Diagnostic value of multi-slice spiral CT in tympanic wall destruction of middle ear cholesteatoma
-
摘要: 目的 探讨中耳胆脂瘤患者术前颞骨计算机断层扫描(CT)的表现与术中鼓室壁表现的相关性。方法 回顾性分析2017年3月—2020年11月手术治疗的胆脂瘤患者。比较患者术前颞骨CT所见鼓室壁状态与术中所见鼓室壁状态。结果 148例(148耳)患者纳入分析,对比CT表现与术中观察,142例经CT检查的鼓室盖与术中观察相同,144例CT显示乳突盖状态与术中所见相同。CT所见18例患者面神经管状态与术中所见不同。CT所见12例鼓室内侧壁破坏中,10例与术中所见一致。CT所见6例乙状窦破坏,其中5例与术中所见一致,CT所见142例乙状窦无破坏,其中1例与术中所见不同。HRCT所见鼓室壁中,对面神经管裸露诊断效能较差(Se=78.6%,Sp=90.0%,PPV=64.7%,NPV=94.7%,AUC=0.84,Kappa=0.63,P < 0.05),对鼓室内侧壁破坏诊断效能较好(Se=83.5%,Sp=98.5%,PPV=83.3%,NPV=98.6%,AUC=0.91,Kappa=0.82,P < 0.05)。结论 CT诊断中耳胆脂瘤鼓室壁破坏效能较好,特别是在检测鼓室盖、乳突盖、鼓室内侧壁及乙状窦的破坏方面。术前颞骨CT扫描对临床术前决策和术中引导是有益的。
-
关键词:
- 胆脂瘤 /
- 鼓室壁 /
- 螺旋计算机断层摄影术
Abstract: Objective To investigate the correlation between preoperative temporal bone Computed Tomography (CT) findings and intraoperative manifestations in patients with middle ear cholesteatoma.Methods The patients with cholesteatoma undergoing surgery in our hospital from March 2017 to November 2020 were retrospectively analyzed.The temporal bone CT findings of tympanoid wall status before operation and the state of tympanic wall during operation were compared.Results A total of 148 cases (148 ears) were included in the analysis. Compared with intraoperative observation, 142 cases showed the same findings of tympanoid lid by preoperative CT examination, and 144 cases showed the same findings of mastoid lid by preoperative CT examination.The CT manifestations of facial nerve canal state in 18 patients was different from intraoperativen findings. Among the 12 cases of lateral wall destruction of the tympanic chamber observed by CT, 10 cases were consistent with the intraoperative findings.CT showed sigmoid sinus destruction in 6 cases, of which 5 cases were consistent with intraoperative findings. In 142 cases no sigmoid sinus destruction was found by CT, but in one case the CT findingswas different from intraoperative findings.The diagnostic efficiency of the exposed opposite neural tube was poor in the tympanoid wall observed by CT(Se=78.6%, Sp=90.0%, PPV=64.7%, NPV=94.7%, AUC=0.84, Kappa=0.63, P < 0.05), but the diagnostic efficiency of lateral wall failure of the drum chamber was good (Se=83.5%, Sp=98.5%, PPV=83.3%, NPV=98.6%, AUC=0.91, Kappa=0.82, P < 0.05).Conclusion CT is effective in preoperative diagnosing of tympanic wall destruction caused by cholesteatoma of the middle ear, especially in detecting the destruction of tympanic lid, mastoid lid, lateral wall of the tympanic chamber and sigmoid sinus.Preoperative temporal bone CT scan is beneficial to clincal preoperative decision-making and intraoperative guidance.-
Key words:
- cholesteatoma /
- tympanoid wall /
- spiral computed tomography
-

-
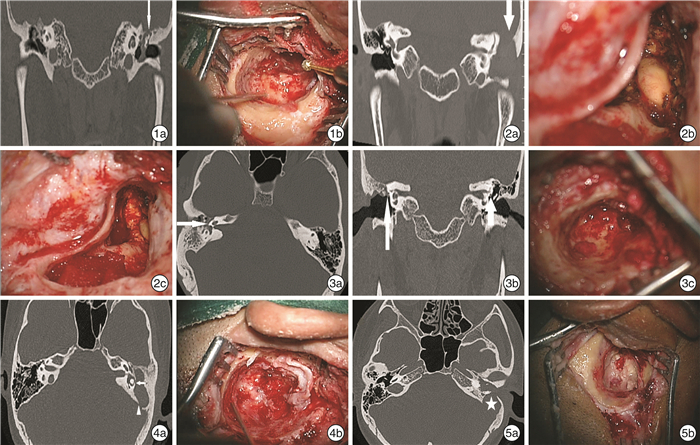
图 1 1例58岁女性患者左耳胆脂瘤鼓室盖破坏情况 1a:CT冠状位见鼓室盖破坏(细箭);1b:术中见鼓室盖0.5 cm×0.3 cm破坏; 图 2 1例37岁男性患者左耳胆脂瘤乳突盖破坏情况 2a:CT冠状位见鼓室乳突内大量软组织密度影填充,乳突盖破坏(粗箭);2b~2c:术中见乳突盖1.2 cm×1.0 cm破坏,硬脑膜裸露及表面肉芽坏死组织; 图 3 1例32岁男性患者右耳胆脂瘤面神经管破坏情况 3a~3b:CT横断面及冠状位见面神经管鼓室段骨质不连续(细长箭);3c:术中见面神经鼓室段裸露; 图 4 1例47岁女性患者左耳胆脂瘤水平半规管骨质破坏情况 4a:CT横断面见水平半规管骨质破坏(短箭),CT另见乙状窦骨质破坏(三角);4b:术中见水平半规管瘘; 图 5 1例67岁女性患者左耳胆脂瘤乙状窦骨质破坏 5a:CT横断面见乙状窦骨质破坏(星号);5b:术中见乙状窦0.7 cm×0.8 cm破坏。
表 1 2名医师对CT所示胆脂瘤鼓室壁状态判读结果的一致性检验
例 甲医师 乙医师 Kappa P 破坏 无破坏 鼓室盖 破坏 11 2 0.87 < 0.01 无破坏 1 134 乳突盖 破坏 8 2 0.79 < 0.01 无破坏 2 136 面神经管 破坏 30 3 0.85 < 0.01 无破坏 5 110 内侧壁 破坏 10 1 0.82 < 0.01 无破坏 3 134 乙状窦 破坏 5 1 0.83 < 0.01 无破坏 1 141 表 2 CT所见鼓室乳突壁破坏情况与术中所见比较
CT 手术 敏感性/% 特异性/% PPV/% NPV/% AUC PAUC Kappa PKappa 破坏 无破坏 鼓室盖 破坏 9 3 75.0 97.8 75.0 97.8 0.86 <0.01 0.73 <0.01 无破坏 3 133 乳突盖 破坏 8 1 72.7 99.3 88.9 97.8 0.86 <0.01 0.79 <0.01 无破坏 3 136 面神经管 裸露 22 12 78.6 90.0 64.7 94.7 0.84 <0.01 0.63 <0.01 无裸露 6 108 内侧壁 破坏 10 2 83.3 98.5 83.3 98.5 0.91 <0.01 0.82 <0.01 无破坏 2 134 乙状窦 破坏 5 1 71.4 99.3 83.3 98.6 0.85 <0.01 0.76 <0.01 无破坏 1 141 -
[1] Kuo CL. Etiopathogenesis of acquired cholesteatoma: prominent theories and recent advances in biomolecular research[J]. Laryngoscope, 2015, 125(1): 234-240. doi: 10.1002/lary.24890
[2] Tos M. Pathology of the ossicular chain in various chronic middle ear diseases[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 1979, 93(8): 769-780. doi: 10.1017/S0022215100087703
[3] Zhang LC, Tong B, Wang ZM, et al. A comparison of three MDCT post-processing protocols: preoperative assessment of the ossicular chain in otitis media[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2014, 271(3): 445-454. doi: 10.1007/s00405-013-2415-2
[4] Fujiwara S, Toyama Y, Miyashita T, etal. Usefulness of multislice-CT using multiplanar reconstruction in the preoperative assessment of the ossicular lesions in the middle ear diseases[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2016, 43(3): 247-253. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2015.08.007
[5] 胡瑞利, 林彦涛, 张青俊, 等. 高分辨率CT对慢性化脓性中耳炎听骨链破坏的评估价值[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2019, 27(2): 184-188. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2019.02.018
[6] Guo Y, Liu Y, Lua QH, et al. CT two-dimensional reformation versus three-dimensional volume rendering with regard to surgical findings in the preoperative assessment of the ossicular chain in chronic suppurative otitis media[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2013, 82(9): 1519-1524. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.03.010
[7] Gül A, Akdaǧ M, Kiniş V, et al. Radiologic and surgical findings in chronic suppurative otitis media[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2014, 25(6): 2027-2029. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000001017
[8] Aljehani M, Alhussini R. The Correlation Between Preoperative Findings of High-Resolution Computed Tomography(HRCT)and Intraoperative Findings of Chronic Otitis Media(COM)[J]. Clin Med Insights Ear Nose Throat, 2019, 12: 1179550619870471.
[9] 黄思达, 吴学文, 金毅, 等. CT三维重建对耳内镜下鼓峡手术参考价值的初步探究[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2018, 16(5): 623-628. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2018.05.007
[10] Moreano EH, Paparella MM, Zelterman D, et al. Prevalence of microfissures in the human temporal bone: a report of 1000 temporal bones[J]. Laryngoscope, 1994, 104(6 Pt 1): 741-746.
[11] Busaba NY. Clinical presentation and management of labyrinthine fistula caused by chronic otitis media[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 1999, 108(5): 435-439. doi: 10.1177/000348949910800503
[12] Copeland BJ, Buchman CA. Management of labyrinthine fistulae in chronic ear surgery[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2003, 24(1): 51-60. doi: 10.1053/ajot.2003.10
[13] Greenberg JS, Manolidis S. High incidence of complications encountered in chronic otitis media surgery in a U.S. metropolitan public hospital[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2001, 125(6): 623-627. doi: 10.1067/mhn.2001.120230
[14] 张威, 袁艺昕, 孙鹏程, 等. 慢性中耳炎并发迷路瘘管的诊治分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(13): 1013-1015. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2018.13.013
[15] Stephenson MF, Saliba I. Prognostic indicators of hearing after complete resection of cholesteatoma causing a labyrinthine fistula[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2011, 268(12): 1705-1711. doi: 10.1007/s00405-011-1545-7
-




 下载:
下载: