Clinical study of the autologous concha cartilage transplantation to repair the auricle defect
-
摘要: 目的 探讨自体耳甲腔软骨游离移植修复耳廓部分缺损的临床效果。方法 对7例外伤后耳廓软骨部分缺损的患者采用自体耳甲腔软骨游离移植修复, 视软骨缺损大小取同侧或者对侧的耳甲腔软骨缝合固定在缺损软骨处再造软骨支架, 取耳周皮瓣转移覆盖软骨, 修复耳廓部分缺损。结果 7例耳廓部分缺损患者采用同侧或者对侧耳甲腔软骨游离移植修复, 再造耳廓形态满意, 随访6个月耳廓软骨未见明显吸收, 形态稳定。结论 采用自体耳甲腔软骨游离移植修复耳廓部分缺损, 可避免取肋软骨, 手术简单, 局部麻醉下即可完成手术, 长期随访软骨未见明显吸收, 效果满意。Abstract: Objective To investigate the curative effect of the auricular defect repaired by the autologous concha cartilage.Methods Seven cases with the auricular defect were repaired using the autologeous concha cartilage which combined with the retroauricular flap or retroauricular fascia with skin graftin.Results Total 7 patients were followed up for 6 months after the surgery. The shape and size of the repaired ears were similar to the healthy ears. The teansplanted cartilages were not absorbed or deformed.Conclusion This method is harmless and simple, which has reliable and satisfactory effects on auricle defect. We can operate under local anethesia and avoid cutting the rib cartilage.
-
Key words:
- concha cartilage /
- earauricle /
- reconstructive surgical procedures
-

-
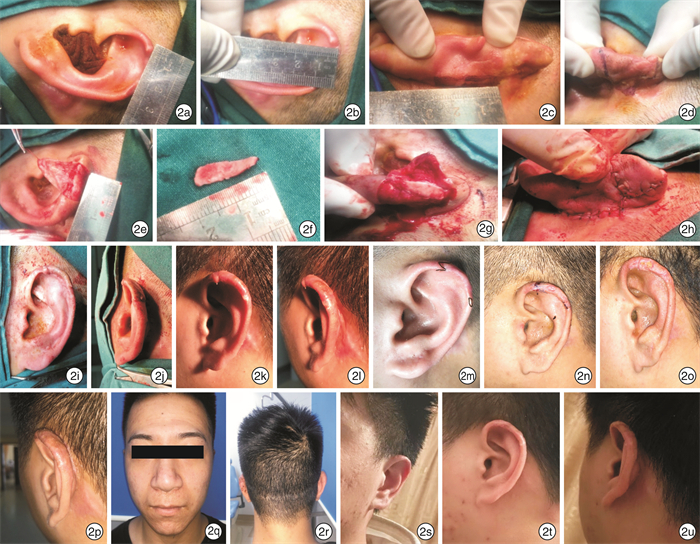
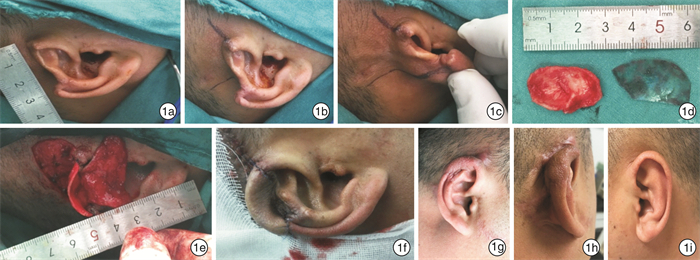
表 1 不同耳廓缺损面积的修复方法
例序 耳廓缺损面积 取软骨部位 修复方法 1 3.0×1.5 健侧耳甲腔 耳甲腔软骨为支架,耳后推进皮瓣覆盖软骨,锁骨上取皮,耳后植皮修复 2 1.6×0.5 同侧耳甲腔 耳甲腔软骨为支架,耳后V形皮瓣,V-Y推进覆盖软骨 3 2.0×1.0 同侧耳甲腔 耳甲腔软骨为支架,耳后推进皮瓣覆盖软骨,取乳突区替尔式皮片,耳后植皮修复 4 1.8×0.7 同侧耳甲腔 耳甲腔软骨为支架,耳后推进皮瓣覆盖软骨,取乳突区替尔式皮片,耳后植皮修复 5 2.2×0.8 同侧耳甲腔 耳甲腔软骨为支架,耳后推进皮瓣覆盖软骨,取乳突区替尔式皮片,耳后植皮修复 6 2.3×1.1 同侧耳甲腔 耳甲腔软骨为支架,耳后推进皮瓣覆盖软骨,取乳突区替尔式皮片,耳后植皮修复 7 2.1×0.9 同侧耳甲腔 耳甲腔软骨为支架,耳后推进皮瓣覆盖软骨,取乳突区替尔式皮片,耳后植皮修复 -
[1] 徐洲, 王珮华, 唐梦遥, 等. 完全断离耳廓软骨原位再植二期修复技术的临床应用[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 53(10): 765-769. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2018.10.009
[2] 李川. 肋软骨采取术后胸廓畸形的研究进展[J]. 中华整形外科杂志, 2017, 33(1): 76-78.
[3] 王长琛, 张晔, 杨美蓉, 等. 自体耳甲腔软骨游离移植修复耳廓畸形[J]. 中华整形外科杂志, 2020, 36(1): 20-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202105009.htm
[4] Magritz R, Siegert R. Reconstruction of the avulsed auricle after trauma[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2013, 46(5): 841-855. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2013.07.004
[5] 徐洲, 王珮华, 陈东. 耳后皮瓣急诊即刻修复耳轮部分缺损的临床应用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(2): 12-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201902003.htm
[6] Stiller MB, Gerressen M, Modabber A, et al. Anteriorly pedicled retroauricular flap for repair of auricular defects [J]. Aesthetic Plast Surg, 2012, 36(3): 623-627. doi: 10.1007/s00266-011-9847-0
[7] Watson D, Hecht A. Repair of Auricular Defects [J]. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am, 2017, 25(3): 393-408. doi: 10.1016/j.fsc.2017.03.010
[8] Park C, Park JY. Classification and Algorithmic Management of Constricted Ears: A 22-Year Experience[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2016, 137(5): 1523-1538. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000002120
[9] 李雪盛, 孙建军. 再生医学之组织工程耳廓软骨再生与功能重建[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(6): 567-571. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201906026.htm
[10] 冀航, 王肃生, 梁刚, 等. 乳突区超量扩张皮瓣与颞浅筋膜瓣联合包裹多孔高密度聚乙烯支架全耳廓成形术[J]. 中华医学美学美容杂志, 2012, 18(1): 16-18.
[11] Hénoux M, Espitalier F, Hamel A, et al. Vascular Supply of the Auricle: Anatomical Study and Applications to External Ear Reconstruction[J]. Dermatol Surg, 2017, 43(1): 87-97. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000000928
[12] 周栩, 欧杨雪, 王悦, 等. 数字化技术辅助自体肋软骨采伐与耳支架雕刻[J]. 组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2018, 14(3): 132-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZCW201803005.htm
[13] Shokrollahi K, Taylor JP, Le Roux CM, et al. The postauricular fascia: classification, anatomy, and potential surgical applications[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 2014, 73(1): 92-97.
[14] 张林, 赵宇, 李小静, 等. 耳后皮瓣在外耳部分缺损的亚单位分区精准修复[J]. 中华整形外科杂志, 2018, 34(8): 625-629.
[15] 杨大平, 韩雪峰, 郭铁芳. 耳后皮瓣血管的显微外科解剖学基础[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志, 2002, 20(3): 166-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLJZ200203001.htm
[16] 宋宇鹏, 庄洪兴, 蒋海越, 等. 获得性耳廓缺损的耳廓再造术[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2010, 24(10): 1204-1207. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXCW201010019.htm
[17] Nagata S. Modification of the stages in total reconstruction of the auricle: Part Ⅱ. Grafting the three-dimensional costal cartilage framework for concha-type microtia [J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1994, 93(2): 231-242.
[18] 陈召阳, 罗春材, 尚骁, 等. 数字化技术在耳廓再造中的应用进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2017, 31(9): 1135-1140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXCW201709022.htm
[19] Zhang YZ, Li YL, Yang C, et al. Reconstruction of the postauricular defects using retroauricular artery perforator-based island flaps: Anatomical study and clinical report[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2016, 95(37): e4853.
[20] 郭佩佩, 蒋海越. 获得性耳廓缺损的外科治疗进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018, 32(9): 1218-1222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXCW201809021.htm
-




 下载:
下载: