Supraglottoplasty with low temperature plasma radiofrequency ablation for severe laryngomalacia
-
-
关键词:
- 喉软骨软化症 /
- 声门上成形术 /
- 低温等离子射频消融术
-

-
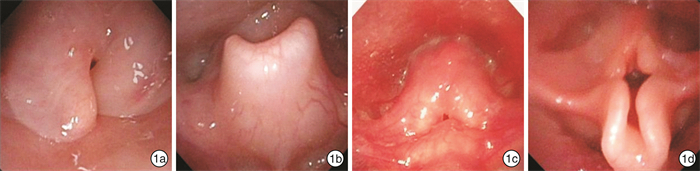
表 1 29例患儿术前临床资料
x±s 项目 不吸氧 吸氧 无创呼吸机 气管插管 合计 例数 6 8 10 5 29 平均年龄/周 24.90±37.44 7.38±5.15 8.92±3.45 8.50±4.14 11.75±17.62 男/女 5/1 3/5 5/5 4/1 17/12 孕龄 足月 5 6 5 2 18 32~37周 1 1 4 2 8 28~32周 0 1 1 1 3 出生体重/kg 3.65±0.33 2.65±0.94 2.74±0.72 2.53±0.35 2.87±0.77 术前体重/kg 6.00±3.49 3.21±0.76 3.27±0.82 3.36±0.83 3.84±1.98 术前营养发育等级 中等 3 0 1 0 4 中下等 1 5 3 1 10 下等 2 3 6 4 15 合并症 神经系统 0 2 3 2 7 心脏 1 4 3 1 9 肺 5 8 10 5 28 综合征 0 0 1 2 3 漏斗胸 6 6 5 2 19 合并气道病变 声门下狭窄 0 1 1 1 3 气管、支气管狭窄 2 0 2 1 5 气管、支气管软化 0 0 1 1 2 合并喂养困难 呛奶 3 5 4 3 15 胃食管反流 0 2 3 2 7 吞咽困难 0 2 4 2 7 术前喉镜表现 Ⅰ型 1 1 3 0 5 Ⅱ型 1 2 2 0 4 Ⅲ型 4 1 1 0 6 Ⅳ型 0 5 4 5 14 表 2 患儿术中及术后临床特点
x±s 指标 术前不吸氧 术前吸氧 术前无创呼吸机 术前气管插管 平均值 平均手术时间/min 19.0±3.75 21.0±2.59 22.0±6.33 28.0±5.70 23.0±5.45 术后ICU气管插管时间/d 3.7±1.51 3.5±0.76 4.4±0.84 5.4±1.95 4.2±1.34 术后总住院天数/d 6.7±1.51 6.5±0.76 7.5±0.85 8.6±1.81 7.2±1.35 表 3 患儿出院及出院后1、3、6个月一般情况
例 项目 出院 1个月 3个月 6个月 喘鸣 消失 19 25 27 27 减轻 9 3 0 1 无变化 1 1 2 1 喂养 鼻饲 4 2 2 2 呛奶或吐奶 10 5 1 1 经口无症状 15 22 25 26 营养等级 中上等 0 0 3 5 中等 4 8 15 21 中下等 10 13 8 1 下等 15 8 3 2 -
[1] Carter J, Rahbar R, Brigger M, et al. International Pediatric ORL Group(IPOG)laryngomalacia consensus recommendations[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 86: 256-261. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.04.007
[2] Hartl TT, Chadha NK. A systematic review of laryngomalacia and acid reflux[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2012, 147(4): 619-626. doi: 10.1177/0194599812452833
[3] Ayari S, Aubertin G, Girschig H, et al. Management of laryngomalacia[J]. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, 2013, 130(1): 15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2012.04.003
[4] 张亚梅, 张天宇. 实用小儿耳鼻咽喉科学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2011: 387-387.
[5] Nielson DW, Ku PL, Egger M. Topical lidocaine exaggerates laryngomalacia during flexible bronchoscopy[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2000, 161(1): 147-151. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.161.1.9811043
[6] Lima TM, Gonçalves DU, Gonçalves LV, et al. Flexible nasolaryngoscopy accuracy in laryngomalacia diagnosis[J]. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol, 2008, 74(1): 29-32. doi: 10.1016/S1808-8694(15)30747-3
[7] Yeung JC, Ali SO, McKeon MG, et al. Carbon dioxide laser versus cold-steel supraglottoplasty: A comparison of post-operative outcomes[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 130: 109843. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.109843
[8] Trial C, Brancati A, Marnet O, et al. Coblation technology for surgical wound debridement: principle, experimental data, and technical data[J]. Int J Low Extrem Wounds, 2012, 11(4): 286-292. doi: 10.1177/1534734612466871
[9] Fastenberg JH, Roy S, Smith LP. Coblation-assisted management of pediatric airway stenosis[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 87: 213-218. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.06.035
[10] Reinhard A, Gorostidi F, Leishman C, et al. Laser supraglottoplasty for laryngomalacia; a 14 year experience of a tertiary referral center[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2017, 274(1): 367-374. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4252-6
[11] Durvasula VS, Lawson BR, Bower CM, et al. Supraglottoplasty outcomes in neurologically affected and syndromic children[J]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2014, 140(8): 704-711. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2014.983
[12] Hartl TT, Chadha NK. A systematic review of laryngomalacia and acid reflux[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2012, 147(4): 619-626. doi: 10.1177/0194599812452833
[13] Miller C, Parikh SR. Does supraglottoplasty improve outcomes in children with laryngomalacia?[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019, 129(2): 285-287. doi: 10.1002/lary.27127
-




 下载:
下载:
