The value of threshold of neural response telemetry on the prediction of behavioral audiometry threshold after cochlear implantation patients
-
摘要: 目的 通过分析正常耳蜗形态与内耳畸形的人工耳蜗植入儿童主观行为测试法阈值和神经反应遥测(NRT)阈值的规律及相关性,探讨利用NRT阈值指导术后调机的价值。方法 对30例正常耳蜗形态(耳蜗正常组)和12例内耳畸形(内耳畸形组)的人工耳蜗植入儿童分别选取1、6、11、16、22号电极进行NRT测试和主观行为测试,并选取代表高频的1号电极、中频的11号电极、低频的22号电极分析NRT阈值与T值、C值的相关关系。结果 耳蜗正常组与内耳畸形组的NRT阈值平均值均大于T值,靠近且略小于C值。内耳畸形组的T值、C值和NRT阈值的平均值均略大于耳蜗正常组。耳蜗正常组与内耳畸形组的高、中、低频段NRT阈值与C值、T值显著相关。与正常耳蜗组相比,内耳畸形组在高、中、低频段两组的NRT阈值与T值的回归系数b相差20.90%、3.02%、9.68%,k相差13.01%、3.92%、5.28%;两组的NRT阈值与C值的回归系数b相差15.74%、2.51%、0.53%,k相差14.44%、0.24%、4.09%,可见在高频段两组植入者的NRT阈值与T值、C值的相关关系有明显区别,而在低、中频段较为相近。结论 NRT阈值与主观行为测试阈值显著相关,所得到的线性回归方程可用于指导人工耳蜗调机,特别是针对内耳畸形儿童的高频段T值与C值,应采用与正常耳蜗儿童不同的回归方程进行预估,以获得更为准确的T值与C值。Abstract: Objective To explore the feasibility of using the threshold of neural response telemetry(NRT) to guide postoperative machine adjustment by analyzing the regularity and correlation between the threshold of subjective behavior test and NRT in cochlear implant patients with normal cochlear morphology and inner ear malformation.Methods Thirty cochlear implant patients with normal cochlear morphology and 12 cochlear implant patients with inner ear malformation were selected for NRT test and subjective behavior test, respectively. Electrode 1 representing high frequency, electrode 11 representing medium frequency and electrode 22 representing low frequency were selected to analyze the correlation between NRT threshold and T value and C value.Results The mean NRT threshold values of the cochlear normal group and the inner ear malformation group were both greater than T value, close to and slightly smaller than C value. The T value, C value and NRT threshold of the inner ear malformation group were slightly higher than those of the cochlear normal group. The NRT thresholds of high, middle and low frequency bands were significantly correlated with C and T values in the normal cochlear group and the inner ear malformation group. Compared with the normal cochlear group, the regression coefficientsBof NRT threshold and T value in the high, medium and low frequency groups were 20.90%, 3.02%, 9.68%, and theKcoefficients were 13.01%, 3.92%, 5.28%. The regression coefficients B of NRT threshold and C value of the two groups were 15.74%, 2.51%, 0.53%, andKwere 14.44%, 0.24%, 4.09%, respectively. It can be seen that the correlation between NRT threshold and T value and C value of the two groups was significantly different in the high frequency band, but similar in the low and middle frequency band.Conclusion The NRT threshold is significantly correlated with the threshold of subjective behavior test. The linear regression equation obtained can be used to guide the cochlear implant tuning machine, especially for the high frequency band T and C values of patients with inner ear malformation implantation. Different regression equations should be used to estimate the T and C values of patients with normal cochlea, so as to obtain more accurate T and C values.
-
人工耳蜗植入术是有效帮助重度及极重度听觉言语残疾患者重建听力的最佳方法[1],术后对人工耳蜗参数进行精准评估与调试,对保证人工耳蜗听力重建效果十分重要,也是术后听觉康复训练的前提[2]。在人工耳蜗调机过程中需要对所刺激的电极进行至少两个水平的设置,即能够引起小声听觉的最小电流强度值(T-level)与能够引起大声听觉而没有不舒服感觉的最大电流强度值成为舒适值(C-level),从而构成了植入者的电听觉动态范围参数[3-4]。因此,确定动态范围参数(T值、C值)是保证患者有效舒适使用人工耳蜗的重要环节[5]。一般临床上以主观心理物理测试(纯音测听及行为测听)为首选,此方法可以获得准确的T值和C值[6]。然而,对小龄婴幼儿和听力障碍合并认知心理疾病且无法配合完成行为测试的患者,即使通过行为观察能够测得T值和C值,其准确性也欠佳,难以提供可靠的测试结果。
目前,神经反应遥测(neural response telemetry,NRT)技术可记录电刺激诱发的听神经动作电位,可用于术后调机的客观检查,其不受主观因素影响,从而可以准确地获得客观阈值,以指导术后调试[7]。杨烨等[8]发现电诱发复合动作电位(electrically evoked compound action potential,ECAP)阈值与行为T值、C值之间呈弱的正相关性,王亮等[9]提出将T值直接设定为ECAP阈值处。越来越多的研究关注NRT阈值与T、C值相关性并指导T、C值的临床调试。近年来,诸多内耳畸形患儿也纳入手术的范围。本研究拟探究正常耳蜗形态与内耳畸形人工耳蜗植入患儿术后NRT阈值与T、C值的特点规律,分析二者间的相关性并总结规律,以指导上述两类群体人工耳蜗的临床编程及调机工作。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
选取天津市第一中心医院2018年2月-2022年4月收治的人工耳蜗植入儿童42例,无手术禁忌证且所有患儿家属均签署知情同意书。其中耳蜗正常组30例,男16例,女14例,平均年龄(37.8±9.8)个月,平均植入年龄为(21.3±9.5)个月;内耳畸形组12例,男8例,女4例,平均年龄(59.5±25.0)个月,平均植入年龄为(13.3±8.2)个月,包括大前庭导水管综合征9例,内耳道狭窄3例。两组患者均植入Cochlear公司人工耳蜗,应用CI512植入体17人,应用CI24RE(CA)植入体13例,CI422植入体12例。开机后1个月左右进行NRT检测。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 NRT测试
采用Cochlear公司提供的Custom Sound 4.3软件,选择AutoNRT测试项。便携式编程系统,测试参数包括:刺激频率900 Hz,刺激脉宽25 μs/相,采用MP1+2刺激模式(单极刺激模式),持续时间为500 μs。测试步骤为:设置初始刺激强度为100 CL,其他参数为默认值,软件根据此强度下是否引出波形增加或降低刺激强度直至达到NRT阈值并记录。当默认参数最大刺激强度下未引出波形时,进行手动操作,增加脉宽设置,此时通过观察判断波形阈值。选择第1、6、11、16、22号刺激电极,以NRT波形即将消失时刺激强度的临界值(可引出波形的最小电流量值)作为NRT阈值。
1.2.2 T值与C值的主观行为测试
测试前向患者仔细讲解所要进行测试指标的含义,以使其理解并取得充分配合。在本底噪声 < 35 dB SPL(A)的电磁屏蔽室中测试,采用Maestro system Software5.0软件给刺激声,应用儿童行为测听法,确定患儿行为测听(T值)和最大舒适阈值(C值)。根据主观行为电量级阈值,对人工耳蜗进行调试并记录数据。
1.3 统计学方法
采用SPSS 23.0统计学软件,对NRT阈值与主观T值、C值之间的关系采用线性回归与相关分析。
2. 结果
2.1 主观T值、C值和NRT阈值测试结果
耳蜗正常组与内耳畸形组的T值、C值和NRT阈值测试结果分别如表 1与表 2所示。两组患儿的NRT阈值平均值均大于T值,靠近且略小于C值。内耳畸形组的T值、C值和NRT阈值的平均值均略大于耳蜗正常组。
表 1 正常耳蜗患者组T值、C值与NRT阈值的测试结果X±S,n=30,CL 电极 1号 6号 11号 16号 22号 T值 135.17±18.51 138.01±15.68 140.67±14.93 135.83±15.87 124.47±18.58 C值 171.77±29.34 175.57±29.52 182.77±24.92 169.20±27.37 159.33±19.45 NRT阈值 169.97±18.26 172.87±15.93 175.47±14.37 167.37±19.32 158.27±26.55 表 2 内耳畸形患者组T值、C值与NRT阈值的测试结果X±S,n=12,CL 电极 1号 6号 11号 16号 22号 T值 135.63±20.53 142.50±16.39 147.51±11.46 138.75±13.64 132.50±19.53 C值 173.88±22.07 185.13±20.46 200.01±19.21 180.88±21.73 169.13±21.78 NRT阈值 170.50±11.26 179.13±19.70 185.13±13.12 177.25±14.94 166.25±16.14 2.2 NRT阈值与T值、C值的相关性分析
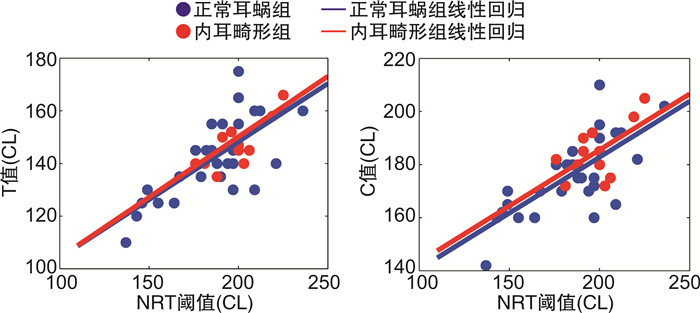
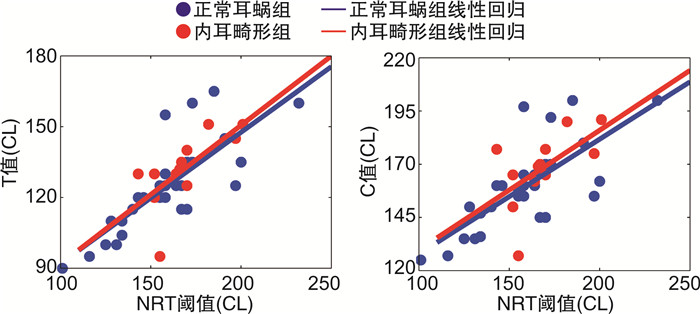
选取1号电极代表高频,11号电极代表中频,22号电极代表低频,耳蜗正常组与内耳畸形组在上述三个频段的NRT阈值与T值、C值的相关关系分别如表 3、4所示,耳蜗正常组高、中、低频段NRT阈值与C值、T值显著相关(P < 0.01),内耳畸形组高、中、低频段NRT阈值与C值、T值显著相关(P < 0.05)。耳蜗正常组与内耳畸形组在这三个频段的NRT阈值与T值、C值线性回归系数分别如表 5、6所示,线性回归方程分别为T=bT+kT×NRT,C=bC+kC×NRT,其相关关系如图 1~3所示,可通过NRT阈值预测T值与C值。
表 3 正常耳蜗患者组T值、C值与NRT阈值的相关关系高频 中频 低频 r P r P r P T值 0.84 < 0.001 0.74 < 0.001 0.79 < 0.001 C值 0.84 < 0.001 0.73 < 0.001 0.74 < 0.001 表 4 内耳畸形患者组T值、C值与NRT阈值的相关关系高频 中频 低频 r P r P r P T值 0.609 0.018 0.758 0.002 0.686 0.007 C值 0.540 0.035 0.592 0.021 0.577 0.025 表 5 正常耳蜗患者T值、C值与NRT阈值的回归系数高频 中频 低频 b k b k b k T值 44.08 0.53 60.13 0.44 36.41 0.56 C值 80.17 0.52 98.59 0.42 73.96 0.54 注:NRT阈值与T值回归方程为T=bT+kT×NRT;NRT阈值与C值回归方程为C=bC+kC×NRT。 表 6 内耳畸形患者T值、C值与NRT阈值的回归系数高频 中频 低频 b k b k b k T值 55.72 0.47 58.37 0.46 33.12 0.59 C值 95.15 0.46 101.12 0.42 73.57 0.56 注:NRT阈值与T值回归方程为T=bT+kT×NRT;NRT阈值与C值回归方程为C=bC+kC×NRT。 3. 讨论
人工耳蜗术后调机设置T值与C值将直接影响植入者的使用效果。目前临床采用的手段为通过指定电极刺激电流,引出波形并获取NRT阈值,以此为客观依据并配合主观性行为测试法调试T值与C值,以达到综合效果最佳。然而,一方面低龄婴幼儿无法配合主观行为测试,调试准确度低[10];另一方面,客观测试的NRT阈值与T值、C值的相关性研究还有待完善,特别是针对正常耳蜗与内耳畸形两类儿童群体,采用相同回归方程预测T值、C值是否合理,尚未明确。
本研究选择1、6、11、16、22号电极,针对耳蜗正常组与内耳畸形组两类植入儿童群体,于开机后1个月左右测试NRT阈值与T值、C值。结果显示,两组患儿的NRT阈值平均值均大于T值,靠近且略小于C值,符合在NRT阈值基础上减20~30 CL预估T值,在NRT阈值附近设置C值的规律[11]。两组患儿从低频到高频各电极NRT阈值的平均值有显著差异,总趋势由低变高,应与两方面因素相关:①低频较高频有更高的残余听力;②耳蜗顶部与底部电极与耳蜗轴的螺旋神经节细胞距离不同。内耳畸形组的T值、C值和NRT阈值的平均值均略大于耳蜗正常组。这是由于内耳畸形患儿残存螺旋神经节细胞数目少且分布异常、神经同步性差、植入直电极时损伤残余听力、耳蜗畸形结构导致内部电极刺激相互干扰、弯电极较直电极具有轻微节能特性[12]等因素,导致内耳畸形患儿NRT阈值增大、记录增益延迟等参数调节较多,甚至无法引出NRT波形[13-15]。
本研究选择1、11、22号电极分别代表高、中、低频段分析T值、C值和NRT阈值间的线性关系,结果表明各频段的T值、C值与NRT阈值存在显著的正相关关系,获取的回归方程对T值、C值的预测具有临床指导意义。将正常耳蜗组与内耳畸形组的相关性分析结果进行对比,在高、中、低频段两组的NRT阈值与T值的回归系数b相差20.90%、3.02%、9.68%,k相差13.01%、3.92%、5.28%;两组的NRT阈值与C值的回归系数b相差15.74%、2.51%、0.53%,k相差14.44%、0.24%、4.09%,可见在高频段两组植入者的NRT阈值与T值、C值的相关关系有明显区别,而在低、中频段较为相近。其原因可能在于内耳畸形患者存在耳蜗死区[16],即耳蜗基膜上某区域的内毛细胞损伤或相接的神经元功能失活或退化,这些死区主要分布在高频区域,降低患者言语识别能力,导致高频区域NRT阈值与T值、C值的相关关系与正常耳蜗患者存在差异。
综上,本研究所得到的线性回归方程可用于指导人工耳蜗植入儿童调机,特别是针对内耳畸形植入儿童的高频段T值与C值,应采用与正常耳蜗患儿不同的回归方程进行预估,以获得更为准确的T值和C值。这一结论对于主观行为测试效果受限的内耳畸形患儿人工耳蜗临床调机具有指导意义。虽然NRT测试的电生理反应可反映外周听神经生理状况,但是无法表征理解、认知等更高层次中枢的生理活动,故客观评估更高级听觉传导通路还需借助电诱发听觉脑干反应及其他测试手段。
基于本研究成果,下一阶段研究需探讨内耳畸形患儿耳蜗死区所在高频段的频率范围,揭示其带宽与NRT阈值的相关关系,进而厘清在高频段导致耳蜗正常与内耳畸形儿童NRT阈值与C、T值相关关系差异的机制。此外,还应进一步分析儿童与成人在NRT阈值与C值、T值测试方法与结果方面的差异,研究面向成人群体效率高、效果好的客观调机方法。
利益冲突 所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
-
表 1 正常耳蜗患者组T值、C值与NRT阈值的测试结果
X±S,n=30,CL 电极 1号 6号 11号 16号 22号 T值 135.17±18.51 138.01±15.68 140.67±14.93 135.83±15.87 124.47±18.58 C值 171.77±29.34 175.57±29.52 182.77±24.92 169.20±27.37 159.33±19.45 NRT阈值 169.97±18.26 172.87±15.93 175.47±14.37 167.37±19.32 158.27±26.55 表 2 内耳畸形患者组T值、C值与NRT阈值的测试结果
X±S,n=12,CL 电极 1号 6号 11号 16号 22号 T值 135.63±20.53 142.50±16.39 147.51±11.46 138.75±13.64 132.50±19.53 C值 173.88±22.07 185.13±20.46 200.01±19.21 180.88±21.73 169.13±21.78 NRT阈值 170.50±11.26 179.13±19.70 185.13±13.12 177.25±14.94 166.25±16.14 表 3 正常耳蜗患者组T值、C值与NRT阈值的相关关系
高频 中频 低频 r P r P r P T值 0.84 < 0.001 0.74 < 0.001 0.79 < 0.001 C值 0.84 < 0.001 0.73 < 0.001 0.74 < 0.001 表 4 内耳畸形患者组T值、C值与NRT阈值的相关关系
高频 中频 低频 r P r P r P T值 0.609 0.018 0.758 0.002 0.686 0.007 C值 0.540 0.035 0.592 0.021 0.577 0.025 表 5 正常耳蜗患者T值、C值与NRT阈值的回归系数
高频 中频 低频 b k b k b k T值 44.08 0.53 60.13 0.44 36.41 0.56 C值 80.17 0.52 98.59 0.42 73.96 0.54 注:NRT阈值与T值回归方程为T=bT+kT×NRT;NRT阈值与C值回归方程为C=bC+kC×NRT。 表 6 内耳畸形患者T值、C值与NRT阈值的回归系数
高频 中频 低频 b k b k b k T值 55.72 0.47 58.37 0.46 33.12 0.59 C值 95.15 0.46 101.12 0.42 73.57 0.56 注:NRT阈值与T值回归方程为T=bT+kT×NRT;NRT阈值与C值回归方程为C=bC+kC×NRT。 -
[1] Nieman CL, Oh ES. Hearing Loss[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2020, 173(11): ITC81-ITC96. doi: 10.7326/AITC202012010
[2] Sheffield AM, Smith R. The Epidemiology of Deafness[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 2019, 9(9).
[3] Fink D. Review of Hearing Loss in Children[J]. JAMA, 2021, 325(12): 1223-1224. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.0387
[4] Carlson ML. Cochlear Implantation in Adults[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 382(16): 1531-1542. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1904407
[5] 罗琼, 黄艳艳, 陈正侬, 等. 人工耳蜗术后编程中神经反应遥测阈值及行为T值的比较分析[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报, 2017, 31(5): 23-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYU201705006.htm
[6] 王铮, 李巍, 田颖, 等. 客观听觉监测技术在人工耳蜗植入中的临床应用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2014, 28(7): 435-439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201407001.htm
[7] 王振晓, 王林娥, 龚树生, 等. 蜗轴缺如畸形患者人工耳蜗植入术后电诱发听性脑干反应特点[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 31(2): 111-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201702009.htm
[8] 杨烨, 高下, 陈杰, 等. 语后聋人工耳蜗植入的参数变化规律及意义[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2012, 10(4): 455-458. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHER201204021.htm
[9] 王亮, 董明敏. 人工耳蜗术后客观调机过程中电诱发听觉脑干反应、电诱发听神经复合动作电位和电诱发蹬骨肌反射的指导作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007, 11(9): 1713-1715. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDKF200709032.htm
[10] 乔晓峰, 王东, 雒星梅. 内耳畸形小儿人工耳蜗植入术后神经反应遥测值的研究[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2014, 21(1): 29-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201401012.htm
[11] 杨烨, 陈杰, 钱晓云, 等. 神经反应遥测用于人工耳蜗植入患儿术后康复效果预估和编程的意义[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2015, 23(5): 522-526. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TLXJ201505020.htm
[12] 陶勇, 郑芸, 王恺, 等. Nucleus 24人工耳蜗系统直电极与弯电极神经反应遥测值的比较[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2012, 26(1): 8-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201201002.htm
[13] Hay-McCutcheon MJ, Brown CJ, Clay KS, et al. Comparison of electrically evoked whole-nerve action potential and electrically evoked auditory brainstem response thresholds in nucleus CI24R cochlear implant recipients[J]. J Am Acad Audiol, 2002, 13(8): 416-427.
[14] Khan AM, Levine SR, Nadol JB Jr. The widely patent cochleovestibular communication of Edward Cock is a distinct inner ear malformation: implications for cochlear implantation[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2006, 115(8): 595-606.
[15] Graham JM, Phelps PD, Michaels L. Congenital malformations of the ear and cochlear implantation in children: review and temporal bone report of common cavity[J]. J Laryngol Otol Suppl, 2000, 25: 1-14.
[16] 王晨露, 史文迪, 张娜, 等. 大前庭导水管综合征患者耳蜗死区分布研究[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2020, 27(11): 633-635. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT202011007.htm
-




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: