-
摘要: 目的 探讨血清总IgE诊断儿童及青少年特应症的价值。方法 选取2005—2006年美国国家健康与营养调查(NHANES)中接受血清总IgE和血清特异性IgE检测及过敏问卷调查且资料完整的6~19岁参与者的相关数据,根据血清特异性IgE检测和问卷结果分为特应症组和非特应症组,鼻炎组和非鼻炎组,比较血清总IgE组间差异,及其与特应症发病风险的关系;通过受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)分析血清总IgE诊断特应症的价值。结果 ① 血清总IgE在非特应症组的几何均数为24.4 kU/L,特应症组为153.1 kU/L,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01)。②血清总IgE每增加10倍特应症发病风险增加17.6倍[95%CI:14.1~22.3],差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01)。③血清总IgE诊断特应症的价值,在总人群中ROC曲线下面积(AUC)为0.857,最佳临界值为54.3kU/L,敏感度为80.0%,特异度为76.4%;鼻炎组中,AUC为0.888,最佳临界值为54.6 kU/L,敏感度为86.7%,特异度为77.0%;非鼻炎组中,AUC为0.841,最佳临界值为59.0 kU/L,敏感度为74.8%,特异度为78.6%。④随着血清总IgE升高,诊断特异度增加,敏感度下降。结论 血清总IgE与儿童及青少年特应症有密切关联性,特应症人群血清总IgE高于非特应症人群,随着血清总IgE的升高特应症发病风险增加,血清总IgE对特应症有较高的诊断价值。Abstract: Objective To explore the value of total IgE in the diagnosis of atopy in children and adolescents.Methods This cross-sectional study analyzed data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2005-2006 included measurement of total and specific IgE levels and allergy questions for 6-19 year old children and adolescents. According to the results of specific IgE, participants were divided into the atopic or non- atopic group. Based on questionnaire, participants were divided into the rhinitis or non-rhinitis group. To compare the difference of total IgE between groups. The relationship between total IgE and atopy was analyzed. The value of total IgE in the diagnosis of atopy was analyzed by ROC curve.Results ① The geometric mean total IgE level in the non-atopic subjects and the atopic subjects were 24.4 kU/L and 153.1 kU/L, respectively. The difference between the two groups was statistically significant(P < 0.01). ②In logistic regression analyses, we observed the adjusted odds ratio(OR) for atopy with a 10-fold increase in total IgE level was 17.6[95%CI: 14.1-22.3], statistically significant changes(P < 0.01). ③The area under the receiver operator characteristic curve(AUC) of total IgE for diagnosing atopy in the total population were 0.857. The specificity and sensitivity of total IgE at the optimal cutoff of 54.3 kU/L on the ROC curve for diagnosing atopy were76.4%, and 80.0%, respectively. At the optimal cutoff of 54.6 kU/L for diagnosing atopy in the population with rhinitis, AUC, specificity, and sensitivity were 0.888, 86.7% and 77.0%, respectively. At the optimal cutoff of 59.0 kU/L for diagnosing atopy in the population with non-rhinitis, AUC, specificity, and sensitivity were 0.841, 74.8% and 78.6%, respectively. ④The diagnostic specificity of atopy increased with total IgE, while the sensitivity decreased.Conclusion There was a close relationship between total IgE and atopy. Total IgE level can be used to discriminates children and adolescents with and without atopy.
-
Key words:
- total IgE /
- atopy /
- child /
- adolescents
-
血清免疫球蛋白E(IgE)在过敏性疾病的发病机制中起着举足轻重的作用。正常人血清IgE水平很低,是血清中含量最少的一种免疫球蛋白。血清IgE检测分为总IgE(total IgE,tIgE)检测和特异性IgE(specific IgE,sIgE)检测。目前多认为血清sIgE>0.35 kU/L为过敏原阳性,提示机体处于致敏状态[1]。机体暴露于过敏原后产生sIgE的倾向称为特应症(atopy)[2]。而当机体存在sIgE并且再次暴露于此过敏原出现相应的临床症状,则为过敏性疾病,例如变应性鼻炎。因此特应症不等同于过敏性疾病。目前已有较多研究证明[3-12],特应症和过敏性疾病患者血清tIgE水平通常高于普通人群,但大多数观点都认为血清tIgE对鼻炎、哮喘、特应性皮炎等过敏性疾病的诊断价值不高[4, 6, 9, 11],而对血清tIgE诊断特应症的价值,不同研究的结论则不一致[3, 7, 9, 11, 13-15]。因此,本研究采用2005—2006年美国国家健康与营养调查(National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey,NHANES)的数据,进一步探讨血清tIgE在儿童及青少年特应症中的诊断价值。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料
本研究选取NHANES 2005—2006年接受过敏性疾病问卷调查及血清tIgE和血清sIgE检测的6~19岁儿童及青少年的数据。该年度参与者共3433人,其中接受鼻炎问卷调查、血清tIgE和血清sIgE检测且资料完整者2857人纳入本研究,其中男1419例,女1438例。受访者一般资料见表 1。
表 1 一般资料例数(%) 几何均数(95%CI)/(kU·L-1 ) 中位数(25%~75%)/(kU·L-1 ) P值 总数 2857(100.0) 65.6(62.0~69.4) 63.1(23.3~190.0) 年龄/岁 0.338 6~11 898(31.4) 64.1(58.0~70.8) 63.8(22.8~175.2) 12~15 950(33.3) 63.2(57.3~69.7) 58.8(22.3~194.8) 16~19 1009(35.3) 69.4(63.1~76.2) 64.4(24.5~202.0) 性别 < 0.01 男 1419(49.7) 78.2(72.2~84.8) 71.7(26.6~236.0) 女 1438(50.3) 55.1(51.0~59.5) 54.2(20.7~154.0) 种族 < 0.01 非西班牙裔白人 740(25.9) 44.7(40.1~49.8) 45.5(16.4~112.2) 非西班牙裔黑人 911(31.9) 90.3(82.0~99.5) 81.8(33.8~262.0) 墨西哥裔美国人 969(33.9) 63.6(57.8~70.0) 64.0(23.3~186.0) 其他种族 237(8.3) 72.2(59.7~87.4) 61.7(23.3~198.0) 家庭教育 0.968 ≤12年级 1536(56.1) 65.8(61.1~71.0) 63.2(23.6~184.0) >12年级 1202(43.9) 65.4(59.8~71.5) 62.7(22.4~202.8) 贫困收入比率 0.005 [0,1.3] 1112(40.6) 71.5(65.6~78.0) 68.2(27.0~194.2) [1.3,3.5] 1008(36.8) 65.7(59.7~72.2) 63.0(23.5~188.8) [3.5,5.0] 622(22.7) 55.8(49.1~63.5) 53.2(17.1~186.8) 血清可替宁/(ng·mL-1
)0.148 低(< 0.015) 508(18.0) 58.1(50.7~66.5) 60.1(19.4~169.8) 中(0.015~10.000) 2054(72.7) 67.0(62.7~71.6) 63.2(23.7~191.8) 高(≥ 10.000) 264(9.3) 72.8(60.8~87.0) 67.3(27.0~205.2) 肥胖 < 0.01 无 1756(61.7) 60.1(55.9~64.6) 58.0(21.0~173.0) 有 1089(38.3) 76.0(69.6~83.1) 72.2(28.6~227.0) 特应症 < 0.01 无 1320(46.2) 24.4(22.9~26.1) 24.8(11.3~52.3) 有 1537(53.8) 153.1(144.0~162.8) 147.0(64.0~346.0) 鼻炎 < 0.01 无 2127(74.4) 56.7(53.2~60.4) 54.1(21.4~154.0) 有 730(25.6) 100.4(89.4~112.8) 101.5(34.5~309.8) 1.2 方法
NHANES 2005—2006年过敏性疾病相关调查包括以下几个方面:①通过家庭访谈问卷收集过敏性疾病信息。对问卷中两个问题的任何一个回答“是”为鼻炎。问题1:在过去12个月内,您是否患过花粉症?问题2:在过去12个月内,您没有感冒时,是否有打喷嚏、流鼻涕或鼻塞?根据问卷结果将研究对象分为鼻炎组和非鼻炎组。②从NHANES移动检测点抽取血样,使用Pharmacia Diagnostics ImmunoCAP 1000系统,检测血清tIgE和血清sIgE,其中血清sIgE共19种,包括15种吸入性过敏原(粉尘螨、屋尘螨、猫、狗、小鼠、大鼠、蟑螂、链格孢、曲霉菌、豚草、黑麦草、百慕大草、橡树、桦树和蓟)和4种食物性过敏原(花生、鸡蛋白、牛奶和虾)。任何一种过敏原达到或高于检测下限值为阳性结果,低于检测下限值为阴性结果。血清tIgE检测下限值为2.00 kU/L,上限值为样本检测值。血清sIgE检测下限值为0.35 kU/L,上限值为1000 kU/L。为了便于统计学计算,阴性结果采用下限值除2的平方根的值来表示(血清sIgE为0.25 kU/L,血清tIgE为1.41 kU/L)。特应症是对所测试的任何一种血清sIgE产生的阳性反应[16]。根据研究对象的血清sIgE检测结果,将其分为特应症组和非特应症组。根据美国医学会的建议,按照同年龄同性别BMI百分位数[17],将研究对象分为正常体重、超重和肥胖,本研究将超重和肥胖归类统一归为肥胖组。
1.3 统计学分析
应用R语言4.0.4软件和EmpowerStats3.0进行统计学分析。偏态分布的连续性资料用几何均数和中位数、上下四分位数描述,采用秩和检验比较一般资料的组间差异。用logistic回归分析血清tIgE与特应症的相关性。通过受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)分析血清tIgE诊断特应症的价值、最佳临界值、敏感度及特异度。检验水准为α=0.05。
2. 结果
2.1 研究人群的一般特征
本研究人群血清tIgE的分布范围为1.41~8 035.0 kU/L,几何均数为65.6 kU/L,25百分位数为23.3kU/L,中位数为63.1kU/L,75百分位数为190.0kU/L。
血清tIgE水平在性别、种族、贫困收入比率和肥胖等方面差异有统计学意义(P<0.01);在年龄、教育水平以及血清可替宁(尼古丁在人体内主要的初级代谢产物)等方面差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。而鼻炎组和特应症组的血清tIgE水平则明显高于非鼻炎组和非特应症组。进一步分析发现,非鼻炎组血清tIgE水平90百分位数为388.4 kU/L,鼻炎组血清tIgE<388.4 kU/L占80.3%,表明鼻炎组和非鼻炎组的血清tIgE数值有很大程度的重叠。非特应症组90百分位数为109.1 kU/L,特应症组血清tIgE<109.1 kU/L占41.4 %,表明特应症组和非特应症组的血清tIgE数值仅有部分重叠。见表 1。
2.2 血清tIgE和特应症的关系
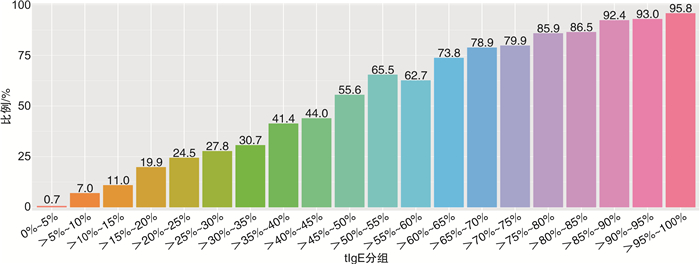
图 1显示,按照血清tIgE数值从小到大进行排序,分成20等分,每等分占总人群的5%,随着血清tIgE的升高,特应症的比例逐步增加。血清tIgE水平0~5百分位数的人群中仅有0.7%为特应症,而在95~100百分位数的人群中则达到95.8%。
采用logistic回归分析血清tIgE和特应症之间的关系,根据Salo等[18]的研究,将年龄、性别、种族、家庭教育、贫困收入比率、血清可替宁水平及肥胖等确定为协变量。将对数正态分布的血清tIgE进行对数转换(以10为底)后作为连续性变量纳入方程。为减少20等分可能产生的统计学误差,另将研究对象4等分,即25百分位数以下为Q1组,26~50百分位数为Q2组,51~75百分位数为Q3组,76~100百分位数为Q4组,作为分类变量纳入方程。如表 2所示,在未调整和调整协变量的模型中,血清tIgE每增加10倍,特应症的发病风险分别增加17.7倍和17.6倍,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01)。以Q1组作为参照组,在未调整和调整协变量的模型中,Q2组发病风险分别增加4.6倍和5.0倍,Q3组发病风险分别增加18.0倍和20.2倍,Q4组发病风险分别增加68.1倍和67.1倍,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01)。提示血清tIgE增高是发生特应症的独立危险因素。
表 2 tIgE和特应症的关系未调整模型 调整模型 OR(95%CI) P值 OR(95%CI) P值 Log10(tIgE) 17.7(14.4,22.1) < 0.001 17.6(14.1,22.3) < 0.01 tIgE分组 Q1组 1.0 1.0 Q2组 4.6(3.6,6.1) < 0.01 5.0(3.7,6.6) < 0.01 Q3组 18.0(13.8,23.9) < 0.01 20.2(15.1,27.3) < 0.01 Q4组 68.1(49.0,96.0) < 0.01 67.1(47.4,96.7) < 0.01 2.3 血清tIgE诊断特应症的价值
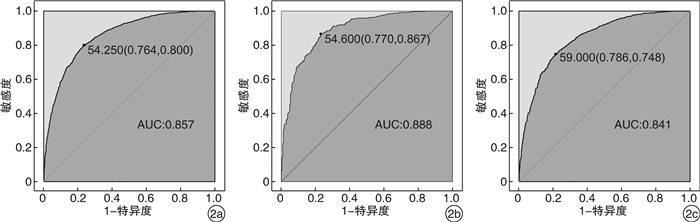
图 2显示,总人群中,血清tIgE最佳临界值为54.3 kU/L,特异度为76.4%,敏感度为80.0%,曲线下面积(AUC)95%CI为0.857(0.843~ 0.871)。鼻炎组血清tIgE最佳临界值为54.6 kU/L,特异度为77.0%,敏感度为86.7%,AUC(95%CI)为0.888(0.863~0.914)。非鼻炎组最佳临界值为59.0 kU/L,特异度为78.6%,敏感度为74.8%,AUC(95%CI)为0.841(0.825~0.858)。提示在总人群、鼻炎组和非鼻炎组中,血清tIgE对特应症均有很高的诊断价值。
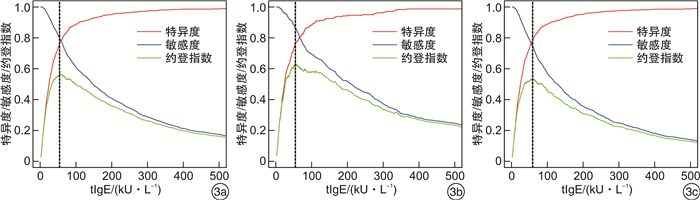
图 3显示不同血清tIgE数值的敏感度和特异度。在总人群、鼻炎组和非鼻炎组中,随着血清tIgE升高,诊断的特异度增加而敏感度下降。当总人群中血清tIgE≤21 kU/L,特异度小于44%,敏感度大于95%;血清tIgE≥190 kU/L,特异度大于95%,敏感度小于42.3%。
3. 讨论
近年来,欧洲、美洲和亚洲的大量研究都得出相同的结果,特应症和过敏性疾病的人群中血清tIgE水平高于正常人群[3-12],说明血清tIgE增高是不同国家、不同种族特应症和过敏性疾病的特征性表现。但大多数研究则认为血清tIgE诊断过敏性疾病的价值并不高[4, 6, 9, 11]。本研究通过鼻炎和特应症人群与非鼻炎和特应症人群血清tIgE水平的比较,表明前者血清tIgE水平明显高于后者。在此基础上,进一步采用logistic回归分析血清tIgE和特应症之间的关系,发现血清tIgE每增加10倍,特应症的发病风险则增加17.6倍,不仅提示随着血清tIgE增高,特应症的比例逐渐增加,也进一步表明血清tIgE与儿童及青少年特应症密切相关,血清tIgE增高是发生特应症的独立危险因素。但由于血清tIgE分布范围广泛,在鼻炎组和非鼻炎组中有很大程度的重叠,非鼻炎组血清tIgE水平90百分位数为388.4 kU/L,鼻炎组血清tIgE<388.4 kU/L占80.3%。因此,血清tIgE虽然与儿童及青少年特应症密切相关,但对变应性鼻炎的诊断价值较低。本研究中的上述结论与大多数的研究结论是相同的。
关于血清tIgE对特应症的诊断价值亦有诸多研究,但结果不尽相同[3, 7, 9, 11, 13-15]。Tu等[9]对台湾地区儿童过敏原检测及过敏性疾病问卷调查的研究显示血清tIgE可以有效区分特应症和非特应症;Sinclair等[13]研究显示,儿童处于低水平的血清tIgE(< 10 kU/L)时,血清sIgE结果几乎都呈阴性。而Al-Mughales等[15]则认为,血清tIgE对食源性和吸入性血清sIgE阳性结果诊断价值不高;Kim等[11]也认为血清tlgE对韩国儿童及青少年特应症的诊断价值不高;另有对科威特及欧洲青年人群的研究均认为血清tIgE不能区分特应症和非特应症[3, 7]。本研究结果表明,与血清tIgE在鼻炎组和非鼻炎组的分布有很大程度的重叠不同,在非特应症组90百分位数为109.1 kU/L,而特应症组<109.1 kU/L仅占41.4 %,因此血清tIgE在特应症组和非特应症组仅在较低水平有部分重叠。进一步通过ROC曲线分析表明,在总人群、鼻炎组和非鼻炎组中,最佳临界值分别为54.3 kU/L、54.6 kU/L和59.0 kU/L。由此表明血清tIgE诊断特应症具有较高的临床价值,且对特应症的诊断不受鼻炎症状的影响。临床上变应性鼻炎常伴随鼻窦炎、睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征及分泌性中耳炎等多种疾病,并可作为病因影响病情和转归,但部分患儿常以伴随疾病的症状就诊,而变应性鼻炎症状不典型,易造成误诊和漏诊,导致疗效不佳。由于在总人群、非鼻炎人群中血清tIgE对特应症的诊断具有较高价值,故可作为初筛,预判特应症,有助于病因诊断和治疗方案的制定。
Chung等[14]在鼻炎人群中研究不同水平的血清tIgE对血清sIgE的诊断价值,发现血清tIgE>150 kU/L,对血清sIgE检测具有较好的阳性诊断价值,而血清tIgE<10 kU/L,具有较好的阴性诊断价值。本研究则说明,不仅在鼻炎组,在总人群和非鼻炎组中,随着血清tIgE升高,诊断的特异度增加而敏感度下降,例如总人群中,血清tIgE≥190 kU/L的人群血清sIgE阳性的概率很高,而血清tIgE≤21 kU/L的人群血清sIgE阴性的概率很高。以此推理,临床上对于血清tIgE明显增高而血清sIgE阴性的检测结果,可能由于过敏原种类繁多而检测种类有限,导致未能检测出相应的过敏原。而对既往研究中血清tIgE对特应症诊断价值的不同结果,可能与检测的过敏原种类不同、数量有限有关,其中有的研究检测的过敏原比较少(仅4种)[7];也有研究说明,血清tIgE较高而皮肤点刺试验呈阴性的儿童随访时出现过敏原阳性的比例明显高于血清tIgE较低的儿童[19],而血清tIgE对特应症诊断价值的研究[3, 7, 9, 11, 13-15]大多为横断面研究,仅对某一时间点进行检测,并非队列研究对不同时间点进行多次检测;还有研究发现,血清tIgE和sIgE水平因季节变化而有所不同[20-21]。本研究发现血清tIgE水平受到性别、年龄、种族、贫困收入及肥胖等因素的影响,因此不同研究结果的差异还应考虑这些可能的影响因素。此外,本研究还说明不同水平的血清tIgE都有特应症和非特应症人群,在血清tIgE较低水平时有特应症的人群,而在较高水平时也有非特应症的人群。因此,血清tIgE水平的高低虽然可以很大程度上预测特应症,但不能精准诊断特应症。
综上所述,特应症人群血清tIgE高于非特应症人群,随着血清tIgE的升高,特应症的发病风险增加,血清tIgE对特应症有较高的诊断价值。本研究采用美国公共卫生数据,以分层复杂抽样调查的方法进行大样本研究,具有代表性,但由于研究人群局限在美国,今后有必要在国内进行全国性的抽样调查,了解中国人群中血清tIgE、血清sIgE以及鼻炎的流行病学资料,并进一步确定血清tIgE的参考值。
利益冲突 所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
-
表 1 一般资料
例数(%) 几何均数(95%CI)/(kU·L-1 ) 中位数(25%~75%)/(kU·L-1 ) P值 总数 2857(100.0) 65.6(62.0~69.4) 63.1(23.3~190.0) 年龄/岁 0.338 6~11 898(31.4) 64.1(58.0~70.8) 63.8(22.8~175.2) 12~15 950(33.3) 63.2(57.3~69.7) 58.8(22.3~194.8) 16~19 1009(35.3) 69.4(63.1~76.2) 64.4(24.5~202.0) 性别 < 0.01 男 1419(49.7) 78.2(72.2~84.8) 71.7(26.6~236.0) 女 1438(50.3) 55.1(51.0~59.5) 54.2(20.7~154.0) 种族 < 0.01 非西班牙裔白人 740(25.9) 44.7(40.1~49.8) 45.5(16.4~112.2) 非西班牙裔黑人 911(31.9) 90.3(82.0~99.5) 81.8(33.8~262.0) 墨西哥裔美国人 969(33.9) 63.6(57.8~70.0) 64.0(23.3~186.0) 其他种族 237(8.3) 72.2(59.7~87.4) 61.7(23.3~198.0) 家庭教育 0.968 ≤12年级 1536(56.1) 65.8(61.1~71.0) 63.2(23.6~184.0) >12年级 1202(43.9) 65.4(59.8~71.5) 62.7(22.4~202.8) 贫困收入比率 0.005 [0,1.3] 1112(40.6) 71.5(65.6~78.0) 68.2(27.0~194.2) [1.3,3.5] 1008(36.8) 65.7(59.7~72.2) 63.0(23.5~188.8) [3.5,5.0] 622(22.7) 55.8(49.1~63.5) 53.2(17.1~186.8) 血清可替宁/(ng·mL-1
)0.148 低(< 0.015) 508(18.0) 58.1(50.7~66.5) 60.1(19.4~169.8) 中(0.015~10.000) 2054(72.7) 67.0(62.7~71.6) 63.2(23.7~191.8) 高(≥ 10.000) 264(9.3) 72.8(60.8~87.0) 67.3(27.0~205.2) 肥胖 < 0.01 无 1756(61.7) 60.1(55.9~64.6) 58.0(21.0~173.0) 有 1089(38.3) 76.0(69.6~83.1) 72.2(28.6~227.0) 特应症 < 0.01 无 1320(46.2) 24.4(22.9~26.1) 24.8(11.3~52.3) 有 1537(53.8) 153.1(144.0~162.8) 147.0(64.0~346.0) 鼻炎 < 0.01 无 2127(74.4) 56.7(53.2~60.4) 54.1(21.4~154.0) 有 730(25.6) 100.4(89.4~112.8) 101.5(34.5~309.8) 表 2 tIgE和特应症的关系
未调整模型 调整模型 OR(95%CI) P值 OR(95%CI) P值 Log10(tIgE) 17.7(14.4,22.1) < 0.001 17.6(14.1,22.3) < 0.01 tIgE分组 Q1组 1.0 1.0 Q2组 4.6(3.6,6.1) < 0.01 5.0(3.7,6.6) < 0.01 Q3组 18.0(13.8,23.9) < 0.01 20.2(15.1,27.3) < 0.01 Q4组 68.1(49.0,96.0) < 0.01 67.1(47.4,96.7) < 0.01 -
[1] 中国医师协会儿科医师分会儿童耳鼻咽喉专业委员会. 儿童变应性鼻炎诊疗——临床实践指南[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志, 2019, 34(3): 169-175.
[2] Hoppin J A, Jaramillo R, Salo P, et al. Questionnaire predictors of atopy in a US population sample: findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2005-2006[J]. Am J Epidemiology, 2011, 173(5): 544-552. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwq392
[3] Ezeamuzie CI, Al-ali SF, Al-dowaisan A, et al. Reference values of total serum IgE and their significance in the diagnosis of allergy among the young adult Kuwaiti population[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 1999, 29(3): 375-381. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.1999.00463.x
[4] Simoni M, Biavati P, Baldacci S, et al. The Po River Delta epidemiological survey: reference values of total serum IgE levels in a normal population sample of North Italy(8-78 yrs)[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2001, 17(3): 231-239. doi: 10.1023/A:1017929831911
[5] Kerkhof M, Dubois AE, Postma DS, et al. Role and interpretation of total serum IgE measurements in the diagnosis of allergic airway disease in adults[J]. Allergy, 2003, 58(9): 905-911. doi: 10.1034/j.1398-9995.2003.00230.x
[6] Sharma S, Kathuria PC, Gupta CK, et al. Total serum immunoglobulin E levels in a case-control study in asthmatic/allergic patients, their family members, and healthy subjects from India[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2006, 36(8): 1019-1027. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2006.02525.x
[7] Carosso A, Bugiani M, Migliore E, et al. Reference values of total serum IgE and their significance in the diagnosis of allergy in young European adults[J]. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2007, 142(3): 230-238. doi: 10.1159/000097025
[8] Gergen PJ, Arbes SJ Jr., Calatroni A, et al. Total IgE levels and asthma prevalence in the US population: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005-2006[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2009, 124(3): 447-453. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.06.011
[9] Tu YL, Chang SW, Tsai HJ, et al. Total serum IgE in a population-based study of Asian children in Taiwan: reference value and significance in the diagnosis of allergy[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(11): e80996. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080996
[10] Ahn JY, Choi BS. Clinical characteristics of total IgE in pediatric allergic disease[J]. Allergy Asthma Respir Dis, 2017, 5(4): 200-204. doi: 10.4168/aard.2017.5.4.200
[11] Kim HY, Choi J, Ahn K, et al. Reference Values and Utility of Serum Total Immunoglobulin E for Predicting Atopy and Allergic Diseases in Korean Schoolchildren[J]. J Korean Med Sci, 2017, 32(5): 803-809. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.5.803
[12] 余悠悠, 罗婷, 潘秀军. 血清过敏原特异性免疫球蛋白IgE检测在喘息患儿中的临床价值[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2019, 23(12): 2077-2080. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4287.2019.12.010
[13] Sinclair D, Peters SA. The predictive value of total serum IgE for a positive allergen specific IgE result[J]. J Clin Pathol, 2004, 57(9): 956-959. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2004.017681
[14] Chung D, Park KT, Yarlagadda B, et al. The significance of serum total immunoglobulin E for in vitro diagnosis of allergic rhinitis[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2014, 4(1): 56-60. doi: 10.1002/alr.21240
[15] Al-Mughales JA. Diagnostic Utility of Total IgE in Foods, Inhalant, and Multiple Allergies in Saudi Arabia[J]. J Immunol Res, 2016, 2016: 1058632.
[16] Roxbury CR, Qiu M, Shargorodsky J, et al. Association Between Rhinitis and Depression in United States Adults[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract, 2019, 7(6): 2013-2020. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2019.02.034
[17] Racette SB, Yu L, Dupont NC, et al. BMI-for-age graphs with severe obesity percentile curves: tools for plotting cross-sectional and longitudinal youth BMI data[J]. BMC Pediatr, 2017, 17(1): 130. doi: 10.1186/s12887-017-0885-x
[18] Salo PM, Calatroni A, Gergen PJ, et al. Allergy-related outcomes in relation to serum IgE: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005-2006[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2011, 127(5): 1226-1235.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.12.1106
[19] Park SC, Kim JH, Lee KH, et al. Association of serum eosinophilia and total immunoglobulin E concentration with the risk of allergic symptoms and allergic sensitization, respectively: A 2-year follow-up study[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 86: 167-171. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.05.005
[20] Carlsson M, Thorell L, Sjölander A, et al. Variability of total and free IgE levels and IgE receptor expression in allergic subjects in and out of pollen season[J]. Scand J Immunol, 2015, 81(4): 240-248. doi: 10.1111/sji.12270
[21] Xu-De Z, Bei-Bei G, Xi-Juan W, et al. Serum IgE Predicts Difference of Population and Allergens in Allergic Diseases: Data from Weifang City, China[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2021, 2021: 6627087.
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 谷悦,沈暘,熊攀辉,官大宇,卢韬,杨玉成. 血清总IgE联合嗜酸性粒细胞对不同年龄阶段变应性鼻炎的诊断价值. 新医学. 2024(10): 779-786 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 胡婧玮,包婺平,赵磊,宋雅君,张旻. 过敏患者总IgE水平分布及与过敏原和外周血嗜酸粒细胞相关性研究. 中国医师进修杂志. 2023(07): 594-599 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)
-

| 引用本文: | 林兴, 许杨杨, 沈翎, 等. 血清总IgE诊断儿童及青少年特应症的价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(4): 269-274. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.04.006 |
| Citation: | LIN Xing, XU Yangyang, SHEN Ling, et al. Diagnostic value of total serum IgE for atopy in children and adolescents[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 36(4): 269-274. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.04.006 |
- 表 1 一般资料
例数(%) 几何均数(95%CI)/(kU·L-1 ) 中位数(25%~75%)/(kU·L-1 ) P值 总数 2857(100.0) 65.6(62.0~69.4) 63.1(23.3~190.0) 年龄/岁 0.338 6~11 898(31.4) 64.1(58.0~70.8) 63.8(22.8~175.2) 12~15 950(33.3) 63.2(57.3~69.7) 58.8(22.3~194.8) 16~19 1009(35.3) 69.4(63.1~76.2) 64.4(24.5~202.0) 性别 < 0.01 男 1419(49.7) 78.2(72.2~84.8) 71.7(26.6~236.0) 女 1438(50.3) 55.1(51.0~59.5) 54.2(20.7~154.0) 种族 < 0.01 非西班牙裔白人 740(25.9) 44.7(40.1~49.8) 45.5(16.4~112.2) 非西班牙裔黑人 911(31.9) 90.3(82.0~99.5) 81.8(33.8~262.0) 墨西哥裔美国人 969(33.9) 63.6(57.8~70.0) 64.0(23.3~186.0) 其他种族 237(8.3) 72.2(59.7~87.4) 61.7(23.3~198.0) 家庭教育 0.968 ≤12年级 1536(56.1) 65.8(61.1~71.0) 63.2(23.6~184.0) >12年级 1202(43.9) 65.4(59.8~71.5) 62.7(22.4~202.8) 贫困收入比率 0.005 [0,1.3] 1112(40.6) 71.5(65.6~78.0) 68.2(27.0~194.2) [1.3,3.5] 1008(36.8) 65.7(59.7~72.2) 63.0(23.5~188.8) [3.5,5.0] 622(22.7) 55.8(49.1~63.5) 53.2(17.1~186.8) 血清可替宁/(ng·mL-1
)0.148 低(< 0.015) 508(18.0) 58.1(50.7~66.5) 60.1(19.4~169.8) 中(0.015~10.000) 2054(72.7) 67.0(62.7~71.6) 63.2(23.7~191.8) 高(≥ 10.000) 264(9.3) 72.8(60.8~87.0) 67.3(27.0~205.2) 肥胖 < 0.01 无 1756(61.7) 60.1(55.9~64.6) 58.0(21.0~173.0) 有 1089(38.3) 76.0(69.6~83.1) 72.2(28.6~227.0) 特应症 < 0.01 无 1320(46.2) 24.4(22.9~26.1) 24.8(11.3~52.3) 有 1537(53.8) 153.1(144.0~162.8) 147.0(64.0~346.0) 鼻炎 < 0.01 无 2127(74.4) 56.7(53.2~60.4) 54.1(21.4~154.0) 有 730(25.6) 100.4(89.4~112.8) 101.5(34.5~309.8) - 表 2 tIgE和特应症的关系
未调整模型 调整模型 OR(95%CI) P值 OR(95%CI) P值 Log10(tIgE) 17.7(14.4,22.1) < 0.001 17.6(14.1,22.3) < 0.01 tIgE分组 Q1组 1.0 1.0 Q2组 4.6(3.6,6.1) < 0.01 5.0(3.7,6.6) < 0.01 Q3组 18.0(13.8,23.9) < 0.01 20.2(15.1,27.3) < 0.01 Q4组 68.1(49.0,96.0) < 0.01 67.1(47.4,96.7) < 0.01
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: