Cholesteatoma of the middle ear combined with intracranial and extracranial complications in children: a case report
-
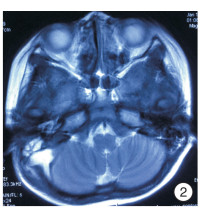
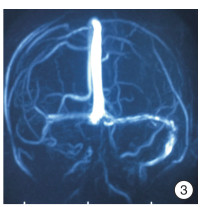
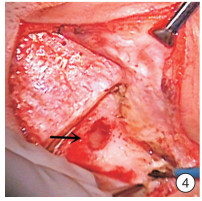
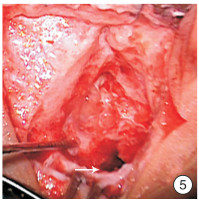
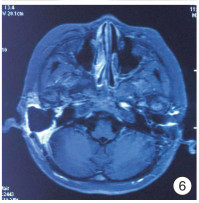
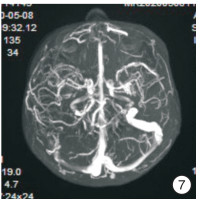
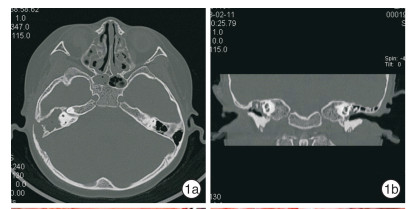
Abstract: In this paper, a case of middle ear cholesteatoma with sigmoid sinus thrombophlebitis and retroauricular subperiosteal abscess was reported. The female patient was hospitalized with bilateral ear abscess for more than 20 days and fever with vomiting for 14 days. Anti-infection treatment after admission, emergency right mastoid radical resection and tympanoplasty were performed under general anesthesia. The patient recovered well after surgery, and there was no recurrence after in the follow-up for more than 2 years.The clinical manifestations, imaging features and prognosis of this disease were discussed and analyzed in the paper.
-
Key words:
- cholesteatoma of middle ear /
- child /
- complications
-

-
[1] 梁晓杰, 杨仕明, 韩东一, 等. 中耳胆脂瘤颅内外并发症的临床分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2005, 40(1): 10-13. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:1673-0860.2005.01.006
[2] 王丹, 倪玉苏. 儿童耳源性乙状窦血栓性静脉炎的诊疗进展[J]. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志, 2017, 17(6): 446-448. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YRBH201706021.htm
[3] 高伟, 訾定京, 杨静, 等. 耳源性乙状窦血栓性静脉炎6例诊治分析[J]. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志, 2020, 20(2): 107-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YRBH202002012.htm
[4] 李瑞香, 吴南, 侯昭晖. 耳源性乙状窦血栓性静脉炎的诊断和治疗(附6例病例分析)[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2017, 15(4): 447-453. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2017.04.012
[5] 陈树斌, 杨本涛, 于子龙, 等. 耳源性乙状窦血栓性静脉炎CT及MRI表现[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2018, 25(2): 79-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201802007.htm
[6] 李倩, 杨雅文, 田成林, 等. CT静脉窦高密度征对不同部位不同阶段颅内静脉窦血栓的诊断意义[J]. 解放军医学院学报, 2015, 36(5): 437-440. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5227.2015.05.008
[7] 刘群, 刘衡, 朱克文, 等. MRI及磁共振静脉血管成像诊断脑静脉窦血栓形成[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2011, 27(6)1121-1124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXX201106010.htm
[8] 黎金葵, 雷军强, 杨品. 磁共振静脉成像对脑静脉窦血栓诊断价值的Meta分析[J]. 中国医学影像学杂志, 2015, 23(11): 876-880. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5185.2015.11.022
[9] 刘丽华, 宋建勋, 李敏, 等. 脑静脉窦血栓形成的影像学表现(附13例病例分析和文献回顾)[J]. 实用放射学杂志, 2013, 29(7): 1046-1049. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1671.2013.07.004
[10] Raja K, Parida PK, Alexander A, et al. Otogenic Lateral Sinus Thrombosis: A Review of Fifteen Patients and Changing Trends in the Management[J]. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 22(3): 208-213. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1604198
[11] Ulanovski D, Yacobovich J, Kornreich L, et al. Pediatric otogenic sigmoid sinus thrombosis: 12-Year experience[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2014, 78(6): 930-933.
[12] Garcia RD, Baker AS, Cunningham MJ, et al. Lateral sinus thrombosis associated with otitis media and mastoiditis in children[J]. Pediatr Infect Dis J, 1995, 14(7): 617-623. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199507000-00013
[13] Sitton MS, Chun R. Pediatric otogenic lateral sinus thrombosis: role of anticoagulation and surgery[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2012, 76(3): 428-432. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2011.12.025
[14] Ropposch T, Nemetz U, Braun EM, et al. Management of otogenic sigmoid sinus thrombosis[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2011, 32(7): 1120-1123. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e31822a1ec0
[15] Novoa E, Podvinec M, Angst R, et al. Paediatric otogenic lateral sinus thrombosis: therapeutic management, outcome and thrombophilic evaluation[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2013, 77(6): 996-1001. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2013.03.030
[16] Moharir MD, Shroff M, Stephens D, et al. Anticoagulants in pediatric cerebral sinovenous thrombosis: a safety and outcome study[J]. Ann Neurol, 2010, 67(5): 590-599.
[17] Ulanovski D, Yacobovich J, Kornreich L, et al. Pediatric otogenic sigmoid sinus thrombosis: 12-Year experience[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2014, 78(6): 930-933.
[18] Scherer A, Jea A. Pediatric Otogenic Sigmoid Sinus Thrombosis: Case Report and Literature Reappraisal[J]. Glob Pediatr Health, 2017, 4: 2333794X17738837.
-




 下载:
下载: