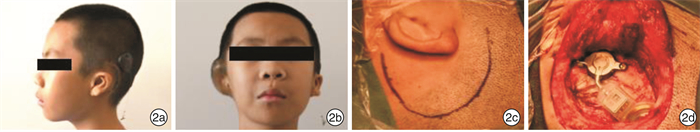
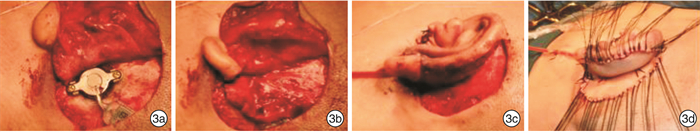
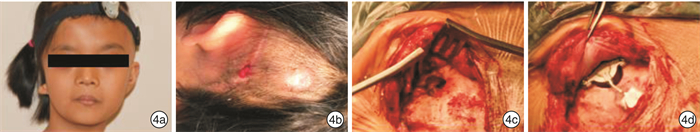
Selection and application in the approach of Bonebridge implantation for bilateral congenital malformation of external and middle ear: selection and application
-
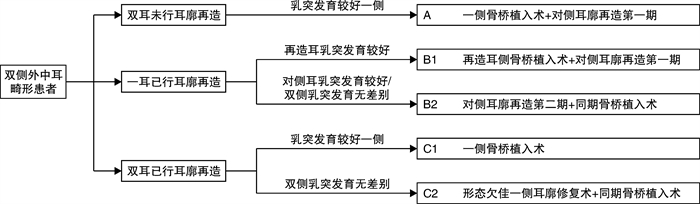
摘要: 目的 根据双侧外中耳畸形患者在骨桥植入术前是否已行耳廓再造术,采用不同的手术方案完成骨桥植入,探讨个性化外形及听力重建的可行性。 方法 对35例双侧外中耳畸形患者制定个体化骨桥植入及耳廓再造综合手术计划,完成单侧骨桥植入术。6例患者采用一侧骨桥植入,对侧同期行耳后皮肤扩张器植入术;7例患者于自体肋软骨耳廓再造术第二期同期行骨桥植入术;22例患者于耳廓再造术后行骨桥植入术。 结果 35例患者均未发生术中并发症,术后无面瘫、眩晕、耳鸣、脑脊液漏等并发症发生。1例患者术后发生植入体表面皮肤感染,取出骨桥植入体7个月后于同侧再次行骨桥植入术,随访16个月无并发症发生。 结论 根据患者个体情况个性化选择不同的骨桥植入手术方式,有利于获得理想的外形和听力效果。Abstract: Objective According to whether auricle reconstruction has been performed before the implantation of Bonebridge, the different surgical plan of combination of ear reconstruction and hearing rehabilitation with Bonebridge were respectively applied for the individuals with congenital outer and middle ear malformation. The study aim to explore the feasibility of personalized comprehensive treatment of congenital outer and middle ear malformation. Methods We developed individualized surgical plans of Bonebridge implantation and auricular reconstruction for 35 patients with bilateral external and middle ear malformation. Six patients underwent Bonebridge implantation on one side, and the post-auricular skin expander implantation on the other sidesimultaneously; seven patients underwent Bonebridge implantation at the same time as the second stage of auricular reconstruction; twenty-two patients had their Bonebridge implantations performed after the reconstruction of the auricles. Results No intraoperative complications occured in 35 patients. No facial paralysis, vertigo, tinnitus and cerebrospinal fluid leakage was reported. One patient had skin infection after Bonebridge implantation. The Bonebridge was removed and 7 months later and the Bonebridge implantation was re-performed on the same side. No complication occurred after 16 months of follow-up. Conclusion According to the individual condition of the patients, different surgical plans of Bonebridge implantation and auricular reconstruction can be selected personally, which is beneficial to obtain the ideal aesthetic and hearing outcome.
-

-
表 1 35例患者一般情况资料
例序 性别 骨桥植入时
年龄/岁综合征 耳廓畸形Marx分级
(右耳/左耳)平均听阈
/dB HL骨桥植入前手术史 植入
侧别骨桥植入
手术方案1 女 11.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅰ 61.25 无 右 A 2 男 10.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅱ 67.50 双侧耳廓再造 左 C2 3 男 13.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 68.75 左侧耳廓再造术 右 B2 4 男 7.0 Treacher Collins
综合征Ⅲ/Ⅰ 66.25 无 左 A 5 女 7.0 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 68.75 左侧耳廓再造术 右 B2 6 男 8.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 72.50 双侧耳廓再造术 左 C2 7 男 18.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅱ 67.50 双侧耳廓再造术 右 C2 8 女 8.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅰ 63.75 双侧耳廓再造术 右 C2 9 男 9.0 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 63.75 双侧耳廓再造术 左 C2 10 女 7.5 Goldenhar综合征 Ⅳ/Ⅰ 63.75 无 右 A 11 男 9.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 67.50 左侧耳廓再造术 右 B2 12 男 10.0 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 76.25 双侧耳廓再造术 左 C1 13 女 11.0 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 68.75 双侧耳廓再造术+右侧耳道再造 右 C2 14 男 9.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 71.25 双侧耳廓再造术 右 C2 15 男 8.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 73.75 双侧耳廓再造术+右侧耳道再造 左 C2 16 男 8.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 65.00 双侧耳廓再造术+左侧耳道再造 右 C2 17 男 9.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 65.00 右侧耳廓再造术 左 A 18 女 11.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 72.50 左侧耳廓再造术 右 B2 19 男 8.0 无 Ⅲ/Ⅱ 68.75 双侧耳廓再造术 右 C1 20 男 7.0 复合畸形 Ⅱ/Ⅲ 68.75 双侧耳廓再造术 左 C1 21 女 8.5 无 Ⅰ/Ⅲ 61.25 无 右 A 22 女 7.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 71.25 双侧耳廓再造术 右 C2 23 女 9.0 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 73.75 双侧耳廓再造术 左 C2 24 女 12.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 71.25 双侧耳廓再造术 右 C2 25 男 26.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 72.50 双侧耳廓再造术 右 C1 26 男 27.0 Treacher Collins
综合征Ⅰ/Ⅰ 68.75 无 右 A 27 男 18.0 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 71.25 左侧耳廓再造术 右 B2 28 男 16.0 无 Ⅱ/Ⅲ 68.75 双侧耳廓再造术 左 C2 29 男 12.0 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 68.75 双侧耳廓再造术 左 C2 30 男 17.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 72.50 双侧耳廓再造术 右 C2 31 女 14.5 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 68.75 左侧耳廓再造术 右 B2 32 女 13.0 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 73.75 双侧耳廓再造术 右 C1 33 女 6.0 复合畸形 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 68.75 右侧耳廓再造术 左 B2 34 男 10.0 无 Ⅲ/Ⅲ 71.25 双侧耳廓再造术 右 C1 35 女 11.0 无 Ⅲ/Ⅱ 68.75 双侧耳廓再造术 右 C1 -
[1] Melnick M, Myrianthopoulos NC, Paul NW. External ear malformations: epidemiology, genetics, and natural history[J]. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser, 1979, 15(9) : i-ix, 1-140.
[2] Deng K, Dai L, Yi L, et al. Epidemiologic characteristics and time trend in the prevalence of anotia and microtiain China[J]. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol, 2016, 106(2) : 88-94. doi: 10.1002/bdra.23462
[3] Cubitt JJ, Chang LY, Liang D, et al. Auricular reconstruction[J]. J Paediatr Child Health, 2019, 55 (5) : 512-517. doi: 10.1111/jpc.14444
[4] Chang SO, Choi BY, Hur DG. Analysis of the longterm hearing results after the surgical repair of aural atresia[J]. Laryngoscope, 2006, 116(10) : 1835-1841. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000233703.52308.73
[5] Fan X, Yang T, Niu X, et al. Long-term Outcomes of Bone Conduction Hearing Implants in Patients With Bilateral Microtia-atresia[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2019, 40 (8) : 998-1005. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002370
[6] Sprinzl GM, Wolf-Magele A. The Bonebridge Bone Conduction Hearing Implant: indication criteria, surgery and a systematic review of the literature[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2016, 41(2) : 131-143. doi: 10.1111/coa.12484
[7] Zernotti ME, Sarasty AB. Active Bone Conduction Prosthesis: Bonebridge(TM)[J]. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2015, 19(4) : 343-348. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1564329
[8] Baumgartner WD, Hamzavi JS, Böheim K, et al. A New Transcutaneous Bone Conduction Hearing Implant: Short-term Safety and Efficacy in Children[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2016, 37(6) : 713-720. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001038
[9] Rahne T, SeiwerthI, Götze G, et al. Functional results after Bonebridge implantation in adults and children with conductive and mixed hearing loss[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2015, 272(11) : 3263-3269. doi: 10.1007/s00405-014-3403-x
[10] Ngui LX, Tang IP. Bonebridge transcutaneous bone conduction implant in children with congenital aural atresia: surgical and audiological outcomes[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2018, 132(8) : 693-697. doi: 10.1017/S0022215118001123
[11] Shonka DC Jr, Livingston WJ 3rd, Kesser BW. The Jahrsdoerfer grading scale in surgery to repair congenital aural atresia[J]. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2008, 134(8) : 873-877. doi: 10.1001/archotol.134.8.873
[12] Vogt K, Frenzel H, Ausili SA, et al. Improved directional hearing of children with congenital unilateral conductive hearing loss implanted with an active boneconduction implant or an active middle ear implant [J]. Hear Res, 2018, 370: 238-247. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2018.08.006
[13] Suzuki Y. Classification of shapes(auricle/ external auditory canal)[J]. Adv Otorhinolaryngol, 2014, 75: 10-12.
[14] 蒋海越, 潘博, 林琳. 先天性小耳畸形的分型及治疗策略[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2013, 11(4) : 476-480. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2013.04.001
[15] 刘强, 张文阳, 石静华, 等. 骨锚式助听器在双侧先天性外中耳畸形患者中的应用效果分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 30(19) : 1521-1524. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201619005.htm
[16] Bento RF, Lopes PT, CabralJunior Fda C. Bonebridge Bone Conduction Implant[J]. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2015, 19(4) : 277-278. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1564567
[17] Jones S, Spielmann P. Device profileofthe Bonebridge bone conduction implant system in hearing loss: an overview of its safety and efficacy[J]. Expert Rev Med Devices, 2020, 17(10) : 983-992. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2020.1834845
[18] Pittman AL. Bone Conduction Amplification in Children: Stimulation via a Percutaneous Abutment versus a Transcutaneous Softband[J]. Ear Hear, 2019, 40 (6) : 1307-1315. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000710
[19] Fan Y, Niu X, Chen Y, et al. Long-term evaluation of development in patients with bilateral microtia using softband bone conducted hearing devices[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 138: 110367. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110367
[20] Wang Y, Xing W, Liu T, et al. Simultaneous auricular reconstruction combined with bone bridge implantation-optimal surgical techniques in bilateral microtia with severe hearing impairment[J]. IntJ Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 113: 82-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.07.004
-




 下载:
下载: