Application of surgery combined with bleomycin irrigation for complex cervical-facial lymphatic malformations in children
-
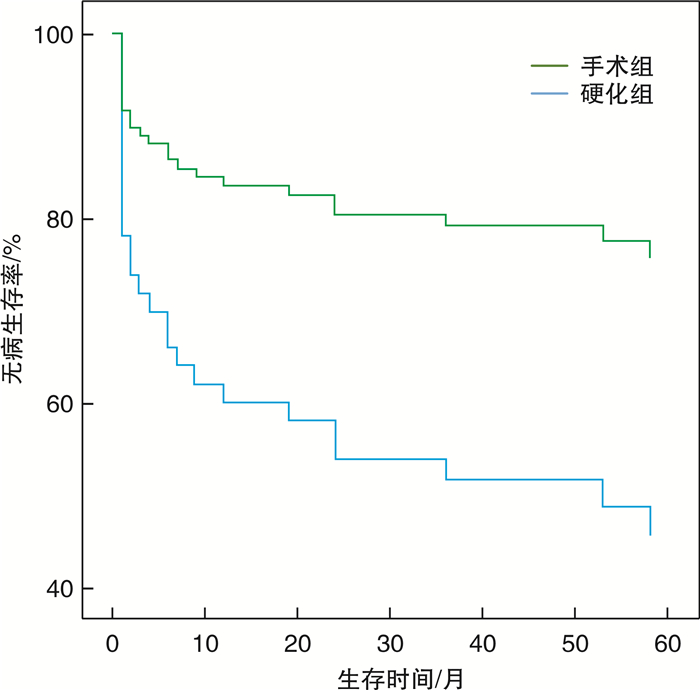
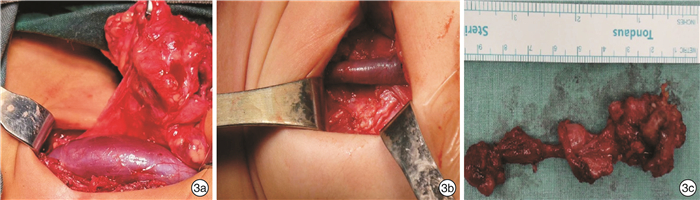
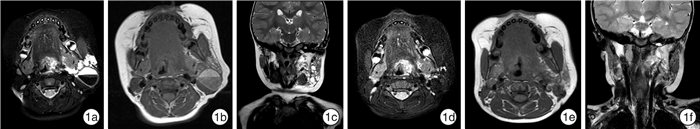
摘要: 目的 探讨手术联合博来霉素术腔盥洗在儿童头颈颌面部复杂淋巴管畸形治疗中的有效性及安全性。方法 回顾性分析2014年8月—2020年12月上海市儿童医院收治的97例头颈颌面部淋巴管畸形患儿的资料,术前及术后均行头颈部MRI及B超检查。将97例患儿分为手术组(81例)和硬化组(16例),手术组行淋巴管瘤切除联合博来霉素术腔盥洗,硬化组采用B超引导下经皮淋巴管瘤穿刺抽液+博来霉素硬化治疗。采用SPSS 21.0软件,卡方检验评估手术组与硬化组病灶的临床治愈率及术后并发症,Kaplan-Meier法计算患儿无病生存率并绘制生存曲线。结果 手术组81例患儿中,治愈64例,有效17例;硬化组16例患儿中,治愈8例,有效8例。Cox比例风险模型发现手术组患儿的治愈率高,5年复发风险低于硬化组,两组比较差异有统计学意义(χ2=5.814,P<0.05),手术组的复发风险为硬化组的35.4%(HR=0.354,P<0.05)。术后并发症方面,两组比较差异无统计学意义(χ2=1.041,P=0.308)。结论 手术联合博来霉素术腔盥洗在儿童头颈颌面部淋巴管畸形诊治中治愈率高,术后并发症低,安全性好。手术原则是在尽量切除病灶的同时保护正常组织的结构功能,当病灶累及舌根,口底,舌体或咽旁及咽后间隙等结构深邃、复杂且操作范围狭小的解剖区域时,可联合等离子刀对病灶进行射频消融,使手术更加微创化、精准化、个性化。Abstract: Objective To present experience and evaluate the safety and efficacy of surgery combined with bleomycin irrigation for the management of head and neck lymphatic malformations in children.Methods The medical records of all patients with cervical-facial lymphatic malformations who presented to Shanghai Children's Hospital from August 2014 to December 2020 were reviewed. 97 children were divided into surgery group(81 cases) and sclerotherapy group(16 cases). Conventional contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) and B-ultrasound examinations were performed both preoperatively and postoperatively. The surgical group received lymphangioma resection combined with bleomycin irrigation. The sclerotherapy group was treated with B-ultrasound-guided percutaneous lymphangioma aspiration and bleomycin sclerotherapy. SPSS 21.0 software was used to evaluate the clinical cure rate and postoperative complications of lesions in both groups by chi-square test. Kaplan-Meier method was used to calculate the disease-free survival rate and draw survival curve.Results In the surgery group of 81 children, 64 cases were cured and 17 cases were effective while in the sclerosis group, 8 cases were cured and 8 cases were effective. Cox proportional risk model found that children in the surgery group had a higher cure rate and a lower risk of 5-year recurrence than those in the sclerotherapy group, with statistically significant differences(χ2=5.814, P < 0.05). The risk of recurrence in the surgery group was 35.4% of that in the sclerotherapy group(HR=0.354, P < 0.05). In regards to postoperative complications, the surgical group had no higher rate of temporal facial paralysis and other nerve injuries compared to the sclerotherapy group(χ2=1.041, P=0.308).Conclusion Surgery combined with bleomycin irrigation in the complex cervical-facial lymphatic malformations was confirmed to be effectively and safely. The principle of the surgery was to protect the structure and function of normal tissue while excising the lesions as much as possible. When the lesions involved the posterior two-thirds of the tongue, the floor of the mouth, parapharynx, retropharynx, or hypopharynx spaces. Radiofrequency ablation was used in the surgical excision, which made the surgery more minimally invasive, accurate and personalized.
-
Key words:
- child /
- lymphatic malformation /
- cervical-facial /
- surgical procedures, operative /
- bleomycin
-

-
[1] Fraulin FO, Flannigan RK, Sharma VK, et al. The epidemiological profile of the Vascular Birthmark Clinic at the Alberta Children's Hospital[J]. Can J Plast Surg, 2012, 20(2): 67-70. doi: 10.1177/229255031202000211
[2] de Serres LM, Sie KC, Richardson MA. Lymphatic malformations of the head and neck. A proposal for staging[J]. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 1995, 121(5): 577-582. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1995.01890050065012
[3] Kennedy TL, Whitaker M, Pellitteri P, et al. Cystic hygroma/lymphangioma: a rational approach to management[J]. Laryngoscope, 2001, 111(11 Pt 1): 1929-1937.
[4] Curran AJ, Malik N, McShane D, et al. Surgical management of lymphangiomas in adults[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 1996, 110(6): 586-589. doi: 10.1017/S0022215100134334
[5] Elluru RG, Balakrishnan K, Padua HM. Lymphatic malformations: diagnosis and management[J]. Semin Pediatr Surg, 2014, 23(4): 178-185. doi: 10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2014.07.002
[6] Jin L, Chen J, Li X. Surgical Excision With Bleomycin Irrigation: A Better Primary Treatment Choice for Pediatric Submandibular Lymphatic Malformations[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2017, 75(2): 437. e1-437. e7. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2016.09.041
[7] Tu JH, Do HM, Patel V, et al. Sclerotherapy for lymphatic malformations of the head and neck in the pediatric population[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2017, 9(10): 1023-1026. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012660
[8] Giguère CM, Bauman NM, Smith RJ. New treatment options for lymphangioma in infants and children[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2002, 111(12 Pt 1): 1066-1075.
[9] Cheng J, Bastidas N. Considerations for Management of Head and Neck Lymphatic Malformations in Children[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2016, 27(4): 908-912. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000002621
[10] Wittekindt C, Michel O, Streppel M, et al. Lymphatic malformations of the head and neck: introduction of a disease score for children, Cologne Disease Score(CDS)[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2006, 70(7): 1205-1212. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2005.12.013
[11] Bonilla-Velez J, Whitlock KB, Ganti S, et al. Active Observation as an Alternative to Invasive Treatments for Pediatric Head and Neck Lymphatic Malformations[J]. Laryngoscope, 2021, 131(6): 1392-1397. doi: 10.1002/lary.29180
[12] Bonilla-Velez J, Moore BP, Cleves MA, et al. Surgical resection of macrocystic lymphatic malformations of the head and neck: Short and long-term outcomes[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 134: 110013. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110013
[13] Lei ZM, Huang XX, Sun ZJ, et al. Surgery of lymphatic malformations in oral and cervicofacial regions in children[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2007, 104(3): 338-344. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2006.12.025
[14] Wang Y, Tang W, Li X. Safety and efficacy of surgery combined with bleomycin irrigation for complex cervical-facial lymphatic malformations of children[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 128: 109724. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.109724
[15] Chen J, Li W, Li X. Retropharyngeal lymphatic malformations: report of two successfully treated cases and review of the literature[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2019, 39(3): 205-209. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-1484
[16] Wang S, Du J, Liu Y, et al. Clinical analysis of surgical treatment for head and neck lymphatic malformations in children: a series of 128 cases[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2019, 139(8): 713-719. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2019.1616818
[17] Motz KM, Nickley KB, Bedwell JR, et al. OK432 versus doxycycline for treatment of macrocystic lymphatic malformations[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2014, 123(2): 81-88. doi: 10.1177/0003489414523561
[18] Wiegand S, Eivazi B, Zimmermann AP, et al. Sclerotherapy of lymphangiomas of the head and neck[J]. Head Neck, 2011, 33(11): 1649-1655. doi: 10.1002/hed.21552
[19] De Maria L, De Sanctis P, Balakrishnan K, et al. Sclerotherapy for lymphatic malformations of head and neck: Systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord, 2020, 8(1): 154-164. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2019.09.007
[20] 郑家伟, 秦中平, 张志愿. 口腔颌面部淋巴管畸形的治疗[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2005, 14(6): 553-556. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7248.2005.06.001
[21] Horbach SE, Lokhorst MM, Saeed P, et al. Sclerotherapy for low-flow vascular malformations of the head and neck: A systematic review of sclerosing agents[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2016, 69(3): 295-304. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2015.10.045
[22] Jain V, Mohta A, Sengar M, et al. Use of intralesional bleomycin as primary therapy in macrocystic lymphangiomas[J]. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol, 2013, 79(4): 524-525. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.113089
-




 下载:
下载: