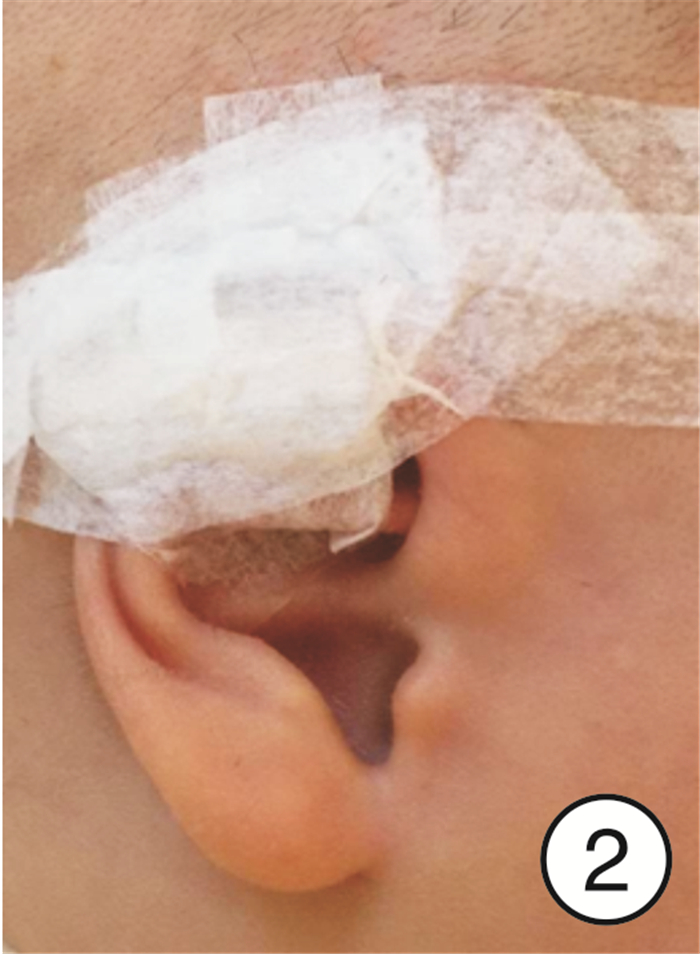
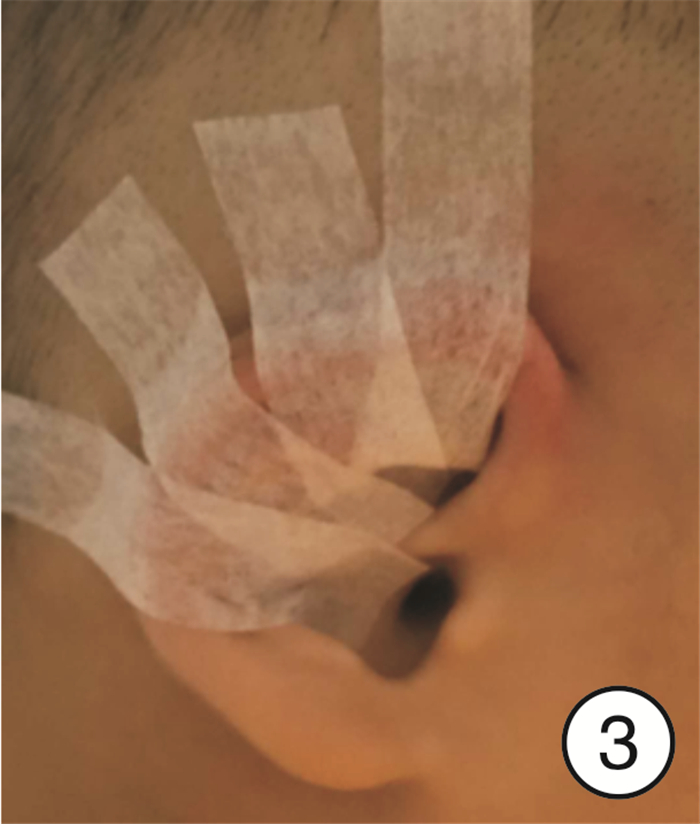
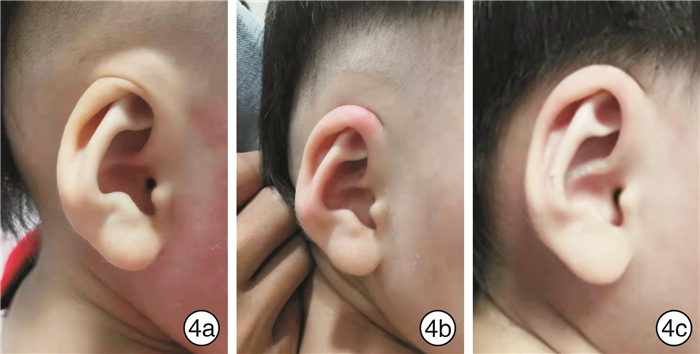
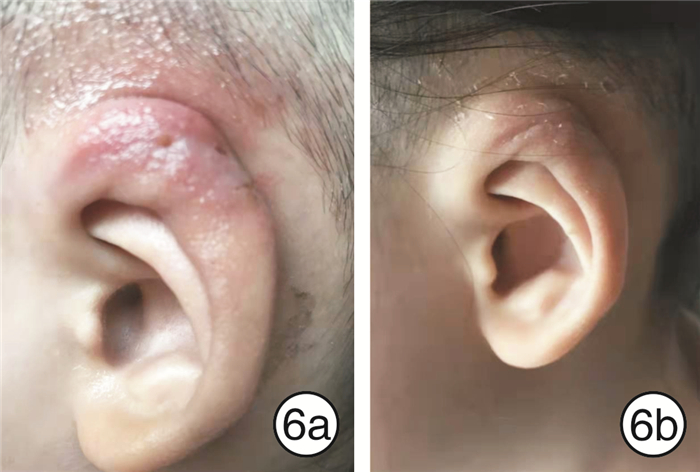
-
摘要: 目的 研究耳廓矫正系统对年龄超过6个月患儿的隐耳畸形矫正疗效。方法 将2017年1月—2021年1月广州市妇女儿童医疗中心耳鼻咽喉科接诊的隐耳畸形患儿按年龄分为研究组(≥6个月)和对照组(< 6个月),均佩戴Earwell耳廓矫正系统,治疗结束后继续随访3~6个月,统计两组矫正疗效、并发症及复发情况。结果 研究组治疗开始阶段和巩固治疗阶段平均时间分别为(20.29±7.14) d和(31.82±9.65) d,对照组分别为(7.5±3.21) d和(16.64±6.53) d,两组治疗时间差异有统计学意义(P=0.001)。研究组有效率90.91%(20/22),对照组96.43%(27/28),两组比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.576);研究组治愈率31.82%(7/22),对照组85.71%(24/28),对照组治愈率高于研究组(P=0.002)。两组患儿均有并发症发生,研究组最常发生的并发症是皮肤红肿18例(81.82%),矫形器脱落16例(72.73%),压疮12例(54.55%);对照组最常发生的并发症是皮肤湿疹9例(32.14%),压疮6例(21.43%),矫形器脱落5例(17.86%)。两组并发症发生率比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 大龄隐耳畸形患儿仍可积极尝试矫形系统矫正隐耳,但仅能拉出被隐藏的耳廓部分,对于合并的其他畸形如耳轮粘连、对耳轮上脚发育不良等不能改善。治疗前需跟家长充分沟通治疗过程中可能出现的并发症情况,鼓励患儿坚持佩戴矫正器是治疗成功的关键。Abstract: Objective To study the clinical application of nonsurgical correction of cryptotia in children older than 6 months.Methods The children with cryptotia deformity treated in Guangzhou Women and Children's Medical Center from January 2017 to January 2021 were divided into two groups according to their ages. The study group was over 6 months old and the control group was under 6 months old. They were treated with a Earwell auricle correction system, the follow-up was continued for 3—6 months, and the correction effects, complications and recurrence after the treatment were calculated in the two groups.Results The average time of the treatment start stage and consolidation stage in the study group was(20.29±7.14) days and(31.82±9.65) days, and respectively the control group was(7.5±3.21) days and(16.64±6.53) days, the difference in treatment time between the two groups was statistically significant(P=0.001). The effective rate in the study group was 90.91%(20/22), and the effective rate in the control group was 96.43%(27/28), there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups(P=0.576). The recovery rate in the study group was 31.82%(7/22), and the recovery rate in the control group was 85.71%(24/28), the cure rate of the control group was higher than that of the study group(P=0.002). Complications occurred in both groups. The most common complications in the study group were skin redness and swelling 18 cases(81.82%) and stent shedding 16 cases(72.73%), pressure ulcers followed by 12 cases(54.55%). The most common complication in the control group was skin eczema 9 cases(32.14%), pressure ulcers 6 cases(21.43%), stent shedding 5 cases(17.86%). There was a statistical difference in the incidence of complications between the two groups(P < 0.05).Conclusion For older children with cryptotia, Earwell correction systems can still be actively tried to correct hidden ears, but only the hidden auricle can be pulled out. Other combined malformations such as helix adhesion, dysplasia of the upper helix, etc. cannot be improved. Before treatment, it is necessary to fully communicate with the parents about possible complications during the treatment process. Encouraging children and parents to insist on wearing the correction system is the key to successful treatment.
-
Key words:
- cryptotia /
- child /
- orthotic devices /
- treatment effectiveness
-

-
[1] Hirose T, Tomono T, Matsuo K, et al. Cryptotia: our classification and treatment[J]. Br J Plast Surg, 1985, 38(3): 352-360. doi: 10.1016/0007-1226(85)90241-3
[2] Paredes AA, Williams JK, Elsahy NI, et al. Cryptotia: principles and management[J]. Clin Plastic Surg, 2002, 29(2): 317-326. doi: 10.1016/S0094-1298(01)00007-4
[3] Kajikawa A, Ueda K, Asai E, et al. A new surgical correction of cryptotia: a new flap design and switched double banner flap[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2009, 123(3): 897-901. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31819e0805
[4] Matsuo K, Hirose T, Tomono T, et al. Nonsurgical correction of congenital auricular deformities in the early neonate: a preliminary report[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1984, 73(1): 38-51. doi: 10.1097/00006534-198401000-00009
[5] Byrd HS, Langevin CJ, Ghidoni LA. Ear molding in newborn infants with auricular deformities[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2010, 126(4): 1191-1200. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181e617bb
[6] Doft MA, Goodkind AB, Diamond S, et al. The newborn butterfly project: a shortened treatment protocol for ear molding[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2015, 135(3): 577e-583e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000000999
[7] Woo T, Kim YS, Roh TS, et al. Correction of Congenital Auricular Deformities Using the Ear-Molding Technique[J]. Arch Plast Surg, 2016, 43(6): 512-517. doi: 10.5999/aps.2016.43.6.512
[8] Daniali LN, Rezzadeh K, Shell C, et al. Classification of Newborn Ear Malformations and their Treatment with the EarWell Infant Ear Correction System[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2017, 139(3): 681-691. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000003150
[9] 张天宇. 耳郭畸形早期矫治与Medpor耳再造技术[J]. 中国医学文摘-耳鼻咽喉科学, 2017, 32(1): 2-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYEB201701003.htm
[10] 齐向东, 周婕. 先天性耳廓畸形无创矫正技术应用及进展[J]. 中国医学文摘-耳鼻咽喉科学, 2017, 32(1): 4-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYEB201701004.htm
[11] 陶佳, 罗仁忠. 超时间窗耳廓形态畸形无创矫形的疗效分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(9): 785-788. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202009005.htm
[12] Yotsuyanagi T, Yamauchi M, Yamashita K, et al. Abnormality of Auricular Muscles in Congenital Auricular Deformities[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2015, 136(1): 78e-88e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000001383
[13] Yotsuyanagi T. Nonsurgical correction of congenital auricular deformities in children older than early neonates[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2004, 114(1): 190-191. doi: 10.1097/01.PRS.0000128819.03187.5D
[14] Zhou Z, Chen C, Bi J, et al. Study on application of ear correction model to infantile cryptotia[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 118: 62-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.12.022
[15] Shin H, Shin J, Song JK, et al. Minimally Invasive Methodsfor Correcting Reducible Cryptotia[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2020, 31(6): 1827-1828. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000006475
[16] Wang D, Jiang H, Yang Q, et al. Non-surgical correction of cryptotia and the analysis of treatment time and other influence factors[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 129: 109771. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.109771
[17] 张天宇, 傅窈窈, 郭英, 等. 先天性耳廓畸形的分类、分型及分度进展[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 56(8): 871-875.
-

| 引用本文: | 陶佳, 罗仁忠. 大龄隐耳耳模矫正疗效分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(3): 176-179. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.03.004 |
| Citation: | TAO Jia, LUO Renzhong. Nonsurgical correction of cryptotia in children older than early neonates[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 36(3): 176-179. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.03.004 |
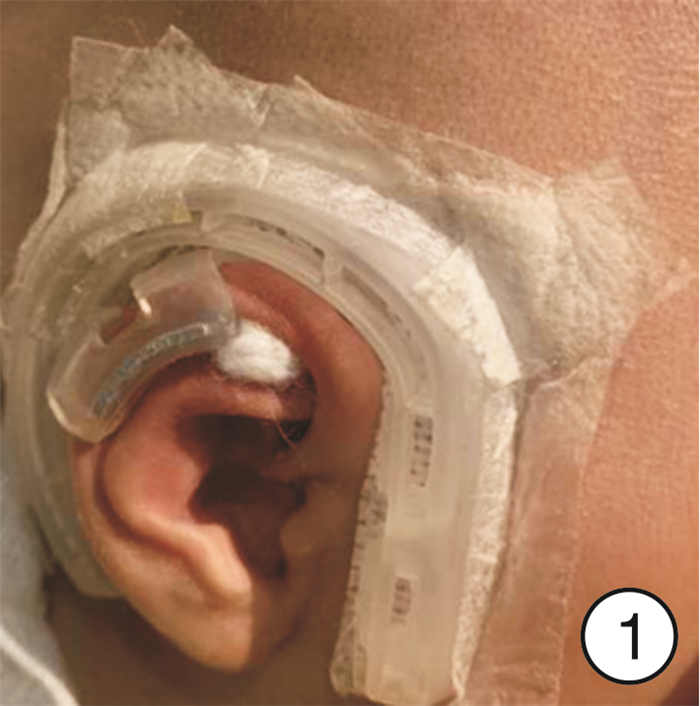
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.
- Figure 5.
- Figure 6.
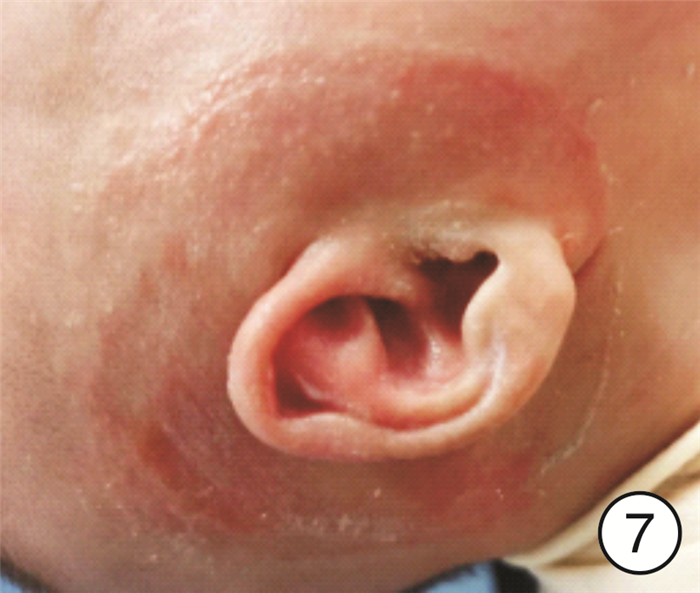
- Figure 7.



 下载:
下载: