Endoscope-assisted transoral resection of parapharyngeal space tumors: a retrospective study
-
摘要: 目的 探讨内镜辅助下经口径路咽旁间隙肿瘤的可行性和安全性。方法 回顾性分析内镜辅助下经口径路切除的22例咽旁间隙肿瘤患者的临床资料。结果 22例患者中,术后病理证实神经鞘瘤10例,多形性腺瘤7例,副神经节瘤、鳃裂囊肿各1例,口咽高分化鳞状细胞癌转移、甲状腺乳头状癌转移和弥漫大B细胞型淋巴瘤等恶性肿瘤各1例,恶性肿瘤患者手术为诊断性手术。手术时间为15~430 min(中位手术时间为105 min),术中出血量为10~500 mL(中位出血量20 mL)。其中21例(95%)顺利完成手术未出现明显手术并发症,1例(5%)复发性神经鞘瘤患者术中并发难控性出血导致肿瘤未能完全切除。术后随访12~72个月,18例完整切除的良性病变患者均未出现复发。结论 内镜辅助下经口径路美容、微创且能较好地完整切除位于颈动脉鞘内侧的咽旁间隙良性肿瘤,但不推荐用于局部复发肿瘤,包绕颈动脉鞘以及位于颈动脉鞘后外侧方的肿瘤。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the feasibility and safety of the endoscope-assisted transoral approach for the parapharyngeal space(PPS) tumors.Method This retrospective study included 22 patients who were diagnosed with PPS tumors and treated with the endoscope-assisted transoral approach.Result The postoperative pathological diagnosis included 10 cases of schwannoma, 7 cases of pleomorphic adenoma, 1 case of paraganglioma, 1 case of branchial cleft cyst, and 3 cases of malignant tumors for a diagnostic purpose. The surgical duration was between 15 minutes and 430 minutes(median duration 105 minutes), and the intraoperative bleeding was between 10ml to 500ml(median bleeding 20 mL). Complete resection with minor complication was performed in 21 cases, 1 case of recurrent schwannoma was done in an incomplete style because of intraoperative massive bleeding. With a 12-to-72-months follow up, there was no relapse on the 18 cases of benign tumor which were completely resected.Conclusion Endoscope-assisted transoral resection provide cosmetic, micro-invasive and increased operative exposure to the PPS, especially for the benign tumors that medial to the carotid sheath. But is not recommend for relapsed cases and lesions that encompassing or lying posterolateral to the carotid sheath.
-
Key words:
- parapharyngeal space tumors /
- surgical procedures, operative /
- endoscopes
-

-
表 1 22例内镜辅助下经口径路咽旁间隙肿瘤切除术患者资料
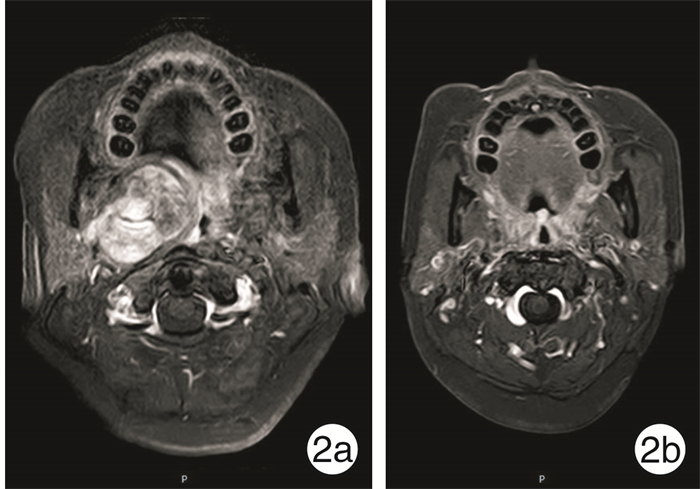
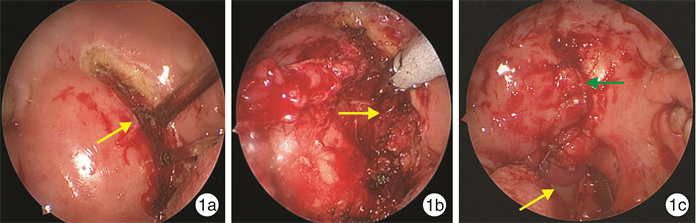
编号 性别 年龄/岁 侧别 病理结果 术中出血/ml 手术时间/min 并发症 影像学表现 大小/mm 1 男 45 左 神经鞘瘤 10 60 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 17×29 2 女 38 右 复发神经鞘瘤 500 430 术中出血5.0 ml 肿瘤在ICA前内 34×32 3 男 76 右 口咽癌转移 10 15 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 50×40 4 女 41 右 多形性腺瘤 15 69 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 25×40 5 男 54 右 神经鞘瘤 150 120 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 19×16 6 男 29 左 神经鞘瘤 20 60 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 20×27 7 女 36 左 神经鞘瘤 20 70 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 35×20 8 女 46 右 神经鞘瘤 10 90 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 17×37 9 男 21 左 多形性腺瘤 20 60 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 31×60 10 女 56 右 神经鞘瘤 100 370 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 61×34 11 女 24 右 神经鞘瘤 40 120 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 22×63 12 女 37 右 多形性腺瘤 200 210 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 61×34 13 女 37 右 甲状腺乳头状癌转移 50 138 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 25×55 14 女 72 左 副神经节瘤 100 330 无 肿瘤在ICA后外 21×54 15 女 37 左 多形性腺瘤 20 142 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 28×50 16 男 83 左 神经鞘瘤 10 120 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 24×39 17 女 51 右 多形性腺瘤 100 120 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 46×29 18 女 51 左 多形性腺瘤 20 75 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 40×32 19 男 45 右 神经鞘瘤 40 90 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 60×30 20 女 34 左 鳃裂囊肿 10 180 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 23×10 21 女 47 右 多形性腺瘤 20 84 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 22×54 22 女 63 左 淋巴瘤 10 60 无 肿瘤在ICA前内 35×24 -
[1] Kuet ML, Kasbekar AV, Masterson L, et al. Management of tumors arising from the parapharyngeal space: A systematic review of 1, 293 cases reported over 25 years[J]. Laryngoscope, 2015, 125(6): 1372-1381. doi: 10.1002/lary.25077
[2] Eisele DW, Richmon JD. Contemporary evaluation and management of parapharyngeal space neoplasms[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2013, 127(6): 550-555. doi: 10.1017/S0022215113000686
[3] Dang S, Shinn JR, Seim N, et al. Diagnosis and treatment considerations of parapharyngeal space masses-A review with case report[J]. Otolaryngol Case Rep, 2019, 11: 100-120.
[4] Cassoni A, Terenzi V, Della Monaca M, et al. Parapharyngeal space benign tumours: our experience[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2014, 42(2): 101-105. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2013.03.002
[5] Riffat F, Dwivedi RC, Palme C, et al. A systematic review of 1143 parapharyngeal space tumors reported over 20 years[J]. Oral Oncol, 2014, 50(5): 421-430. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2014.02.007
[6] 陶磊, 石小玲, 李筱明, 等. 188例咽旁间隙肿瘤的回顾性分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(2): 129-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201802013.htm
[7] López F, Suárez C, Vander Poorten V, et al. Contemporary management of primary parapharyngeal space tumors[J]. Head Neck, 2019, 41(2): 522-535.
[8] Dallan I, Seccia V, Muscatello L, et al. Transoral endoscopic anatomy of the parapharyngeal space: a step-by-step logical approach with surgical considerations[J]. Head Neck, 2011, 33(4): 557-561. doi: 10.1002/hed.21488
[9] Goodwin WJ Jr, Chandler JR. Transoral excision of lateral parapharyngeal space tumors presenting intraorally[J]. Laryngoscope, 1988, 98(3): 266-269.
[10] Van Rompaey J, Suruliraj A, Carrau R, et al. Access to the parapharyngeal space: an anatomical study comparing the endoscopic and open approaches[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123(10): 2378-2382.
[11] Iseri M, Ozturk M, Kara A, et al. Endoscope-assisted transoral approach to parapharyngeal space tumors[J]. Head Neck, 2015, 37(2): 243-248. doi: 10.1002/hed.23592
[12] 文锋, 沈泓, 高为华, 等. 72例咽旁间隙肿瘤患者的诊疗分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(17): 1343-1347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201817012.htm
[13] Wang X, Gong S, Lu Y, et al. Endoscopy-assisted transoral resection of parapharyngeal space tumors: a retrospective analysis[J]. Cell Biochem Biophys, 2015, 71(2): 1157-1163. doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-0323-8
[14] Fan S, Lin SG, Zhang HQ, et al. A comparative study of the endoscopy-assisted transoral approach versus external approaches for the resection of large benign parapharyngeal space tumors[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2017, 123(2): 157-162. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2016.09.010
[15] 杨党卫, 周华磊, 李建兴, 等. 内镜下经口入路咽旁间隙手术的解剖标志[J]. 局解手术学杂志, 2016, 25(6): 391-394. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJXZ201606002.htm
-




 下载:
下载: