-
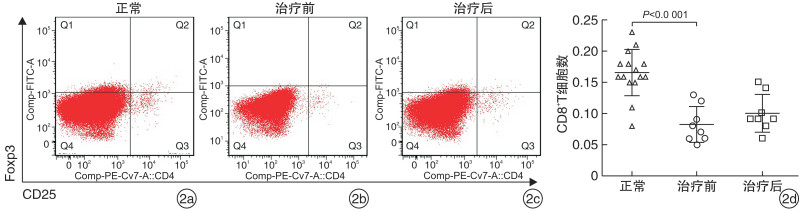
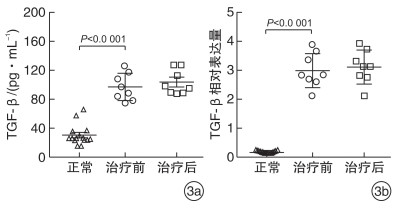
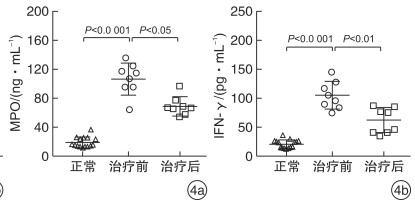
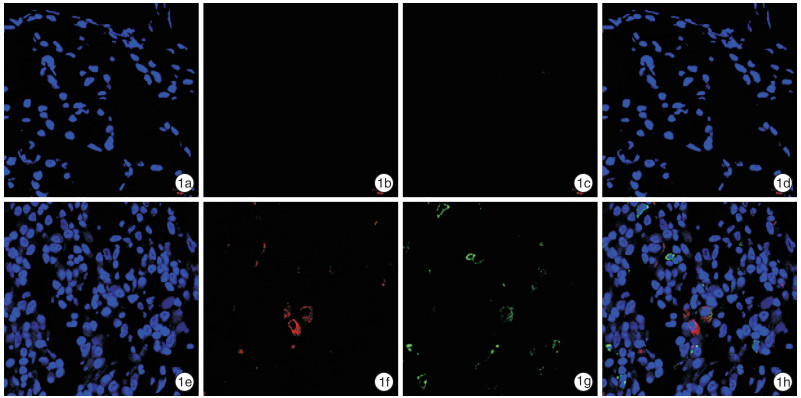
摘要: 目的 探讨布地奈德对CD8+CD25+Foxp3+Treg细胞的影响,并评估其在嗜中性粒细胞性鼻息肉(NP)中的作用。 方法 招募8例嗜中性粒细胞性CRSwNP患者,并予以布地奈德鼻喷剂治疗3个月。分别从正常鼻黏膜组织和NP中获取样本,进行体外培养,分别从正常鼻黏膜组织和NP中分离和提纯CD8+CD25+Foxp3+Treg细胞,也进行体外培养。随后检测该Treg细胞培养液中转化生长因子-β(TGF-β)及其mRNA的含量。将体外培养的CD8+CD25+Foxp3+Treg细胞加入NP培养液中,并对该组织培养液中髓过氧化物酶(MPO)和IFN-γ的浓度进行检测。 结果 NP中CD8+CD25+Foxp3+Treg细胞所占CD8+T细胞的百分比较正常黏膜组织有所降低,而布地奈德喷鼻治疗并未升高该Treg细胞的百分比,TGF-β及其mRNA在该细胞培养液中的浓度高于正常黏膜组织来源的Treg细胞,CD8+CD25+Foxp3+Treg细胞干预体外培养的NP后,组织培养液中MPO和IFN-γ的浓度较干预前降低。 结论 CD8+CD25+Foxp3+Treg细胞可以调节嗜中性粒细胞性NP中的炎症反应,而布地奈德的治疗对该细胞的作用有限。Abstract: Objective CD8+CD25+Foxp3+regulatory T(Treg) cells are reduced in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps(CRSwNP). However, the role of these cells in nasal polyps(NP) has not been fully investigated. The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of budesonide treatment on these cells and to assess their roles in neutrophilic NP. Method Eight neutrophilic CRSwNP patients were enrolled and received budesonide nasal spray treatment for three months. Nasal samples were obtained from normal mucosa or NP and cultured in vitro. CD8+CD25+Foxp3+Treg cells were isolated and purified from normal or NP tissues and cultured in vitro. Then transforming growth factor-β(TGF-β) and its mRNA were examined in those cell cultures. After that, those cells were administered into NP cultures. Finally, the concentrations of myeloperoxidase(MPO) and interferon(IFN) -γ were evaluated in those tissue cultures. Result CD8+CD25+Foxp3+Treg cells were decreased in NP compared to normal tissues. Budesonide treatment did not increase the percentage of those cells in NP. TGF-β and its mRNA were enhanced in CD8+CD25+Foxp3+Treg cell cultures from NP versus those from normal tissues. In addition, levels of MPO and IFN-γ were reduced after CD8+CD25+Foxp3+Treg cells administration. Conclusion These findings indicated that CD8+CD25+Foxp3+Treg cells may play a role in the regulation of neutrophilic inflammation, and budesonide treatment may not influence these Treg cells.
-
Key words:
- neutrophils /
- nasal polyps /
- treg cells /
- budesonide
-

-
[1] Soyka MB, Wawrzyniak P, Eiwegger T, et al. Defective epithelial barrier in chronic rhinosinusitis: The regulation of tight junctions by IFN-gamma and IL-4[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2012, 130(5): 1087-1096. e10. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.05.052
[2] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012[J]. Rhinol Suppl, 2012, 23: 3p preceding table of contents: 1-298.
[3] Jankowski R, Bouchoua F, Coffinet L, et al. Clinical factors influencing the eosinophil infiltration of nasal polyps[J]. Rhinology, 2002, 40(4): 173-178.
[4] Zhang N, Van Zele T, Perez-Novo C, et al. Different types of T-effector cells orchestrate mucosal inflammation in chronic sinus disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2008, 122(5): 961-968. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.07.008
[5] Wing K, Sakaguchi S. Regulatory T cells exert checks and balances on self tolerance and autoimmunity[J]. Nat Immunol, 2010, 11(1): 7-13. doi: 10.1038/ni.1818
[6] Robb RJ, Lineburg KE, Kuns RD, et al. Identification and expansion of highly suppressive CD8(+)FoxP3(+)regulatory T cells after experimental allogeneic bone marrow transplantation[J]. Blood, 2012, 119(24): 5898-5908. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-396119
[7] Vaidyanathan S, Barnes M, Williamson P, et al. Treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis with oral steroids followed by topical steroids: a randomized trial[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2011, 154(5): 293-302. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-154-5-201103010-00003
[8] Wen W, Liu W, Zhang L, et al. Increased neutrophilia in nasal polyps reduces the response to oral corticosteroid therapy[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2012, 129(6): 1522-1528. e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.01.079
[9] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组. 中国慢性鼻窦炎诊断和治疗指南(2018)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 54(1): 81-100.
[10] Park SK, Lee WJ, Yang YI. Organ culture at the air-liquid interface maintains structural and functional integrities of inflammatory and fibrovascular cells of nasal polyps[J]. Am J Rhinol, 2007, 21(4): 402-407. doi: 10.2500/ajr.2007.21.3050
[11] Ho J, Bailey M, Zaunders J, et al. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells(ILC2s)are increased in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps or eosinophilia[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2015, 45(2): 394-403. doi: 10.1111/cea.12462
[12] Meltzer EO, Hamilos DL, Hadley JA, et al. Rhinosinusitis: Establishing definitions for clinical research and patient care[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2004, 114(6): 155-212. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2004.09.029
[13] Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, et al. Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2009, 124(3): 478-484, 484. e1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.05.017
[14] Hissaria P, Smith W, Wormald PJ, et al. Short course of systemic corticosteroids in sinonasal polyposis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial with evaluation of outcome measures[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2006, 118(1): 128-133. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2006.03.012
[15] Peric A, Vojvodic D, Matkovic-Jozin S. Effect of long-term, low-dose clarithromycin on T helper 2 cytokines, eosinophilic cationic protein and the'regulatedon activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted' chemokine in the nasal secretions of patients with nasal polyposis[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2012, 126(5): 495-502. doi: 10.1017/S0022215112000485
[16] Gershon RK, Kondo K. Cell interactions in the induction of tolerance: the role of thymic lymphocytes[J]. Immunology, 1970, 18(5): 723-737.
[17] Cosmi L, Liotta F, Lazzeri E, et al. Human CD8+CD25+thymocytes share phenotypic and functional features with CD4+CD25+regulatory thymocytes[J]. Blood, 2003, 102(12): 4107-4114. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-04-1320
[18] Kiniwa Y, Miyahara Y, Wang HY, et al. CD8+Foxp3+regulatory T cells mediate immunosuppression in prostate cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2007, 13(23): 6947-6958. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0842
[19] Pant H, Hughes A, Schembri M, et al. CD4+and CD8+regulatory T cells in chronic rhinosinusitis mucosa[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2014, 28(2): 83-89. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2013.28.4014
-

| 引用本文: | 蔺林, 戴飞, 魏瑾瑾, 等. 布地奈德对嗜中性粒细胞性鼻息肉中CD8+CD25+Foxp3+Treg细胞的作用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(8): 701-705. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.08.006 |
| Citation: | LIN Lin, DAI Fei, WEI Jinjin, et al. The role of budesonide on CD8+CD25+Foxp3+ Treg cells in neutrophilic nasal polyps[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2020, 34(8): 701-705. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.08.006 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.



 下载:
下载: