, Mokhtar E. Sublingual thyroglossal duct cyst(SLTGDC): An unusual location[J]. J Pediatr Surg Case Rep, 2016, 10(C): 3-6.
[14] Horisawa M, Niinomi N, Ito T. Anatomical reconstruction of the thyroglossal duct[J]. J Pediatr Surg, 1991, 26(7): 766-769. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(91)90134-F
[15] Inarejos Clemente E, Oyewumi M, Propst EJ, et al. Thyroglossal duct cysts in children: Sonographic features every radiologist should know and their histopathological correlation[J]. Clin Imaging, 2017, 46: 57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2017.07.002
[16] Pitner H, Elmaraghy C, Fischer B, et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Midline Pediatric Neck Masses[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 160(6): 1111-1117. doi: 10.1177/0194599819827845
[17] 徐夏, 李力, 刘环海, 等. 扩大舌骨及周围组织切除治疗复发性感染性甲状舌管囊肿及瘘管[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2010, 45(2): 160-161.
[18] 刘平凡, 林宗通, 杨中婕, 等. 54例保留舌骨的儿童甲状舌管囊肿切除术疗效分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(6): 505-507. https://lceh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=90e035a0-e9c8-4ce2-acaa-01edf9ebcff1
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 张海港,樊明月,姬维仓,赵兴贺. 儿童复发性甲状舌管囊肿和瘘管的复发因素及二次手术效果的临床研究. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志. 2025(05): 482-485 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 张军军,赵倩倩,梁乐平,赵大庆,丁雪瑞. 15例甲状舌管囊肿误诊病例分析. 重庆医学. 2024(10): 1504-1507 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 梁发雅,韩萍,林沛亮,林惜君,陈仁辉,王静怡,邹鑫,黄晓明. 免充气经口下唇前庭入路机器人辅助甲状舌管囊肿切除术临床分析. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志. 2023(07): 524-528 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)
-




 下载:
下载: