Profiles of IgE sensitization to dust mite allergen components in patients with allergic rhinitis and asthma
-
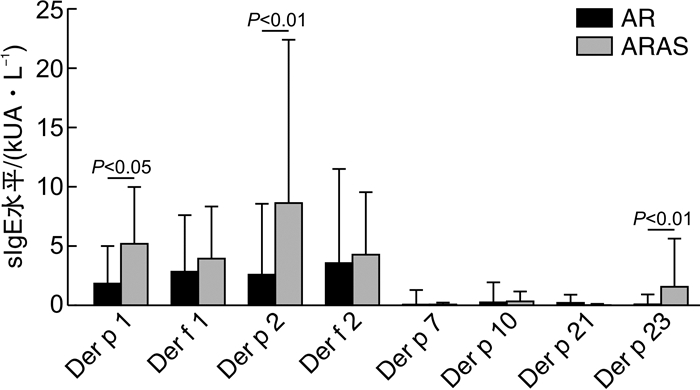
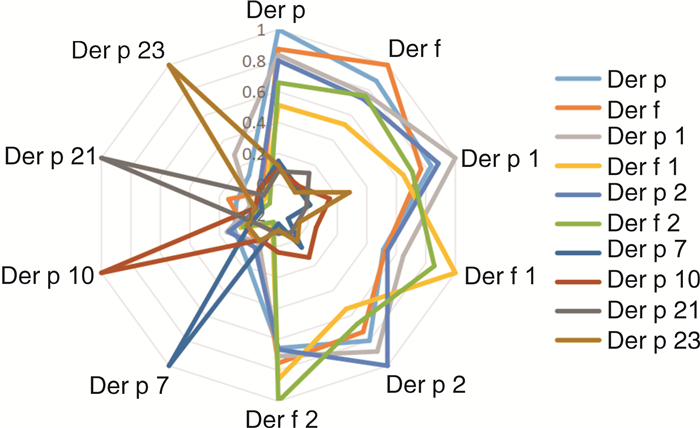
摘要: 目的 研究变应性鼻炎(AR)、AR伴哮喘综合征(ARAS)患者的尘螨致敏组分蛋白差异及其临床意义。方法 回顾性分析42例AR伴或不伴哮喘患者的临床资料,分为AR组和ARAS组。采用ImmunoCAP过敏原检测系统检测体外血清户尘螨和粉尘螨sIgE浓度。同时采用蛋白芯片法进行户尘螨组分(Der p 1、Der p 2、Der p 7、Der p 10、Der p 21、Der p 23)和粉尘螨组分(Der f 1、Der f 2)检测,分析尘螨过敏原及其组分在AR组和ARAS组中的表达差异。结果 31例AR和11例ARAS纳入研究。户尘螨阳性率为100.0%,粉尘螨为97.6%。尘螨组分蛋白致敏率由高到低依次为Der p 1(73.8%)、Der f 1(66.7%)、Der f 2(64.3%)、Der p 2(61.9%)。ARAS组的尘螨组分蛋白Der f 1(100.0%和54.8%,P=0.006)、Der p 2(90.9%和51.6%,P=0.021)、Der f 2(100.0%和51.6%,P=0.004)致敏率显著高于AR组。AR组户尘螨sIgE浓度显著低于ARAS组[(7.65±12.15) kUA/L和(15.20±18.77) kUA/L,P < 0.05]。ARAS组Der p 1[(5.39± 4.61) kUA/L和(2.03±2.97) kUA/L,P=0.013]、Der p 2[(8.82± 13.58) kUA/L和(2.78±5.80) kUA/L,P=0.001]、Der p 23[(1.76± 3.88) kUA/L和(0.28±0.65) kUA/L,P < 0.001]的sIgE浓度显著高于AR组。相关性分析发现Der p 1、Der p 2、Der f 1、Der f 2具有高度正相关性(P < 0.01)。户尘螨组分致敏表现出多重致敏的特点,42例患者中,66.7%出现≥2种的户尘螨组分蛋白阳性,AR组为58.1%,ARAS组为90.9%。ARAS组更倾向于多种组分致敏,≥3种的组分致敏率显著高于AR组(54.6%和29.1%,P < 0.05)。结论 ARAS较AR患者尘螨浓度更高,Der p 1、Der f 1、Der p 2、Der f 2是主要致敏蛋白组分,致敏率在ARAS患者中更高。Der p 1、Der p 2、Der p 23的浓度在ARAS患者中更高。ARAS患者更倾向于多重组分致敏。
-
关键词:
- 变应性鼻炎伴哮喘综合征 /
- 户尘螨 /
- 粉尘螨 /
- 致敏组分
Abstract: Objective To study the differences and clinical significance of dust mite allergen components in allergic rhinitis(AR) and allergic rhinitis with asthma syndrome(ARAS) patients.Methods The clinical data of 42 AR patients were retrospectively analyzed and patients were divided into AR and ARAS group. The serum sIgE concentrations of house dust mites were detected by ImmunoCAP system. The allergen components of Der p(Der p 1, Der p 2, Der p 7, Der p 10, Der p 21, Der p 23) and Der f(Der f 1, Der f 2) were analyzed by protein microarray method. The concentration differences of dust mite allergen and its components in AR and ARAS groups were analyzed.Results Thirty-one cases of AR and 11 cases of ARAS were included. The positive rate of Der p and Der f was 100.0% and 97.6%, respectively. The highest sensitization rates of Der p allergen components were as following: Der p 1(73.8%), Der f 1(66.7%), Der f 2(64.3%) and Der p 2(61.9%). The sensitization rates of Der f 1(100.0% vs 54.8%, P=0.006), Der p 2(90.9% vs 51.6%, P=0.021) and Der f 2(100.0% vs 51.6%, P=0.004) in ARAS group were significantly higher than those in AR group. The sIgE concentrations of Der p in AR group were significantly lower than those in ARAS group([7.65±12.15]kUA/L vs[15.20±18.77]kUA/L, P < 0.05). The sIgE concentrations of Der p 1([5.39±4.61]kUA/L vs[2.03±2.97]kUA/L, P=0.013), Der p 2([8.82± 13.58]kUA/L vs[2.78±5.80]kUA/L, P=0.001), Der p 23([1.76± 3.88]kUA/L vs[0.28±0.65]kUA/L, P < 0.001) was significantly higher in ARAS group than that of AR group. Correlation analysis showed that Der p 1, Der p 2, Der f 1 and Der f 2 had high positive correlation(P < 0.01). The dust mite components sensitization showed a multiple-sensitized mode. 66.7% of the 42 patients were positive for two or more components while it was 58.1% of the AR group and 90.9% of the ARAS group. The sensitization rate of 3 or more components in ARAS group was significantly higher than that in AR group(54.6% vs 29.1%, P < 0.05).Conclusion The concentration of dust mites allergens in ARAS group is higher than that in AR group. Der p 1, Der f 1, Der p 2 and Der f 2 are the main allergen components with a higher sensitization rate in ARAS group. The concentrations of Der p 1, Der p 2 and Der p 23 were higher in ARAS group. The ARAS group is prone to multi-sensitzed to allergen components. -

-
表 1 AR组和ARAS组尘螨及其组分的阳性率比较
% 过敏原/组分 AR+ARAS AR组 ARAS组 χ2 P值 Der p 100.0 100.0 100.0 Der f 97.6 96.8 100.0 0.363 0.547 Der p 1 73.8 67.7 90.9 2.254 0.133 Der f 1 66.7 54.8 100.0 7.452 0.006 Der p 2 61.9 51.6 90.9 5.316 0.021 Der f 2 64.3 51.6 100.0 8.280 0.004 Der p 7 11.9 12.9 9.1 0.113 0.737 Der p 10 23.8 16.1 45.5 3.849 0.050 Der p 21 7.1 9.7 0 1.146 0.284 Der p 23 21.4 19.4 27.3 0.302 0.582 表 2 户尘螨致敏蛋白组分阳性数在AR组和ARAS组中的差异
% 组分阳性数 AR+ARAS AR组 ARAS组 0 14.3 16.1 9.0 1 19.0 25.8 0 2 31.0 29.0 36.4 3 26.2 22.6 36.4 4 7.1 6.5 9.1 5 2.4 0 9.1 -
[1] Meng Y, Wang C, Zhang L. Recent developments and highlights in allergic rhinitis[J]. Allergy, 2019, 74(12): 2320-2328. doi: 10.1111/all.14067
[2] Ozdoganoglu T, Songu M. The burden of allergic rhinitis and asthma[J]. Ther Adv Respir Dis, 2012, 6(1): 11-23. doi: 10.1177/1753465811431975
[3] Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma(ARIA)2008 update(in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2) LEN and AllerGen)[J]. Allergy, 2008, 63 Suppl 86: 8-160.
[4] Samitas K, Carter A, Kariyawasam HH, et al. Upper and lower airway remodelling mechanisms in asthma, allergic rhinitis and chronic rhinosinusitis: The one airway concept revisited[J]. Allergy, 2018, 73(5): 993-1002. doi: 10.1111/all.13373
[5] 程雷, 周文成, 陆美萍. 中国变应性鼻炎和哮喘舌下免疫治疗指南英文版精要解读[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(4): 292-295. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-LCEH202004002.htm
[6] 王晓艳, 王洪田, 王学艳. 尘螨的生物学特性与除螨措施及其效果[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 55(7): 720-725. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20200226-00131
[7] Steering Committee Authors, Review Panel Members. A WAO-ARIA-GA2LEN consensus document on molecular-based allergy diagnosis(PAMD@): Update 2020[J]. World Allergy Organ J, 2020, 13(2): 100091. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2019.100091
[8] Cao H, Liu Z. Clinical significance of dust mite allergens[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2020, 47(8): 6239-6246. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05613-1
[9] Hellings PW, Seys SF, Marien G, et al. ARIA masterclass 2018: From guidelines to real-life implementation[J]. Rhinology, 2019, 57(5): 392-399.
[10] D'souza N, Weber M, Sarzsinszky E, et al. The Molecular Allergen Recognition Profile in China as Basis for Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 719573. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.719573
[11] Matricardi PM, Kleine-Tebbe J, Hoffmann HJ, et al. EAACI Molecular Allergology User's Guide[J]. Pediatr Allergy Immunol, 2016, 27 Suppl 23: 1-250.
[12] Tian M, Zhou Y, Zhang W, et al. Der p 1 and Der p 2 specific immunoglobulin E measurement for diagnosis of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus allergy: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Allergy Asthma Proc, 2017, 38(5): 333-342. doi: 10.2500/aap.2017.38.4073
[13] Hu H, Luo W, Wu Z, et al. A pilot study on the allergen-specific IgE to molecular components on polysensitized mite allergic asthmatic patients in Guangzhou, China[J]. Mol Immunol, 2019, 105: 38-45. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.11.004
[14] Zheng YW, Li J, Lai XX, et al. Allergen micro-array detection of specific IgE-reactivity in Chinese allergy patients[J]. Chin Med J(Engl), 2011, 124(24): 4350-4354.
[15] Yang Y, Zhu R, Huang N, et al. The Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus Molecular Sensitization Profile of Allergic Rhinitis Patients in Central China[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2018, 32(5): 397-403. doi: 10.1177/1945892418787116
[16] Zeng G, Luo W, Zheng P, et al. Component-Resolved Diagnostic Study of Dermatophagoides Pteronyssinus Major Allergen Molecules in a Southern Chinese Cohort[J]. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol, 2015, 25(5): 343-351.
[17] Wang HY, Gao ZS, Zhou X, et al. Evaluation of the Role of IgE Responses to Der p 1 and Der p 2 in Chinese House Dust Mite-Allergic Patients[J]. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2015, 167(3): 203-210. doi: 10.1159/000438724
[18] Jeong KY, Lee JY, Son M, et al. Profiles of IgE Sensitization to Der f 1, Der f 2, Der f 6, Der f 8, Der f 10, and Der f 20 in Korean House Dust Mite Allergy Patients[J]. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res, 2015, 7(5): 483-488. doi: 10.4168/aair.2015.7.5.483
[19] Zou X, Hu H, Huang Z, et al. Serum levels of specific immunoglobulin E to Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus allergen components in patients with allergic rhinitis or/and asthma[J]. Allergy Asthma Proc, 2021, 42(1): e40-e46. doi: 10.2500/aap.2021.42.200105
[20] Weghofer M, Grote M, Resch Y, et al. Identification of Der p 23, a peritrophin-like protein, as a new major Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus allergen associated with the peritrophic matrix of mite fecal pellets[J]. J Immunol, 2013, 190(7): 3059-3067. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202288
[21] Mueller GA, Randall TA, Glesner J, et al. Serological, genomic and structural analyses of the major mite allergen Der p 23[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2016, 46(2): 365-376. doi: 10.1111/cea.12680
[22] Jiménez-Feijoo R, Pascal M, Moya R, et al. Molecular Diagnosis in House Dust Mite-Allergic Patients Suggests That Der p 23 Is Clinically Relevant in Asthmatic Children[J]. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol, 2020, 30(2): 127-132. doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0431
[23] Muddaluru V, Valenta R, Vrtala S, et al. Comparison of house dust mite sensitization profiles in allergic adults from Canada, Europe, South Africa and USA[J]. Allergy, 2021, 76(7): 2177-2188. doi: 10.1111/all.14749
[24] Mueller GA, Randall TA, Glesner J, et al. Serological, genomic and structural analyses of the major mite allergen Der p 23[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2016, 46(2): 365-376. doi: 10.1111/cea.12680
[25] Celi G, Brusca I, Scala E, et al. House dust mite allergy in Italy-Diagnostic and clinical relevance of Der p 23(and of minor allergens): A real-life, multicenter study[J]. Allergy, 2019, 74(9): 1787-1789. doi: 10.1111/all.13776
[26] Limão R, Spínola Santos A, Araújo L, et al. Molecular Profile of Sensitization to Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus Dust Mite in Portugal[J]. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol, 2021, 32(1): 33-39.
[27] Huang Z, Zou X, Chen H, et al. Identifying Potential Co-Sensitization and Cross-Reactivity Patterns Based on Component-Resolved Diagnosis[J]. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2020, 181(2): 81-93. doi: 10.1159/000504320
[28] Xu Q, Jiang Q, Yang L, et al. IgE and IgG4 Repertoire in Asymptomatic HDM-Sensitized and HDM-Induced Allergic Rhinitis Patients[J]. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2021, 182(12): 1200-1211. doi: 10.1159/000517824
[29] Huang Y, Wang C, Lin X, et al. Association between component-resolved diagnosis of house dust mite and efficacy of allergen immunotherapy in allergic rhinitis patients[J]. Clin Transl Allergy, 2019, 9: 64. doi: 10.1186/s13601-019-0305-4
[30] Resch Y, Michel S, Kabesch M, et al. Different IgE recognition of mite allergen components in asthmatic and nonasthmatic children[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2015, 136(4): 1083-1091. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.03.024
[31] Batard T, Baron-Bodo V, Martelet A, et al. Patterns of IgE sensitization in house dust mite-allergic patients: implications for allergen immunotherapy[J]. Allergy, 2016, 71(2): 220-229.
[32] Tan KW, Ong TC, Gao YF, et al. NMR structure and IgE epitopes of Blo t 21, a major dust mite allergen from Blomia tropicalis[J]. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287(41): 34776-34785.
[33] Morjaria JB, Caruso M, Emma R, et al. Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis as a Strategy for Preventing Asthma[J]. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep, 2018, 18(4): 23.
[34] Agache I, Lau S, Akdis CA, et al. EAACI Guidelines on Allergen Immunotherapy: House dust mite-driven allergic asthma[J]. Allergy, 2019, 74(5): 855-873.
[35] Calderón MA, Bousquet J, Canonica GW, et al. Guideline recommendations on the use of allergen immunotherapy in house dust mite allergy: Time for a change?[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2017, 140(1): 41-52.
[36] 孔勇刚, 焦沃尔, 陶泽璋, 等. 变应原免疫治疗对变应性鼻炎的作用机制研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(12): 1149-1152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202112021.htm
[37] Chen KW, Zieglmayer P, Zieglmayer R, et al. Selection of house dust mite-allergic patients by molecular diagnosis may enhance success of specific immunotherapy[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2019, 143(3): 1248-1252. e12.
[38] Rodríguez-Domínguez A, Berings M, Rohrbach A, et al. Molecular profiling of allergen-specific antibody responses may enhance success of specific immunotherapy[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2020, 146(5): 1097-1108.
[39] Fujimura T, Okamoto Y. Antigen-specific immunotherapy against allergic rhinitis: the state of the art[J]. Allergol Int, 2010, 59(1): 21-31.
-




 下载:
下载: