Indications for resection of parapharyngeal space tumors by transoral robotic surgery and prevention and treatment of complications
-
摘要: 目的 探讨经口机器人手术(TORS)切除咽旁间隙肿瘤的临床适应证及常见并发症的预防和处理。方法 回顾性分析2020年7月—2022年2月在复旦大学附属眼耳鼻喉科医院行TORS治疗的23例咽旁间隙肿瘤患者的临床资料,手术分为单纯TORS手术和TORS联合内镜或经颈手术。手术切口采取直接缝合或部分缝合。对术腔靠近口咽平面以下有压迫气道风险者行预防性气管切开。根据术腔是否放置引流管分为引流组8例,非引流组15例。23例患者中,17例肿瘤位于鼻咽顶水平及口咽下界水平之间,行单纯TORS手术切除肿瘤; 1例肿瘤近颅底且上极和腮腺深叶边界不清行TORS联合经颈及内镜手术; 5例瘤体超过鼻咽顶水平行TORS联合内镜手术。结果 仅1例术后术腔出血即行紧急止血,3例术后术腔积液即行穿刺及扩开排液。患者均未出现术腔感染、气道阻塞等并发症。引流组的切口及术腔愈合明显优于非引流组。结论 TORS对于大小和部位适合的咽旁间隙肿瘤是一种安全微创的手术方法。术腔积液是TORS术后常见并发症,对于术腔较大且向咽旁深部延伸或术腔的下方低于手术切口下方的肿瘤,术后放置经鼻负压引流管能够促进口咽黏膜切口及术腔的愈合,减少积液感染术腔并发症的发生。Abstract: Objective This study investigated the clinical indications, prevention and management of common complications of TORS resection of parapharyngeal space tumors.Methods The clinical data of 23 patients with parapharyngeal space tumors treated with TORS in the Eye & ENT Hospital of Fudan University from July 2020 to February 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. The surgical methods were divided into simple TORS surgery and TORS combined endoscopic or cervical surgery. The surgical incision can be directly sutured or partially sutured. If the surgical cavity is below the oropharyngeal plane and there is a risk of airway compression, preventive tracheotomy would be performed. No drainage(15 cases) or transnasal negative pressure drainage tube(8 cases) was placed in the operation cavity. In 17 cases, tumors were located between the top of nasopharynx and the lower boundary of oropharynx and these patients underwent simple TORS surgery; one case received combined cervical and endoscopic surgery, as the tumor was located near the skull base with unclear boundary with the deep lobe of parotid gland; five cases underwent combined endoscopic surgery, as the tumor reached the upper part of the nasopharynx or the outer part of the parapharyngeal space.Results One case underwent emergency hemostasis for postoperative bleeding, and three cases underwent puncture and drainage for postoperative effusion. No complication occurred such as postoperative infection and airway obstruction. The healing grade of surgical incision and surgical cavity in transnasal drainage group was significantly better than that in non-drainage group.Conclusion TORS operation is a safe and minimally invasive method in treating parapharyngeal space tumors with appropriate size and location. Postoperative effusion is a common complication after TORS. In case that surgical cavity extends to the deep parapharyngeal space or the lower part of the surgical cavity is beneath the surgical incision, the placement of transnasal negative pressure drainage tube after operation can improve postoperative recovery and reduce the incidence of complications such as effusion and infection.
-

-
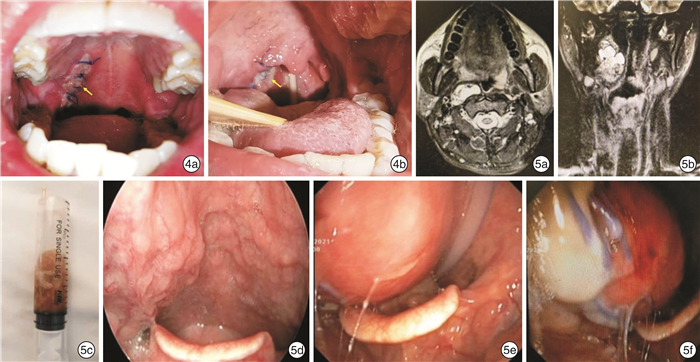
图 4 咽旁间隙肿瘤术后口咽黏膜切口愈合等级典型病例资料 4a:右侧口咽至软腭切口甲级愈合,黏膜对位良好,无开裂、糜烂及红肿,并且切口周围黏膜无隆起; 4b:右侧口咽至鼻咽部切口乙级愈合,黏膜切口愈合欠佳,局部糜烂开裂,但未化脓 图 5 典型术后术腔积液并发症患者临床资料 右侧咽旁间隙淋巴结转移性甲状腺乳头状癌病例,术腔积液,经穿刺抽液及扩开排液后乙级愈合; 5a:术前增强MRI T2加权水平位; 5b:术前增强MRI T2加权冠状位; 5c:术后术腔表面黏膜明显膨隆,穿刺抽出黄色稍浑浊积液,细菌培养为阴性; 5d:术前右侧口咽及喉咽部肿瘤压迫性隆起; 5e、5f:术后术腔积液,口咽及喉咽旁积液,可见切口缝线,咽后壁左侧可见鼻饲管。
表 1 TORS切除23例咽旁间隙肿瘤患者的临床资料
例序 性别 年龄/岁 肿瘤大小/cm 手术方式 出血量/mL 手术时间/h 术后病理 是否放置引流 切口/术腔愈合等级 住院天数 术腔相关并发症 1 男 28 5.7 TORS 30 2.0 神经鞘瘤 是 甲/甲 6 无 2 女 29 2.5 TORS 30 2.0 多形性腺瘤 是 甲/甲 11 无 3 男 42 4.0 TORS 5 1.3 神经鞘瘤 是 甲/甲 5 无 4 女 31 5.3 TORS 40 1.4 神经鞘瘤 是 甲/甲 7 无 5 男 40 7.5 TORS+经颈及内镜 300 5.2 多形性腺瘤 是 甲/甲 10 无 6 女 55 4.0 TORS 150 2.0 基底细胞腺瘤 是 甲/甲 5 无 7 男 25 5.0 TORS 30 1.3 多形性腺瘤 是 甲/甲 6 无 8 男 35 4.5 TORS 35 1.5 多形性腺瘤 是 甲/甲 6 无 9 男 55 4.5 TORS+内镜 150 4.0 非角化型癌 否 乙/乙 15 积液 10 男 49 2.4 TORS+内镜 80 2.5 非角化型癌 否 乙/乙 14 隆起 11 女 61 3.7 TORS+内镜 80 2 多形性腺瘤 否 甲/甲 7 无 12 女 66 4.7 TORS+内镜 120 2.5 多形性腺瘤 否 甲/甲 9 无 13 男 46 5.0 TORS+内镜 180 3 多形性腺瘤 否 乙/乙 10 积液 14 女 61 4.0 TORS 20 1.00 多形性腺瘤 否 甲/甲 5 无 15 女 67 4.7 TORS 180 1.00 多形性腺瘤 否 甲/乙 6 出血 16 男 46 5.0 TORS 150 1.00 多形性腺瘤 否 甲/乙 3 隆起 17 女 42 4.8 TORS 30 1.00 甲状腺乳头状癌淋巴结转移 否 乙/乙 6 积液 18 女 25 3.0 TORS 10 1.33 囊性淋巴管瘤 否 甲/甲 5 无 19 女 51 3.2 TORS 20 2.00 囊肿 否 甲/甲 6 无 20 男 56 5.3 TORS 10 1.50 脂肪瘤 否 乙/乙 6 隆起 21 男 26 6.0 TORS 25 2.10 神经鞘瘤 否 乙/乙 7 隆起 22 男 54 3.2 TORS 30 2.2 神经鞘瘤 否 甲/甲 7 无 23 男 52 3.5 TORS 25 1.5 神经鞘瘤 否 甲/甲 6 无 -
[1] Thaler ER. History and Acceptance of Transoral Robotic Surgery[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2020, 53(6): 943-948. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2020.07.006
[2] 房居高, 孟令照, 王建宏, 等. 经口机器人切除咽喉肿瘤的可行性及安全性探讨[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 53(7): 512-518. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2018.07.006
[3] De Virgilio A, Costantino A, Mercante G, et al. Trans-oral robotic surgery in the management of parapharyngeal space tumors: A systematic review[J]. Oral Oncol, 2020, 103: 104581. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104581
[4] 张星, 李梦华, 陈树伟, 等. 经口机器人手术治疗咽旁间隙肿瘤7例临床分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 56(7): 730-735. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20201101-00846
[5] 胡未鸣, 苏立众, 余凯, 等. 机器人辅助下咽旁间隙肿瘤切除2例[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 52(8): 613-615. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2017.08.012
[6] Sethi RKV, Chen MM, Malloy KM. Complications of Transoral Robotic Surgery[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2020, 53(6): 1109-1115. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2020.07.017
[7] Boyce BJ, Curry JM, Luginbuhl A, et al. Transoral robotic approach to parapharyngeal space tumors: Case series and technical limitations[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126(8): 1776-1782. doi: 10.1002/lary.25929
[8] Panda S, Sikka K, Thakar A, et al. Transoral robotic surgery for the parapharyngeal space: expanding the transoral corridor[J]. J Robot Surg, 2020, 14(1): 61-67. doi: 10.1007/s11701-019-00932-3
[9] Lim JY, Park YM, Kang MS, et al, et al. Comparison of Surgical Outcomes of Robotic and Conventional Approaches in Patients with Pre-and Poststyloid Parapharyngeal Space Tumors[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2020, 27(11): 4535-4543. doi: 10.1245/s10434-020-08536-0
[10] Maglione MG, Guida A, Pavone E, et al. Transoral robotic surgery of parapharyngeal space tumours: a series of four cases[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2018, 47(8): 971-975. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2018.01.008
[11] Moffa A, Fiore V, Rinaldi V, et al. Management of Parapharyngeal Space Tumor Using Transoral Robotic Surgery: The Tonsillar Fossa Battlefield[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2020, 31(6): 1819-1821. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000006453
[12] 侯佳欣, 王玲, 曾泉, 等. 咽旁间隙肿瘤影像学与治疗方式选择[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(10): 937-941. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202010018.htm
[13] 赵建东, 文艺, 纵亮, 等. 原发性咽旁间隙肿瘤治疗的回顾性分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(8): 743-747. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202008015.htm
[14] Dimitrijevic MV, Jesic SD, Mikic AA, et al. Parapharyngeal space tumors: 61 case reviews[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2010, 39(10): 983-989. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2010.06.005
[15] Zhi K, Ren W, Zhou H, et al. Management of parapharyngeal-space tumors[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2009, 67(6): 1239-1244. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2008.09.003
[16] O'Malley BW Jr, Quon H, Leonhardt FD, et al. Transoral robotic surgery for parapharyngeal space tumors[J]. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec, 2010, 72(6): 332-336. doi: 10.1159/000320596
[17] Virós Porcuna D, Pardo Muñoz L, Viña Soria C, et al. A retrospective analysis of surgery in prestyloid parapharyngeal tumors: Lateral approaches vs transoral robotic surgery[J]. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol, 2021, 6(5): 1062-1067. doi: 10.1002/lio2.662
[18] 何龙, 谢景华, 高雄辉. 内镜辅助下经口径路咽旁间隙肿瘤切除术临床分析. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(9): 824-827, 835. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202009013.htm
[19] 龚霄阳, 卫亚楠, 林子萍, 等. 等离子及内镜系统辅助下口内径路治疗咽旁间隙肿瘤疗效分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(3): 204-208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202103003.htm
[20] Lee HS, Kim J, Lee HJ, et al. Transoral robotic surgery for neurogenic tumors of the prestyloid parapharyngeal space[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2012, 39(4): 434-437. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2011.10.021
[21] 侯银龙, 娄卫华, 王亮. 咽旁间隙肿瘤手术并发症分析及防治措施[J]. 河南医学研究, 2011, 20(4): 466-468. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-437x2011.04.029
[22] 王丽, 孙慧子, 杨艳. 咽旁间隙肿瘤手术并发症分析及防治措施[J]. 现代预防医学, 2012, 39(16): 4326-4327. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDYF201216122.htm
[23] 张睿贞, 白松涛, 刘大顺, 等. 口内径路切除咽旁间隙良性肿瘤可行性探讨[J]. 当代医学, 2018, 24(27): 8-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2018.27.004
-




 下载:
下载: