Role of gut microbiota in children with allergic rhinitis with high serum total IgE level
-
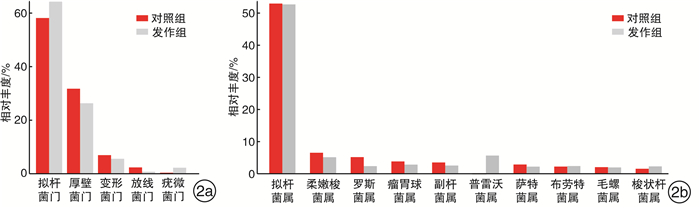
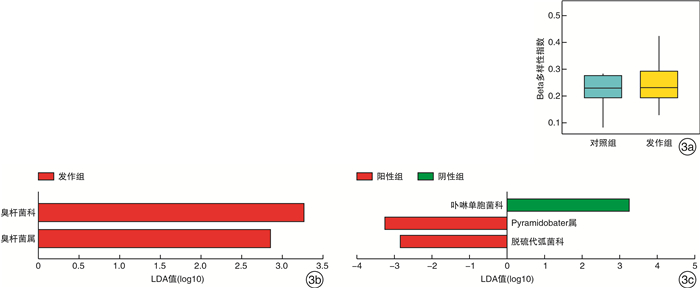
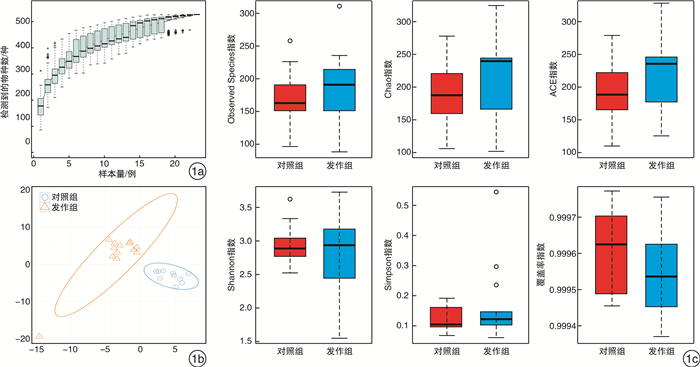
摘要: 目的 探究肠道菌群在血清tIgE水平升高的变应性鼻炎儿童发病中的作用。方法 纳入上海交通大学医学院附属上海儿童医学中心收治的5~6级重度户尘螨过敏的变应性鼻炎患儿17例,收集所有受试者一般临床资料,采集外周血检测其血清tIgE、sIgE水平。收集发作期、控制期粪便样本进行细菌DNA提取,并行16S rDNA高通量测序。采用R软件、Mother软件以及LEfSe软件进行肠道菌群多样性、相对丰度及差异物种分析。结果 共收集粪便样本23份,其中发作期13份(发作组),控制期10份(对照组)。发作期样本中血清tIgE阳性6例(阳性组),阴性7例(阴性组)。与控制期相比,变应性鼻炎患儿发作期肠道菌群的Alpha多样性、Weighted Unifrac的Beta多样性无显著差异(P>0.05)。臭杆菌科臭杆菌属相对丰度在发作期患儿中显著升高(LDA绝对值>2)。血清tIgE阳性患儿卟啉单胞菌科相对丰度下降(LDA绝对值>2),显著低于阴性患儿,而脱硫代弧菌科Pyramidobacter属相对丰度增加。结论 儿童变应性鼻炎发作期和控制期具有不同的肠道菌群特征,肠道菌群与儿童变应性鼻炎血清tIgE水平升高有关,特定微生物改变在患儿发病中发挥潜在作用。Abstract: Objective To study the role of gut microbiota in children with allergic rhinitis with high serum total IgE level.Method A total of 17 cases of children in Shanghai Children's Medical Center of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, who suffered from perennial allergic rhinitis of grade 5-6, were enrolled in this study. Baseline information were collected from all participants. Peripheral blood was collected to test the level of serum total IgE and specific IgE. Fecal samples were collected for bacterial DNA extraction and sequenced by 16S rDNA high-throughput sequencing. R, Mother and LEfSe softwares were used for diversity analysis, relative abundance calculation and differential species detection.Result Twenty-three fecal samples were collected in total, including thirteen in attack period(attack group) and ten in control period(control group). In the attack group, six cases were serum total IgE positive(positive group) and seven were negative(negative group). Compared with the control group, there was no significant difference in either Alpha diversity or Beta diversity of Weighted Unifrac in the attack group(P>0.05). The relative abundance of odoribacteraceae and odoribacter were significantly increased in the attack group(LDA score>2). The relative abundance of Porphyromonadaceae in positive group were significantly lower than that in negative group, while family Dethiosulfovibrionaceae genus Pyramidobacter was definitely higher on the contrast(LDA score>2).Conclusion Children with allergic rhinitis have different characteristics of intestinal flora during the attack and control period. Gut microbiota is associated with high serum total IgE level in children with allergic rhinitis. Specific microbial alterations play a potential role in disease pathophysiology.
-
Key words:
- rhinitis, allergic /
- child /
- gut microbiota /
- immunoglobulin E
-

-
[1] 中国医师协会儿科医师分会儿童耳鼻咽喉专业委员会. 儿童过敏性鼻炎诊疗——临床实践指南[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志, 2019, 34(3): 169-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSEK201903001.htm
[2] Bernstein DI, Schwartz G, Bernstein JA. Allergic Rhinitis: Mechanisms and Treatment[J]. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am, 2016, 36(2): 261-278. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2015.12.004
[3] Zhang Y, Zhang L. Increasing Prevalence of Allergic Rhinitis in China[J]. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res, 2019, 11(2): 156-169. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.2.156
[4] Liu AH. Revisiting the hygiene hypothesis for allergy and asthma[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2015, 136(4): 860-865. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.08.012
[5] Mastrorilli C, Posa D, Cipriani F, et al. Asthma and allergic rhinitis in childhood: what's new[J]. Pediatr Allergy Immunol, 2016, 27(8): 795-803. doi: 10.1111/pai.12681
[6] Bridgman SL, Kozyrskyj AL, Scott JA, et al. Gut microbiota and allergic disease in children[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2016, 116(2): 99-105. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2015.10.001
[7] Koppen I, Bosch A, Sanders E, et al. The respiratory microbiota during health and disease: a paediatric perspective[J]. Pneumonia(Nathan), 2015, 6: 90-100. doi: 10.15172/pneu.2015.6/656
[8] Park SC, Kim JH, Lee KH, et al. Association of serum eosinophilia and total immunoglobulin E concentration with the risk of allergic symptoms and allergic sensitization, respectively: A 2-year follow-up study[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 86: 167-171. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.05.005
[9] Kreft L, Hoffmann C, Ohnmacht C. Therapeutic Potential of the Intestinal Microbiota for Immunomodulation of Food Allergies[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 1853. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01853
[10] Cukrowska B, Bierła JB, Zakrzewska M, et al. The Relationship between the Infant Gut Microbiota and Allergy. The Role of Bifidobacterium breve and Prebiotic Oligosaccharides in the Activation of Anti-Allergic Mechanisms in Early Life[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(4): 946. doi: 10.3390/nu12040946
[11] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组、小儿学组, 中华儿科杂志编辑委员会. 儿童变应性鼻炎诊断和治疗指南(2010年, 重庆)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2011, 46(1): 7-8. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10611-1014044856.htm
[12] 何珊, 牟喆, 彭丽, 等. 气象环境因素对儿童变应性鼻炎自觉症状影响的研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 29(16): 1458-1462, 1466. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201516014.htm
[13] 许洋, 任健君, 王晶, 等. 益生菌治疗变应性鼻炎的研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 31(17): 1322-1327. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201717006.htm
[14] Jiang L, Xie M, Chen G, et al. Phenolics and Carbohydrates in Buckwheat Honey Regulate the Human Intestinal Microbiota[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2020, 2020: 6432942.
[15] Liang X, Liu CS, Wei XH, et al. Mahuang Fuzi Xixin Decoction Ameliorates Allergic Rhinitis in Rats by Regulating the Gut Microbiota and Th17/Treg Balance[J]. J Immunol Res, 2020, 2020: 6841078. doi: 10.1155/2020/6841078
[16] Melli LC, do Carmo-Rodrigues MS, Araújo-Filho HB, et al. Intestinal microbiota and allergic diseases: A systematic review[J]. Allergol Immunopathol(Madr), 2016, 44(2): 177-188. doi: 10.1016/j.aller.2015.01.013
[17] Chiu CY, Chan YL, Tsai MH, et al. Gut microbial dysbiosis is associated with allergen-specific IgE responses in young children with airway allergies[J]. World Allergy Organ J, 2019, 12(3): 100021. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2019.100021
[18] McKenzie C, Tan J, Macia L, et al. The nutrition-gut microbiome-physiology axis and allergic diseases[J]. Immunol Rev, 2017, 278(1): 277-295. doi: 10.1111/imr.12556
[19] Kim WG, Kang GD, Kim HI, et al. Bifidobacterium longum IM55 and Lactobacillus plantarum IM76 alleviate allergic rhinitis in mice by restoring Th2/Treg imbalance and gut microbiota disturbance[J]. Benef Microbes, 2019, 10(1): 55-67. doi: 10.3920/BM2017.0146
[20] Brandsma E, Kloosterhuis NJ, Koster M, et al. A Proinflammatory Gut Microbiota Increases Systemic Inflammation and Accelerates Atherosclerosis[J]. Circ Res, 2019, 124(1): 94-100. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313234
[21] Gomez-Arango LF, Barrett HL, McIntyre HD, et al. Increased Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure Is Associated With Altered Gut Microbiota Composition and Butyrate Production in Early Pregnancy[J]. Hypertension, 2016, 68(4): 974-981. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.07910
[22] Wang Y, Gao X, Ghozlane A, et al. Characteristics of Faecal Microbiota in Paediatric Crohn's Disease and Their Dynamic Changes During Infliximab Therapy[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2018, 12(3): 337-346. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjx153
[23] Luo XM, Edwards MR, Mu Q, et al. Gut Microbiota in Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and a Mouse Model of Lupus[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2018, 84(4): e02288-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02288-17
[24] Sun Y, Chen Q, Lin P, et al. Characteristics of Gut Microbiota in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis in Shanghai, China[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2019, 9: 369. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00369
[25] Di Costanzo M, Carucci L, Berni Canani R, et al. Gut Microbiome Modulation for Preventing and Treating Pediatric Food Allergies[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(15): 5275. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155275
[26] Rehaume LM, Matigian N, Mehdi AM, et al. IL-23 favours outgrowth of spondyloarthritis-associated pathobionts and suppresses host support for homeostatic microbiota[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2019, 78(4): 494-503. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214381
[27] Li N, Qiu R, Yang Z, et al. Sputum microbiota in severe asthma patients: Relationship to eosinophilic inflammation[J]. Respir Med, 2017, 131: 192-198. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2017.08.016
[28] Ye F, Shen H, Li Z, et al. Influence of the Biliary System on Biliary Bacteria Revealed by Bacterial Communities of the Human Biliary and Upper Digestive Tracts[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(3): e0150519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150519
[29] Brożek JL, Bousquet J, Agache I, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma(ARIA)guidelines-2016 revision[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2017, 140(4): 950-958. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.03.050
[30] Huber S, Lang R, Steiner M, et al. Does clinical outcome of birch pollen immunotherapy relate to induction of blocking antibodies preventing IgE from allergen binding? A pilot study monitoring responses during first year of AIT[J]. Clin Transl Allergy, 2018, 8: 39. doi: 10.1186/s13601-018-0226-7
[31] Sun W, Pan L, Yu Q, et al. The skin prick test response after allergen immunotherapy in different levels of tIgE children with mite sensitive Asthma/Rhinitis in South China[J]. Hum Vaccin Immunother, 2018, 14(10): 2510-2515. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1482171
[32] Karaman S, Can D, Erdem SB, et al. Is There Any Parameter Helpful for Predicting a Suitable Candidate for Mite Immunotherapy?[J]. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2016, 15(2): 105-111.
-




 下载:
下载: